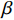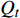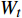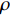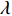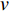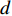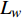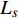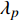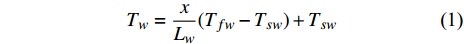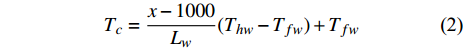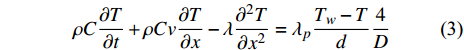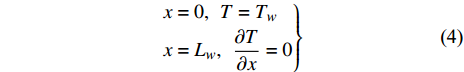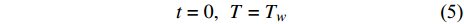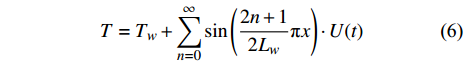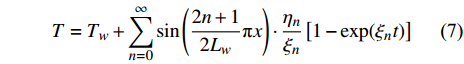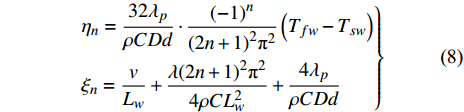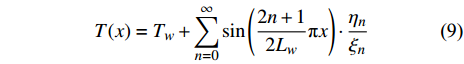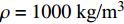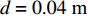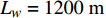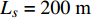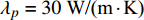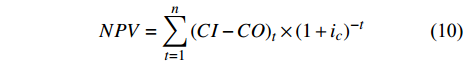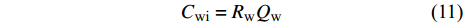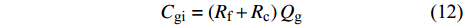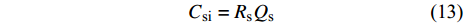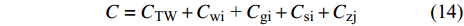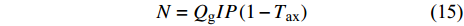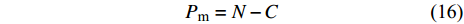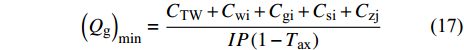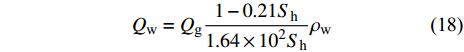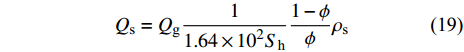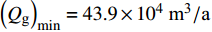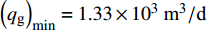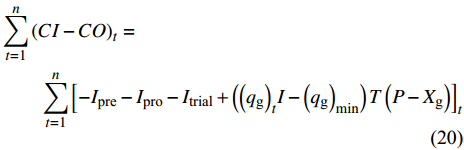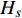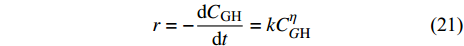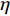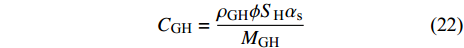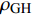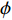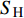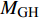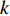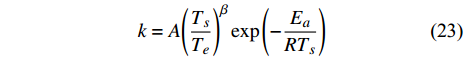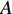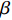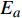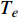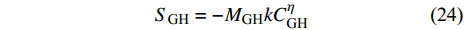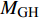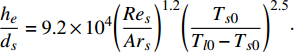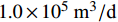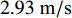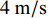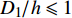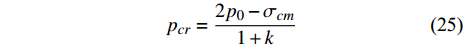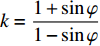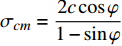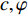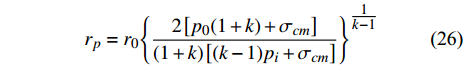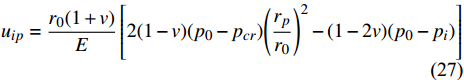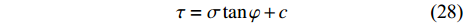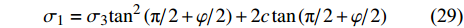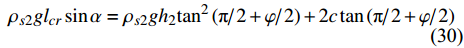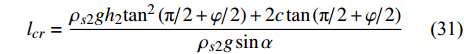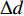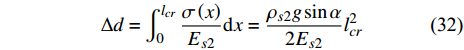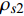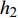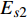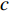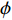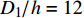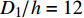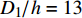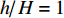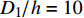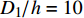REVIEW ON THE MECHANICAL-THERMAL COMBINED EXPLOITATION METHODS OF DEEP SEA NATURAL GAS HYDRATE
-
摘要: 天然气水合物由于储量大、污染低等优点, 已成为我国非常重要的战略能源, 世界各国也加快了天然气水合物的勘探和开发工作. 经济高效的开采方法以及相关的灾害控制和环境保护是对天然气水合物进行商业化开采必须要解决好的两个关键问题. 目前, 注热法和降压法的联合使用被认为是最为有效的天然气水合物开采方法. 在降压法和注热法中, 天然气水合物开采涉及传热、相变、渗流和变形等物理过程和效应, 而传热最慢且相变会消耗大量的热量, 无法直接采用常规的单纯依靠渗流原理的油气开采方案来开采天然气水合物. 我国南海的天然气水合物主要赋存于粉砂质黏土和粉细砂等类型的沉积物中, 胶结性差且埋深较浅. 常规的开采方法还不适合我国南海的水合物开采, 需要考虑新型的开采方式, 这其中提高沉积层中的热传导效率是天然气水合物开采的关键. 郑哲敏提出了机械−热联合开采的新概念方法, 利用无穷无尽表层海水的热量, 基于对流传热的原理和管道输送技术, 并兼顾类似采煤挖掘可能导致的深海浅软地层安全问题. 天然气水合物机械−热联合开采法是一种新的概念模式, 具有开采可控、高效且能有效降低地层安全性风险的优点. 本文针对该新方法的能量、装备、经济可行性进行综合评估, 阐述了针对核心问题管道含相变气液固多相流动、地层安全方面的研究进展, 展望了未来推广应用的空间.Abstract: Gas hydrates are an important sort of strategic energy resource in China because of their enormous reserves and small contamination compared to traditional fossil fuels. Many countries have accelerated the exploitation and research of gas hydrates. Profitable extraction methods, disaster control and environmental protection are two key issues that need to be addressed in the commercial exploitation of natural gas hydrates. Currently, the combined use of heat injection and pressure reduction methods is considered to be the most effective method of recovery of gas hydrates. In the method of depressurization and heat injection, natural gas hydrate production includes physical processes and effects such as heat transfer, phase change, seepage, and deformation. The heat transfer is the slowest and the phase change consumes a lot of heat, so it is impossible to directly use the conventional oil and gas extraction scheme that relies solely on the seepage principle to extract natural gas hydrates. Natural gas hydrates in the South China Sea occur mostly in silty clay and silty sand and other sediment types, with poor cementing and shallow burial depth. Conventional extraction methods are not suitable for hydrated extraction in the Southern Sea, and new methods of extraction have to be envisaged. Among these, the improvement of the efficiency of heat transfer in the sedimentary layer is the key to the exploitation of natural gas hydrate. Che-Min Cheng presents a mechanical-thermal combined recovery method, utilizing the heat of seawater, convective heat transfer, and pipe transportation, considering the stratum safety similar to coal mining. The mechanical-thermal combined method for gas hydrate exploitation is a new concept, which has the advantages of high efficiency and controllability, and meanwhile, the safety of formation can be reduced effectively. This paper presents a comprehensive estimation of the energy, apparatus, and economic feasibility of the new method demonstrates the advances in multiphase flow with phase transformation and stratum safety and gives some suggestions for the potential application of these results.
-
Keywords:
- gas hydrate /
- mechanical-thermal combined /
- dissociation model /
- multiphase flow /
- safety of stratum
-
引言
我国的深海资源的开发与利用正按“深海进入、深海探测、深海开发”三步曲展开. 天然气水合物(以下简称水合物)是天然气(主要成分甲烷)和水在高压和低温条件下形成的类冰固体化合物, 是一种清洁能源, 其资源量约是当前已探明化石燃料总量的两倍, 是未来全球能源发展的战略制高点之一[1-3]. 海域水合物资源量占95%以上, 水合物填充到海底砂、粉土、黏土等沉积物孔隙中形成水合物沉积物, 主要分布在水深800~3000 m、海底以下数十米到数百米的沉积层中. 水合物成藏和稳定存在需要高压低温条件、有充足气源、气体运移通道和充足的水源环境[4-5].
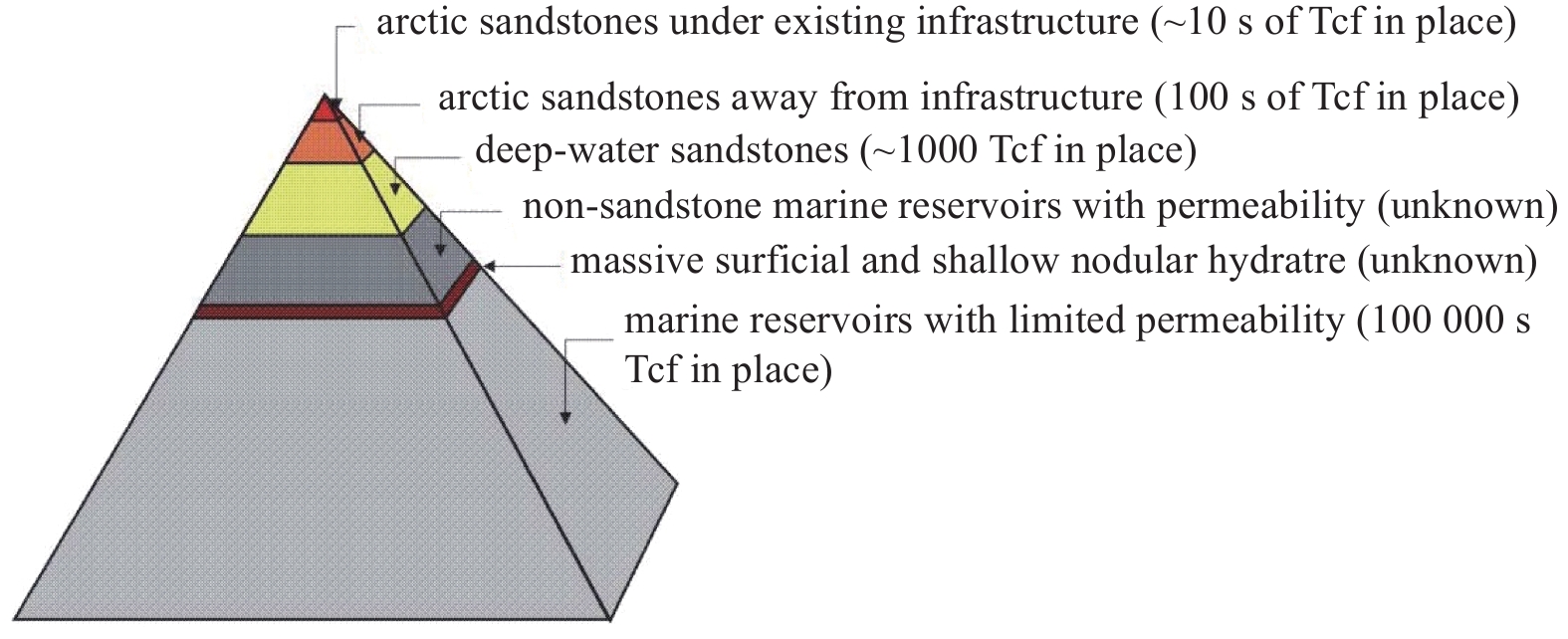
从全球各个国家和地区进行的水合物沉积层的调查和研究来看, 水合物沉积层在深海中一般分布在大洋边缘板块的会聚带、被动大陆边缘、泥底辟、海底泥火山活动区、海底滑塌区域等圈闭结构[6-8]. 深海水合物在各类储层中的比例如图1所示, 越是靠近金子塔的底层, 水合物的储量越大, 但开采难度也越高, 尤其在粉黏土、黏土或淤泥中赋存的比例最高[9]. 我国在南海海域、东海的冲绳海槽、青藏高原冻土区等地具备水合物孕育和赋存的条件, 且目前我国已探明海域水合物远景资源量高达800亿吨油当量[10].
水合物的开采同常规化石能源的区别在于[11]: 水合物以固体化合物形式赋存在储层的沉积物中, 必须通过温压扰动, 并供给水合物分解所需的热量, 打开水分子氢键约束, 释放出甲烷气体分子, 涉及相变与吸热的过程; 水合物地层一般具有3°~15°的坡度, 水合物分解相变后, 地层强度大幅降低, 孔隙压力升高, 对井筒结构及地层稳定构成威胁; 上覆层可能具有一定的渗透性或者薄弱区, 水合物开采过程中需避免气体上浮导致甲烷气体穿过水合物地层的上覆层向海洋环境或大气中的泄漏, 引起环境问题.
在郑哲敏先生的组织领导下, 中国科学院力学研究所自2004年开始进行水合物的研究[12], 提出了三个研究方向: (1)水合物勘探关键技术; (2)水合物开采原理与技术; (3)含水合物矿区的环境和灾害力学问题研究以及上部覆盖水合物层的油气田安全开采的保障. 通过水合物热分解引起地层软化和破坏研究, 发现水合物分解相变存在传热、渗流、应力重分布的多物理效应, 是一个多相、多尺度、多过程的科学问题, 由相似分析得到水合物相变、热传导、渗流和应力重分布特征时间相差2个量级以上, 其中传热最慢, 这是整个问题的核心. 当前国际试采证实单纯依靠渗流原理的油气开采方案来开采水合物难以实现商业化开采, 而水合物的分解要消耗大量的热, 这是整个问题的瓶颈. 由于所处地层的特殊性, 压裂法的适用性和有效性, 也是有待研究的问题, 急需寻找合适的经济高效的开采方法[13]. 郑哲敏先生敏锐地指出必须突破依赖热传导的传统油气开采方案的瓶颈, 因而前瞻性地部署类似采煤、采矿的机械开挖方案研究, 可以利用表层相对温热海水对流加热从海底提升的沉积物, 并在一定的高度将沉积物分离并回填到挖掘区, 提高开采效率的同时保障地层安全, 并称之为机械−热联合开采水合物方法[14].
机械−热联合开采水合物方法的基本思路是[15-17]: 由于提高热传导效率是水合物开采的核心, 要达到这个目的, 可以减小传热的尺度, 增加传热表面积. 因此, 像采矿一样通过机械设备挖掘水合物地层并将水合物粉碎成小颗粒, 然后与一定温度的海水掺混, 沿管道输送一定距离后在分解仓/管道分解完毕, 将沉积物土颗粒和水分离, 土体回填、气体通过开采管道收集. 如图2所示, 其基本流程是: 地下挖掘→粉碎→传送→与海水混合/分解/分离/回填→颗粒流输送→气体输送与收集, 即像采煤采矿一样通过机械设备挖掘水合物地层并将水合物粉碎成小颗粒, 然后在预先设计的水合物分解仓内实现较热海水的供给、小颗粒与海水的掺混、水合物分解、沉积物的分离回填、气体通过开采管道的收集. 这种方法将水合物沉积物转变成可以随流体流动的小颗粒, 因此, 既可借助海水与对流传热这个巨大的热源供给水合物分解的热量, 又可将沉积物的回填恢复一定的地层强度, 也避免水合物分解的气体从覆盖层的泄漏.
机械−热联合法可充分利用海水的巨大热量, 提高开采效率, 同时将回收的土颗粒及时回填可有效地降低地层变化和破坏的安全性风险, 适合于开采水合物分布集中且储量大的未成岩的水合物地层. 机械−热联合法的重要内涵之一是避免将水合物沉积物全部举升到海平面, 使水合物在管道中的适当高度完全分解, 然后在此处进行气−液−固的分离, 最终只有分解产生的气体通过管道输送到海平面, 大大降低了管道输送所需要的能量, 同时不需要破坏上覆盖层.
相比于传统油气开采方案, 机械−热联合开采水合物的优势在于[17]:
(1)该方法可以在更大空间内对水合物地层进行开挖, 机械开挖可以满足水合物的供应量与供应效率需求; 将水合物沉积物粉碎成小颗粒, 缩短了热传导特征时间, 容易调控水合物的开采效率和开采程度, 比如1 m尺度的热传导特征时间约为106 s, 而切割成1.5 cm的颗粒后热传导的特征时间约为10 s, 避免了井筒降压法开采受分解范围限制的缺陷.
(2)可以充分利用海水的巨大热量, 将表层海水输送到下部水合物层, 与粉碎的水合物沉积物小颗粒进行掺混, 然后通过管道输送方式将混合物向上部提升; 降低地层安全性风险系数, 可对地层开挖方式和开挖空间预先设计优化, 控制开挖间隔、开挖孔洞尺寸、开挖支护等, 对地层安全性可控; 可以考虑将气体膨胀做功利用到沉积物提升过程与注入海水的能量消耗等.
1. 机械−热联合开采装备、能量与经济性评价
1.1 装备与能量评价[14]
从装备角度看, 机械−热联合开采地层挖掘装备在采煤、采矿工程中有类似的装置, 如滚筒式采煤机、液压牵引采煤机、电牵引采煤机、盾构机等, 目前的滚筒式采煤机对各种煤层适应性强, 能适应较复杂的顶底板条件, 还有利于实现综采设备配套和自动控制, 主要工作参数包括生产率、采高(主要决定于滚筒的直径)、截深(一般小于1 m)、截割速度(3.5~5.0 m/s)、牵引速度、装机功率等. 破碎设备有颚式破碎机, 复摆颚式破碎机的进料最大粒度在120~1200 mm, 排料口尺寸最小10 mm, 处理能力在6~1000 t/kW之间, 可以根据实际情况进行多次破碎. 在中、细碎方面, 对于产量较小的情况可以选择颚式破碎机; 产量较大时, 选择圆锥破碎机.
深海地层中作业涉及长期的高压、高腐蚀、地层未成岩、长距离动力供应与信号传输等复杂环境条件, 往往需要作业装备小型化、智能化及配套的动力系统, 尤其深海无人作业未来要考虑建立环保、安全、自动控制、连续机械开挖并生产的一体化开采方式, 机械−热联合开采装备和开采总体方案的设计也应结合我国水合物成藏特点、深海开发战略要求等, 进行前瞻性的研究和开发. 目前海底水合物地层挖掘粉碎形式有带螺旋输送的钻头破碎、喷嘴射流破碎等, 在现场试验中采用无隔水管钻杆钻进到水合物层并形成开采井口空间, 进行破碎、射流、抽吸等, 验证了设备的可行性[18-19].
针对机械−热联合开采, 采掘粉碎可考虑如下流程: 绞碎装置, 主要用于水合物地层中混合物的绞碎, 绞碎范围取决于水合物的开采量以及连接软管的装载量; 连接软管, 设计直径10~40 cm, 主要用于在地层中倾斜铺展、伸缩, 便于水合物吸收进来以及海水的汇入; 活塞式推进装置, 由过滤网和推进回填机械传动两部分组成, 既可以起到过滤网的作用, 只允许气体和水通过, 又可以向前推进, 将多余的沉积物再次回填到绞碎区域; 吸力装置, 采用渣浆泵系统, 可以提供一定的吸力, 促使混合液体和水合物沉积物颗粒流动到软管内, 其中气体到达该吸力装置处时可以利用膨胀做功转化为提供吸力的能量; 再连接竖直井筒, 设计直径10~40 cm, 用于流体的输送; 输水管道, 用于较高温度海水的注入, 加速软管内水合物的分解; 注海水系统, 置于开采平台上, 将海平面较高温度的海水注入到输水管道中; 开采平台, 用于气体的收集, 以及开采系统的安装布置, 并配有远程控制系统, 控制吸力装置、活塞推进装置、注海水系统等, 将来可考虑深海小型核电站装置、太阳能发电、风力发电等提供动力源.
从能量角度看, 能量产耗比结合机械−热采的基本流程, 将各个流程的能量消耗细节进行大致估算, 综合考虑机械−热开采模式的各个流程中的能量消耗以及能量产出. 在此定义能量产耗比的概念, 即能量产耗比
$\;\beta $ =能量产出${Q_t}$ /能量消耗${W_t}$ . 选取1天产气量为标准状况下10000 m3为基本单位, 我国南海每天的挖掘、传送、粉碎、输送摩阻、海水注入、沉积物提升、气体膨胀做功的能量消耗分别为2.4 GJ, 1.8 GJ, 0.2 GJ, 0.01 GJ, 0.1 GJ, 1.0 GJ, 5.7 GJ. 考虑将沉积物提升到海床进行气、水和土颗粒的分离, 气体膨胀能量基本等于其他各个流程的能量消耗. 若能充分利用气体膨胀做功产生的能量则可抵消机械能消耗[14, 16].1.2 注入海水温度评价[14]
假定海水以2.0 m/s的流速从温度25 °C的海水表面注入管道, 输送到水合物层, 途经1200 m的海水到达3.5 °C的海床, 再穿入200 m的覆盖层到达水合物层(9.5 °C), 那么管道中海水的温度分布及到达水合物层后的温度是多少?
假定: (1)海水温度沿深度方向线性降低, 覆盖层温度沿深度方向以地温梯度为3 °C/100 m升高; (2)注入海水沿管道向周围环境传递的热量能够迅速消耗; (3)管道中海水径向等温, 那么问题可以简化为含有源和流动的热传导问题.
基本参数: 海水密度
$\rho $ , 比热$C$ , 热传导系数$\lambda $ , 注入速度$v$ ; 管道直径D, 壁厚$d$ , 海水段长度${L_w}$ , 覆盖层段长度${L_s}$ , 热传导系数${\lambda _p}$ ; 海水环境沿深度方向温度分布$$ {T_w} = \frac{x}{{{L_w}}}({T_{fw}} - {T_{sw}}) + {T_{sw}} $$ (1) 覆盖层环境沿深度方向温度分布
$$ {T_c} = \frac{{x - 1000}}{{{L_w}}}({T_{hw}} - {T_{fw}}) + {T_{fw}} $$ (2) 数学描述: 由于管道在海水层的传热与在覆盖层的传热是类似的, 这里仅推导海水层的热传导过程. 管道内部输送海水时, 沿着管道长度方向任意位置存在管道外部与内部流动之间的温差, 因而引起两者之间的热量传递, 一般地, 若考虑外部热交换远快于内外之间的热交换的三维问题时, 外部温度作为边界条件, 而在考虑一维问题时, 则以热源项的形式存在.
控制方程
$$ \rho C\frac{{\partial T}}{{\partial t}} + \rho Cv\frac{{\partial T}}{{\partial x}} - \lambda \frac{{{\partial ^2}T}}{{\partial {x^2}}} = {\lambda _p}\frac{{{T_w} - T}}{d}\frac{4}{D} $$ (3) 边界条件
$$\left. \begin{split} & x = 0,\;\;T = {T_w} \\ & x = {L_w},\;\;\frac{{\partial T}}{{\partial x}} = 0 \end{split}\right\} $$ (4) 初始条件
$$ t = 0,\;\;T = {T_w} $$ (5) 对方程与边界进行傅里叶级数展开
$$ T = {T_w} + \sum\limits_{n = 0}^\infty \sin \left({\frac{{2n + 1}}{{2{L_w}}}} \text{π} x\right) \cdot U(t) $$ (6) 求解得到
$$ T = {T_w} + \sum\limits_{n = 0}^\infty \sin\left( {\frac{{2n + 1}}{{2{L_w}}}} \text{π} x \right)\cdot \frac{{{\eta _n}}}{{{\xi _n}}}\left[ {1 - \exp ({\xi _n}t)} \right] $$ (7) 其中
$$\left. \begin{split} & {\eta _n} = \frac{{32{\lambda _p}}}{{\rho CDd}} \cdot \frac{{{{( - 1)}^n}}}{{{{(2n + 1)}^2}{\text{π} ^2}}}\left( {{T_{fw}} - {T_{sw}}} \right) \\ & {\xi _n} = \frac{v}{{{L_w}}} + \frac{{\lambda {{(2n + 1)}^2}{\text{π} ^2}}}{{4\rho CL_w^2}} + \frac{{4{\lambda _p}}}{{\rho CDd}} \end{split} \right\}$$ (8) 考虑时间较长以后的情况
$$ T(x) = {T_w} + \sum\limits_{n = 0}^\infty \sin\left( {\frac{{2n + 1}}{{2{L_w}}}} \text{π} x\right) \cdot \frac{{{\eta _n}}}{{{\xi _n}}} $$ (9) 传热情况主要取决于管筒的热传导系数、管径、壁厚和流动速度. 热传导系数越小, 则交换的热量越小, 管径和壁厚越大, 交换的热量越小. 当流动速度较大时, 降温较慢.
取参数值如下: 海水密度
$\rho = 1000{\text{ kg/}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{3}}}$ , 比热$C = 4211{\text{ J/(kg}} \cdot {\text{K)}}$ , 热传导系数$\lambda = 0.56{\text{ W/(m}} \cdot {\text{K)}}$ , 注入速度$v = 2{\text{ m/s}}$ ; 管道直径$D = 0.4{\text{ m}}$ , 壁厚$d = 0.04{\text{ m}}$ , 海水段长度${L_w} = 1200{\text{ m}}$ , 覆盖层段长度${L_s} = 200{\text{ m}}$ , 热传导系数${\lambda _p} = 30{\text{ W/(m}} \cdot {\text{K)}}$ .保持较小的流速且管道不隔热, 海水输送到水合物地层还能保持在15 °C以上, 比水合物分解所需温度还高出5 °C左右, 若管道镀一定的隔热材料, 则输送到海底的温度会更高. 在充足的海水供给的条件下, 足够水合物分解所需热量保证. 这样节省了加热带来的巨额费用.
从注入海水供应热量估计和能量优化角度, 为了避免水合物分解过程中的不稳定流、结冰或水合物二次生成, 同时保证固体颗粒悬浮, 原位挖掘天然气水合物地层后粉碎的颗粒直径可设定在0.1~1.0 cm 之间, 控制水流速度0.22~0.67 m/s, 温差5 K 以上, 混合物中水的体积分数在0.85 以上[16].
1.3 经济性评价
深海作业的费用主要包括: 海洋平台成本、勘探开发费用、开采井费用、海上处理费用、操作费用、泵送费用等. 经计算, 若采用20口井, 这些费用总额度为8000万元左右. 按照日产气量10000 m3/d, 2年之内即可收回这些成本. 由于这些费用是深海开采所必需的, 目前暂不计入下面现值法经济性估算中.
借鉴油气田开发中经济产量的定义[20], 把现有技术经济条件下, 能够达到企业经营目标的水合物产量定义为水合物经济产量. 类似地, 水合物经济产量临界值依据投入产出平衡原理进行计算. 将投资、成本和费用、税金等视为投入, 将天然气销售收入视为产出, 能够平衡投入和产出的水合物产量即为水合物产量临界值, 高于该临界值的水合物产量即为水合物经济产量.
净现值法(NPV)是被国内外广泛应用的投资效果评价方法之一[21]. 净现值是根据企业追求的投资效果, 以企业目标收益率为贴现率来计算项目在使用年限内发生的现金流入和现金流出的现值总和. 净现值为正的项目能够确保企业获得预期的投资收益, 项目可行; 净现值为负的项目不能满足企业的投资收益要求, 项目不可行或者有待改进. 项目净现值依据下式进行计算
$$ NPV = \sum\limits_{t = 1}^n {{{\left( {CI - CO} \right)}_t} \times {{\left( {1 + {i_c}} \right)}^{ - t}}} $$ (10) 其中, CI表示现金流入量(万元); CO表示现金流出量(万元); n表示计算周期(年); ic表示企业目标收益率, 石油行业一般取12%[22].
以采油项目为依据, 水合物机械−热开采项目的成本费用是指企业在生产经营活动中按照规定发生的一切消耗和费用的总和, 主要包括水合物开采成本、管理费用、销售费用和财务费用, 其中后三项是在水合物开采过程中发生的费用, 不计入水合物开采成本, 而作为当期损益直接从销售收入中扣除[22-23].
借鉴油气开采成本会计报表[24], 水合物开采成本主要包括以下13项: 动力费、材料费、燃料费、生产人员工资、福利费、气体处理费、地下作业费、测试费、修理费、生产维护费、折旧费、储量占用费和其他开采费用. 动力费是指在水合物开采过程中直接消耗的电力等; 材料费是指在水合物开采过程中机械设备直接消耗的各种材料; 燃料费是指在水合物开采过程中直接消耗的固体、气体和液体燃料费用; 生产人员工资是指直接从事水合物开采的工作人员的工资、奖金和各种补贴; 福利费是指按生产工人工资总额的14%提取的各种福利费; 气体处理费是指天然气净化罐装费, 包括相应设备的折旧在内; 地下作业费是指地下机械设备和设施的折旧费; 测试费是指水合物开采过程中的测井测试费; 修理费是指地下及地面设施的修理费; 生产维护费是指保持开采持续进行的维护费用, 如技术改造费等; 折旧费是指生产设施和房屋建筑等按规定提取的折旧费; 储量占用费是指按企业规定提取的, 用于企业扩大再生产而寻找新增储量发生的费用; 其他开采费用主要是指厂、矿两级管理及组织开采过程中发生的各种费用.
把上述13项成本划分为以下5种成本定额, 即与开采井(竖直输送管道)个数有关的费用、与产气量有关的费用、与产水量有关的费用、与产砂量有关的费用和与固定资产有关的费用[22]. 与水合物开采井个数有关的费用CTW主要包括材料费、燃料费、动力费、工人工资及福利、修理费、地下作业费、测井测试费和其他开采费. 与产水量有关的费用Cwi满足下式
$$ {C_{{\text{wi}}}} = {R_{\text{w}}}{Q_{\text{w}}} $$ (11) 其中, Rw是水处理费用定额(元/t); Qw是年产水量(104 t). 与产气量有关的费用Cgi满足下式
$$ {C_{{\text{gi}}}} = \left( {{R_\text{f}} + {R_\text{c}}} \right){Q_\text{g}} $$ (12) 其中, Rf 是气田维护费用定额(元/立方米); Rc是储量使用费用定额(元/立方米); Qg是年产气量(104 m3). 与固定资产有关的费用Czj主要涉及设备的折旧计算, 根据固定投资及运转情况, 结合财务报表数据和开发年费, 得到合适的设备折旧率, 从而确定固定资产的折旧费用. 与产砂量有关的费用Csi满足下式
$$ {C_{{\text{si}}}} = {R_\text{s}}{Q_\text{s}} $$ (13) 其中, Rs是砂处理(泥砂回填)费用定额(元/立方米); Qs是年产砂量(104 t). 因此, 机械−热开采的单井成本模型满足下式
$$ C = {C_{{\text{TW}}}} + {C_{{\text{wi}}}}{\text{ + }}{C_{{\text{gi}}}} + {C_{{\text{si}}}} + {C_{{\text{zj}}}} $$ (14) 其中, Czj表示与固定资产有关的折旧费.
单井扣税之后的销售收入N可表示为
$$ N = {Q_\text{g}}IP\left( {1 - {T_{{\text{ax}}}}} \right) $$ (15) 其中, P表示天然气售价(元/立方米), I表示天然气商品率, Tax表示综合税率.
单井开采的利润Pm满足下式
$$ {P_{\text{m}}} = N - C $$ (16) 由水合物产量临界值定义(即Pm = 0)可知, 单井的经济极限年产气量满足下式
$$ {\left( {{Q_\text{g}}} \right)_{\min }} = \frac{{{C_{{\text{TW}}}} + {C_{{\text{wi}}}} + {C_{{\text{gi}}}} + {C_{{\text{si}}}} + {C_{{\text{zj}}}}}}{{IP\left( {1 - {T_{{\text{ax}}}}} \right)}} $$ (17) 以采油项目[16]为参考, 取固定操作费用CTW为20万元/(井·年), 水处理费用定额Rw为13.9元/立方米, 砂处理费用定额Rs为13.9元/立方米, 天然气价格P取2元/立方米, 天然气商品率I取0.96, 综合税费Tax取0.15元/立方米, 每年的折旧费Czj取5万元.
水合物按I型结构考虑, 根据其分子式能够确定产水量与产气量满足下式
$$ {Q_\text{w}} = {Q_\text{g}}\frac{{1 - 0.21{S_\text{h}}}}{{1.64 \times {{10}^2}{S_\text{h}}}}{\rho _\text{w}} $$ (18) 产砂量与产气量满足下式
$$ {Q_\text{s}} = {Q_\text{g}}\frac{1}{{1.64 \times {{10}^2}{S_\text{h}}}}\frac{{1 - \phi }}{\phi }{\rho _\text{s}} $$ (19) 以南海北部海域水合物储层为例, 孔隙度
$\phi $ 和水合物饱和度$ {S_\text{h}} $ 均取0.4, 经计算获得单井的经济极限年产气量${\left( {{Q_\text{g}}} \right)_{\min }} = 43.9 \times {10^4}\;{{{{\text{m}}^{\text{3}}}} /{{\text{a}}}}$ ; 假设单井每年工作时间T为330 d[16], 则经济极限日产气量为$ {\left( {{q_\text{g}}} \right)_{\min }} = 1.33 \times {10^3}\;{{{{\text{m}}^{\text{3}}}} /{{\text{d}}}} $ .水合物机械−热开采项目的净现金流量可按下式进行计算
$$ \begin{split} & \sum\limits_{t = 1}^n {{{\left( {CI - CO} \right)}_t}} = \\ &\qquad \sum\limits_{t = 1}^n {{{\left[ - {I_{{\text{pre}}}} - {I_{{\text{pro}}}} - {I_{{\text{trial}}}} + \left( {{{\left( {{q_\text{g}}} \right)}_t} I - {{\left( {{q_\text{g}}} \right)}_{\min }}} \right) T \left( {P - {X_\text{g}}} \right) \right]}_t}} \end{split} $$ (20) 其中, Ipre表示前期研究费用, 取200万元; Ipro表示前期工程建设费用, 取300万元; Itrial表示试生产费用, 取100万元[16]; Xg表示天然气的储量使用费, 以采油项目[16]为参考取0.15元/立方米.
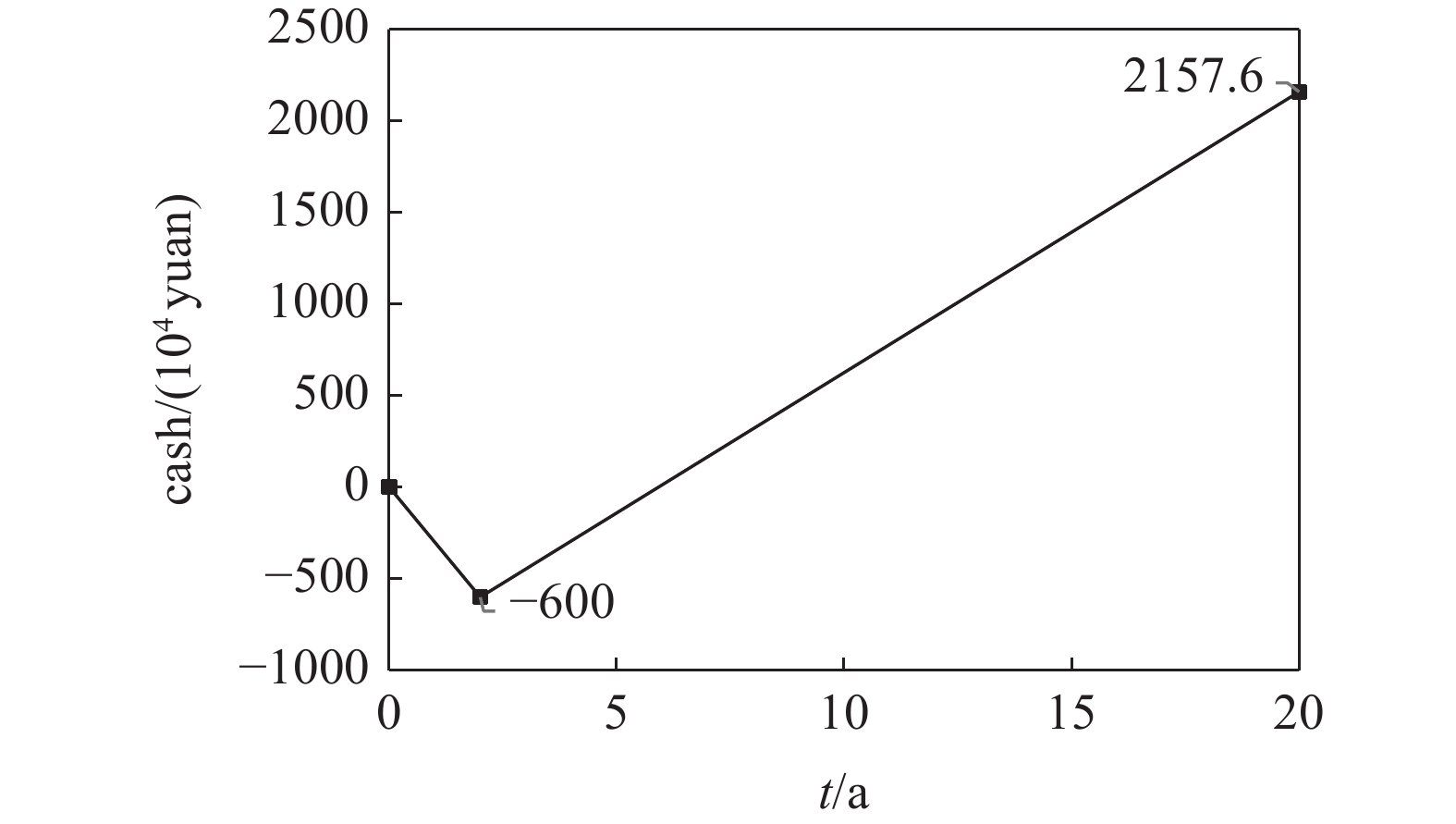
现取日平均产气量为qg = 4.0 × 103 m3/d, 与此日平均产气量对应的日平均水合物沉积物挖掘量为qV = 73.2 m3/d. 普通的机械设备即可能实现上述日平均挖掘量. 假设水合物机械−热开采项目的开采时间为20年, 前2年为投资建设期. 在上述日平均产气量的条件下, 20年内净现金流量如图3所示, 可以看出水合物机械−热开采项目在第6年由亏损转入盈利, 该项目在资金投入与产出方面是可行的.
2. 管道含水合物相变气液固多相流动研究进展
2.1 小块体水合物沉积物分解速率问题
准确掌握水合物的分解规律是描述管道内气液固三相流动规律的基础. 通常来说, 水合物的分解速率包括本征分解速率、传热速率和传质速率. 通过实验测量得到的分解速率只有首先排除掉传热和传质速率的影响, 得到的本征分解速率才是通用的, 进而可以在本征分解速率的基础上考虑传热和传质的影响[25]. 目前关于水合物分解动力学的实验研究主要依靠高压反应釜和流动环道两种装置[26].
前期开展的水合物分解实验大多在高压反应釜内进行. Kim等[27]在半间歇式搅拌釜反应器中进行了甲烷水合物的分解实验. 在高速搅拌的情况下, 可以忽略气相主体到粒子表面的传质阻力和水相主体到粒子表面的传热阻力. 通过假定水合物的分解速率和粒子总表面积与气体逸度差成正比建立了Kim分解模型. Kim模型描述了水合物的本征分解速率, 被认为是用来描述水合物分解过程最经典和常用的模型, 它建立的分解速率模型可表示为驱动力、相界面面积和速率常数的乘积. 这一模式为后续诸多研究者所认可和采纳, 并基于此模型开展了大量的研究[28]. 在Kim模型的基础上, Jamaluddin等[29]将传热和传质速率与本征分解速率耦合在一起建立了一个新的模型. 孙长宇等[30]通过假定水合物的分解速率和剩余水合物的量成正比研究了甲烷和二氧化碳水合物的分解性质. Oyama等[31]研究了多孔介质中水合物的分解, 在考虑传热和偏离相平衡的基础上提出了一个沉积物中的水合物分解模型. 沉积物中的孔隙结构会影响水合物的相平衡温压条件和分布状态, 从而会对水合物的分解速率产生影响. Yang等[32]研究了水的盐度对多孔介质中二氧化碳水合物分解的影响. Misyura等[33]通过实验研究了冰点以上和冰点以下水合物颗粒的大小对分解速率的影响.
水合物在管道流动状态下分解时, 各相界面之间的传热、传质特点以及管道中的浓度、速度分布都会对水合物的分解产生影响, 水合物的分解机理与在反应釜中存在区别. Sean等[25]假设水合物分解的驱动力是水合物和周围水之间的摩尔吉布斯自由能之差, 通过实验研究建立了水流条件下纯水合物颗粒的分解速率模型. 付强等[34]建立了一个管道流动条件下纯甲烷水合物的分解模型, 考虑了管道内压力、温度的连续变化以及固液两相速度差对分解速率的影响, 此模型尚缺乏实验的验证. 目前不同学者开展的流动环道实验多是研究气液流中水合物的成核、生长、沉积、堵塞和分解过程, 通过控制管道的压力和温度条件来达到合成和分解水合物的目的, 进而了解水合物堵塞输送管道的机理, 以达到合理控制水合物风险的目的[35].
综上所述, 目前描述沉积层水合物分解速率的模型大都采用Kim-Bishnoi模型或是看作Kamath模型, 这些模型主要是描述某一温度和压力下稳定状态时的分解, 但是含水合物的沉积物颗粒在管道中流动时, 水合物的本征分解速率、固体颗粒中的传热和传质过程、水合物饱和度、颗粒浓度以及两相之间的速度差都是影响水合物分解的重要因素.
含水合物沉积物颗粒在管道流动状态下的分解与注热、降压等使得储层孔隙中的水合物分解有本质的不同, 传统方法以渗流和热传导为主要的控制机制, 而流动环境下的分解以对流传热为主要控制机制, 传热面积和传热效率大大提高, 目前关于此机制的研究非常缺乏, 有必要首先通过实验研究对流传热条件下含水合物沉积物颗粒的分解参数, 确定分解速率模型. 小颗粒的分解率问题越清楚, 有助于优化设计颗粒粉碎尺度大小, 也利于更充分高效地调控管道中水合物的分解过程.
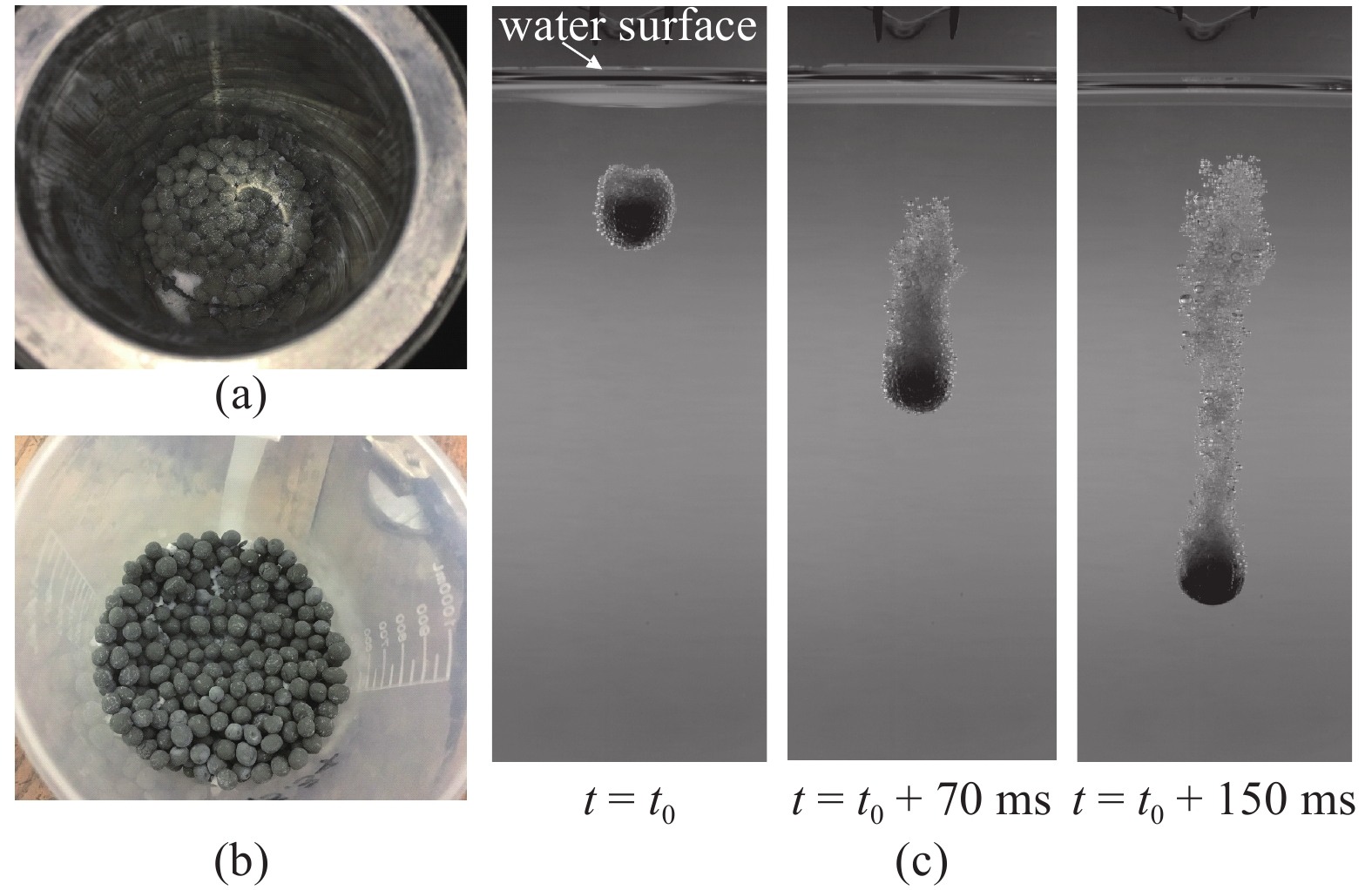
中国科学院力学研究所李鹏等[36-37]搭建了管道流动体系下含水合物球形土颗粒分解速率测量的实验装置(图4), 包括球形土颗粒制备模块、含水合物球形土颗粒的制备与分解模块、供气模块、供水模块、分解产气测量模块、数据收集记录系统. 利用在实验室中合成的含二氧化碳水合物沉积物球形小颗粒, 开展了单个颗粒在水中下落过程中的分解实验(图5). 通过高速摄像机记录颗粒在水中下落过程中的分解现象. 通过单颗粒分解实验测量了不同粒径、不同水温条件下分解所需的总时长, 总的分解时长随颗粒直径的增大而增大, 随水温的增加而减小, 最终利用实验数据分析得到了水合物在对流传热条件下的分解速率模型.
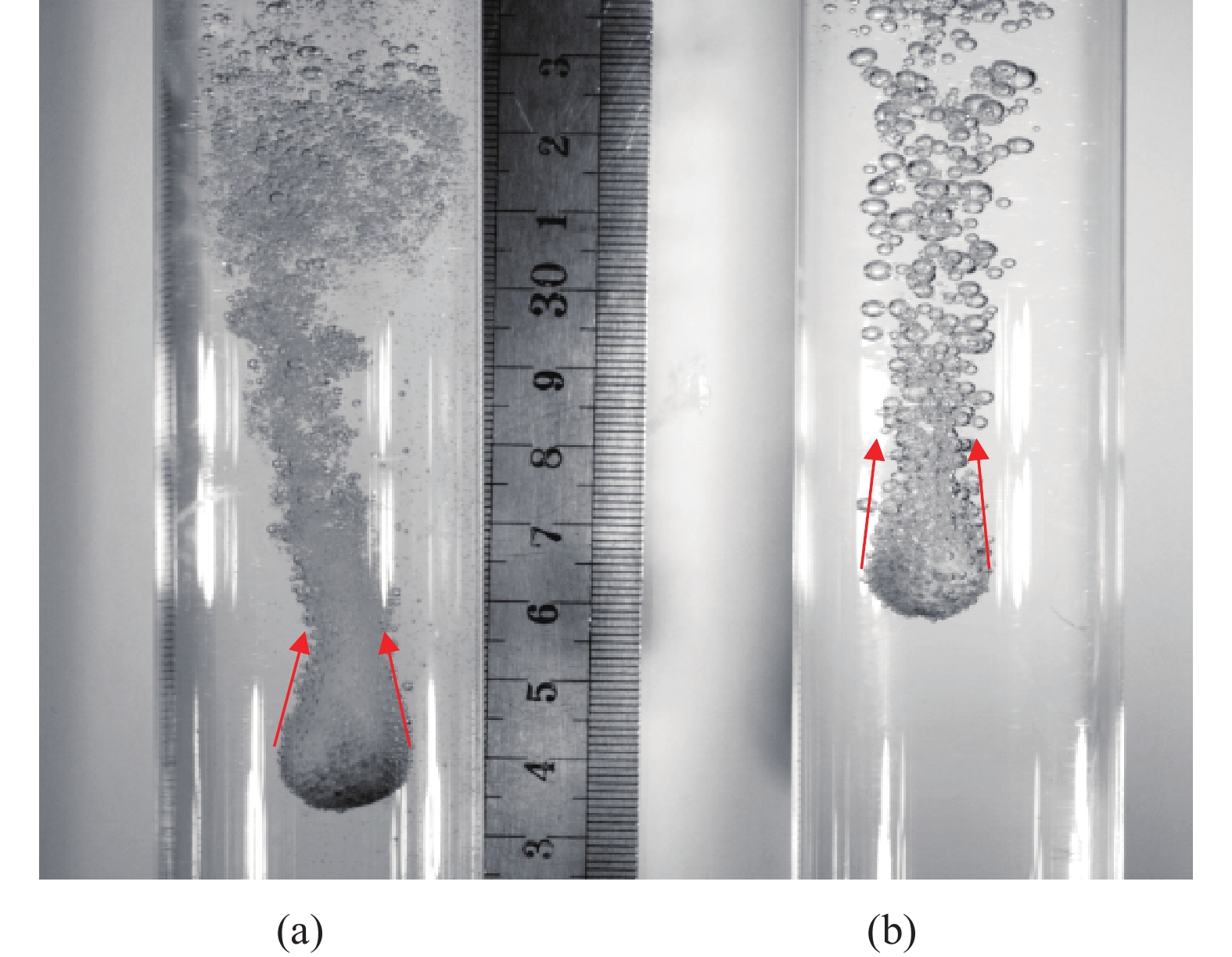
同时, 利用上述装置测量了含水合物颗粒在水中的下落行为, 研究了气泡与颗粒之间的相互作用机制(图6). 含水合物颗粒在水中下落时, 水合物分解产生的气体从颗粒的孔隙中流出形成大量的气泡包裹在颗粒的周围. 颗粒前端产生的气泡在浮力的驱动下会沿着颗粒表面向上滑动, 并在颗粒后端的某一位置脱离颗粒继续向上运动. 为了深入理解水合物分解后产生的气泡对颗粒输送高度的影响, 通过实验研究测量了含水合物颗粒在水中下落时的沉降速度、气泡尺寸等参数, 阐明了水合物分解后形成的气泡对颗粒沉降特征及阻力系数的影响规律, 并给出了气泡对颗粒运动作用的机制[38].
2.2 管道中含相变的气液固多相输送问题
深入了解管道中含水合物分解的气液固三相流动的演化特征可为工程施工参数优化和管道输送的安全性设计提供重要的理论支撑. 管道输送含水合物沉积物颗粒的流动过程涉及多种组分和多个物理过程, 影响因素众多, 主要包括: 气体和水的各项物性参数; 沉积物颗粒的密度、直径、水合物饱和度等; 管道的直径; 入口处水和颗粒的流量以及初始温度等. 最终需要探究在不同参数影响下管道输送过程中气液固各相的浓度、速度、温度分布以及压降和产气量等信息, 目前针对这种稠密颗粒反应系统主要通过数值模拟和物理实验的手段进行研究.
含水合物分解的多相流动的研究主要在于管道中多相流动的建模、工程工艺参数分析等. 魏纳等[39]和黄鑫等[40]通过建立的井筒多相流动数学模型计算了固体流化开采不同施工参数条件下多相流特性和对工程安全的影响. 徐海良等[41]和陈卫等[42]以绞吸式开采海底水合物为工程背景, 利用管道温压方程、水合物分解方程和多相流动方程计算了水合物在水力提升管道中的分解特性和流动参数变化对分解的影响, 得到了整个流动过程中温度和压力的变化以及水合物颗粒分解速率和分解量的变化. 王志远等[43]通过在质量、动量和能量守恒方程中加入源项来考虑水合物的分解, 计算了深水钻探时井筒中含水合物相变的环空多相流动. 刘艳军等[44]以固体流化开采为工程背景, 研究了水合物浆体的管输特性. 通过守恒方程的源项将水合物分解和多相流动耦合在一起, 考虑了各相之间的相间作用力, 计算了水合物分解与多相流动之间的互相影响. 在实验研究方面, 杨浦等[22]自行研制了一套大型水射流固体流化模拟实验装置, 并利用该装置探究了水合物储集层临界破碎速度、采空区直径和固体流化效果. 赵金洲等[18]研制了水合物固体流化开采大型物理模拟实验系统, 并基于此系统开展了水合物样品快速制备、高效破碎及管道输送等物理模拟实验, 验证了固体流化开采相关理论模型的准确性, 揭示了开采过程中关键参数的变化规律. 实验研究的结果为在南海北部荔湾开展的固体流化试采奠定了基础[19].
数值模拟由于可以描述各相之间复杂的相互作用以及传热传质过程所带来的质量、动量和能量在各相之间的相互传递, 同时可以提供物理实验难以测量得到的细节, 是目前主要的研究手段[45]. 现有的研究结果表明, 在管道入口处, 固相和气相的浓度均以管道中心为轴呈对称分布, 浓度的峰值分布于管道中心的两端; 而在管道出口处, 固相中心区域的浓度远高于两侧近壁面处的浓度. 气体的产生对固体颗粒的输送有明显的减阻作用[44]. 增大液相流量, 可显著降低管道内温度和水合物相平衡压力, 使水合物分解的临界位置上移, 可显著提高气、液、固相速度, 使气相和固相含量降低[39]. 颗粒直径改变, 对管流温压、相平衡压力、水合物开始分解位置基本没有影响[41]. 然而, 由于水合物分解动力学机理研究尚不成熟以及相间作用力模型还不完善, 现有的数值模拟结果的精度还有待实验结果的验证. 目前的物理实验结果大多是关注流动状态的定性观察, 定量测量的结果还较为缺乏[46]. 同时, 以往的研究大都是基于某些有量纲量的变化来考察流动状态, 得到的结果会受限于所研究对象的几何尺寸, 同时不同的量同时变化时可能会带来不同的结果, 难以准确把握整个流动过程的主要控制因素及各个效应的物理机制.
对于海底油气输运管道的水平管路内同样存在水合物生成的问题[47], 基于欧拉双流体模型分析水平管道内水合物浆液的流通特性可知, 水平管道内压力分布主要受流速和水合物颗粒体积分数影响[48]. 前期研究揭示了在管道流中水合物颗粒的生长、聚集、沉积和堵塞机理, 以及这些现象对多相流流型、温度与压力分布等的影响机制. 在水合物储层进行水平井钻进可有效提高泄流面积, 提高开发效率. 我国于2020 年在南海北部神狐海域采用水平井钻采技术进行了泥质粉砂型天然气水合物的试验性开采. 水平井开采受复杂工艺流程的限制, 现有的数学模型与实验结果无法精细描述水平试采井筒内复杂多相流动过程的温压时空变化特征, 有必要构建针对水平井开采段复杂多相流的新模型, 综合考虑防砂筛管、管道多级变径、射孔间距等因素的影响.
郑哲敏先生判断含水合物颗粒在管道内的输送过程涉及水合物分解、传热传质、多相流动等多个物理效应, 是一个新的多场多尺度的科学问题. 含水合物颗粒在管道内的输送过程包含了丰富的多相流动状态和新的信息, 具有多个过程以及相互之间的转化, 即固−液两相流→固−液−溶解气流动→固−液−气泡流动→液−气流动等. 这种含相变的气液固多相流动问题是一个全新的流体力学问题. 研究含水合物分解的气液固三相流动的控制因素与演化特征, 通过机理的研究从实验室尺度认识未来的工程尺度应用, 对于水合物新型开采方法的可行性和安全性评价至关重要.
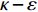
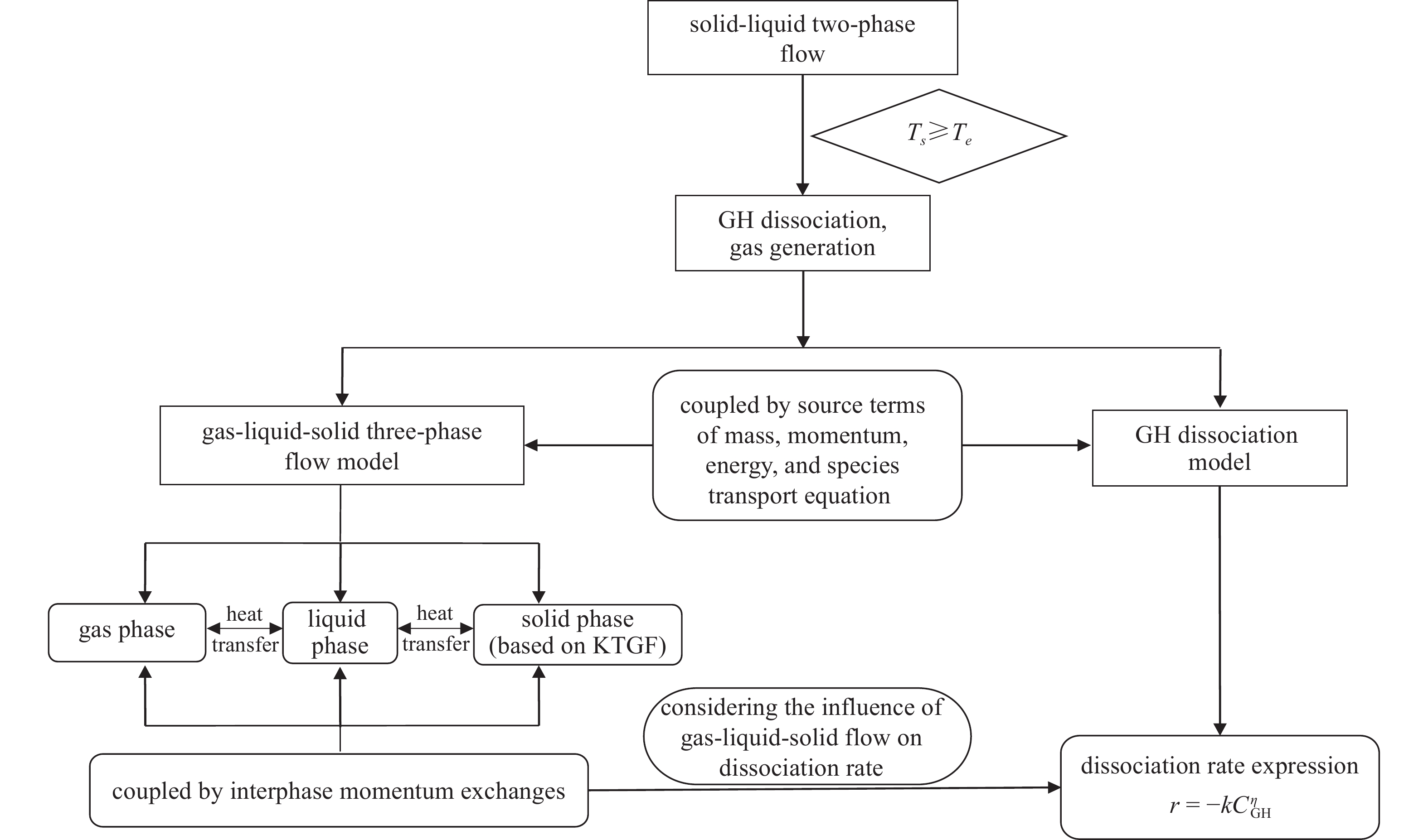
针对垂直管道中含水合物沉积物颗粒的输送问题, 李鹏等[49]基于颗粒动理学理论建立了欧拉三相流三维数学模型, 气液固三相都看作是相互渗透的连续相, 液相采用标准
$\kappa - \varepsilon $ 湍流模型来描述, 颗粒相采用颗粒动理学理论进行描述, 并引入了水合物的分解模型, 同时考虑了气液固三相流动对水合物分解速率的影响. 水合物分解导致的各相之间的质量、动量和能量传输以源项的形式出现在守恒方程中, 并且考虑了气固和液固的相间传热以及三相之间的相互作用. 沉积物颗粒看作是由水合物、水和土骨架三种组分组成, 考虑了由于水合物分解而导致的颗粒内部各种组分的含量变化(图7).考虑各相内部和各相之间的传热, 但忽略气相和固相之间的热传递. 各相的能量方程采用焓方程来进行表示. 水合物分解可以看作一种反应, 反应的焓变等于产物的总生成焓与反应物生成焓之差, 也即潜热, 当差值为负时, 是放热反应; 为正时, 是吸热反应. 固相比焓
${H_s}$ 是土颗粒和颗粒内包含的甲烷水合物、水的焓值的线性叠加, 而甲烷水合物的标准状态焓由相变生成的水和气的标准焓加上潜热计算得到. 而在计算时相变采用有限速率反应方法, 定义反应方程式中每一种组分的标准状态焓.假设水合物的分解速率与剩余水合物的浓度成如下的指数关系
$$ r = - \frac{{{\rm{d}}{C_{{\text{GH}}}}}}{{{\rm{d}}t}} = kC_{G{\rm H}}^\eta $$ (21) 其中,
$r$ 表示分解速率,${C_{{\text{GH}}}}$ 表示未分解水合物的摩尔浓度,$\eta $ 表示速率指数.摩尔浓度
${C_{{\text{GH}}}}$ 定义为如下的形式$$ {C_{{\text{GH}}}} = \frac{{{\rho _{{\text{GH}}}}\phi {S_{\text{H}}}{\alpha _\text{s}}}}{{{M_{{\text{GH}}}}}} $$ (22) 其中,
${\rho _{{\text{GH}}}}$ 表示水合物的密度,$\phi $ 表示颗粒的孔隙度,${S_{\text{H}}}$ 表示水合物的饱和度,${M_{{\text{GH}}}}$ 表示水合物的摩尔质量. 分解速率常数$k$ 通过Arrhenius型的方程来描述$$ k = A{\left( {\frac{{{T_s}}}{{{T_e}}}} \right)^\beta }\exp \left( { - \frac{{{E_a}}}{{R{T_s}}}} \right) $$ (23) 其中,
$A$ 表示前置因子,$\beta $ 表示温度指数,${E_a}$ 表示活化能,${T_e}$ 表示水合物的相平衡温度.水合物分解的源项定义为
$$ {S_{{\text{GH}}}} = - {M_{{\text{GH}}}}kC_{{\text{GH}}}^\eta $$ (24) 其中,
${M_{{\text{GH}}}}$ 表示水合物的摩尔质量.通过对实验室尺度下垂直管道中含水合物分解的多相流动进行的数值模拟系统考察了管道中多相流动的浓度场、速度场、压力场和温度场分布规律. 最初, 固液两相流处于稳定状态. 由于水和颗粒发生对流传热, 当固体颗粒的温度达到水合物的相变温度时, 颗粒中的水合物开始分解产生甲烷气体, 此时管道中由最初的固液两相流转变为气液固三相流, 气体的体积分数逐渐增加, 固体的体积分数逐渐减小. 固体颗粒在水流和气泡的作用下向上流动, 增加了整个床层的孔隙度. 图8显示了固体和气体体积分数瞬时的分布云图. 伴随着固体颗粒的上升, 气泡的连续产生导致固相体积分数的重新分布.
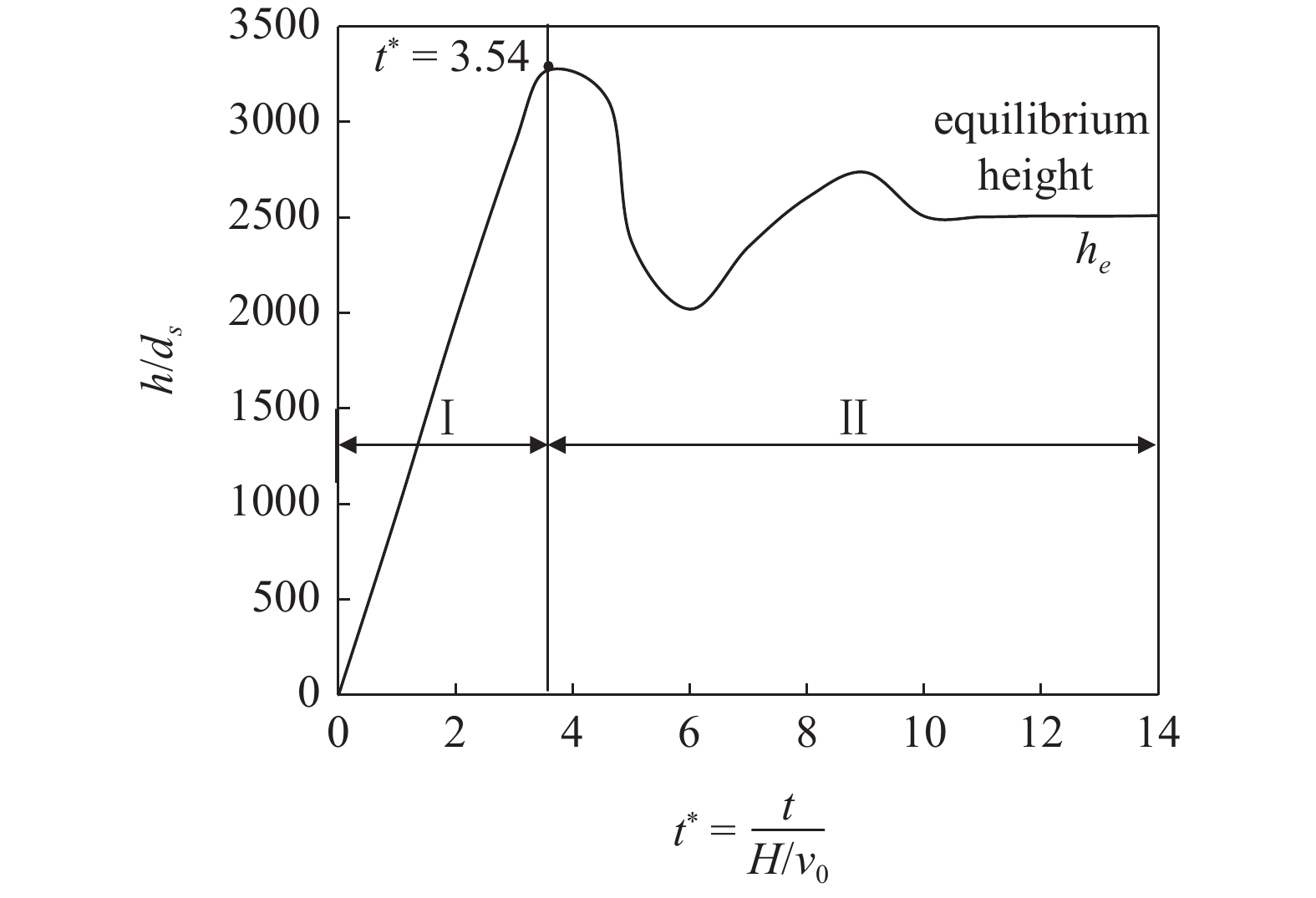
同时, 多相流动产生的速度场和浓度场会明显地影响分解的进行, 而分解引起的传热传质反过来又会作用于多相流动. 研究结果表明所建立的模型能较好地捕捉含水合物沉积物颗粒在管道流动中的分解以及管道中由固液两相流到气液固三相流的转变现象. 含水合物的沉积物颗粒中由水合物分解所释放的气体导致管内压力梯度的波动, 这有利于颗粒的提升[49]. 管道中连续供料条件下的含相变流动研究发现在非稳态流动过程存在着一个水合物完全分解平衡高度, 如图9. 进一步建立了相对加热温度、水合物含量、固体浓度以及新的无量纲数与平衡高度的定量关系
$\dfrac{{{h_e}}}{{{d_s}}} = 9.{\text{2}} \times {10^4}{\left( {\dfrac{{R{e_s}}}{{A{r_s}}}} \right)^{1.{\text{2}}}} {\left( {\dfrac{{{T_{s0}}}}{{{T_{l0}} - {T_{s0}}}}} \right)^{{\text{2}}{\text{.5}}}}\cdot {\alpha _{s0}}\sqrt {\phi {S_H}}$ , 作为水下固液分离位置及机械热采方案优化的理论依据[50].含水合物的沉积物颗粒在管道中输送时, 最优工况可通过管道输送的安全性、产气量和分解平衡高度三个方面来进行考虑, 即在管道不发生堵塞风险的前提下同时满足产气量以及分解平衡高度的约束条件.
如若增加天然气井的产气量, 则必须尽可能增加管道直径、入口速度和入口固相体积分数的值, 然而为了保证输送过程中管道不会发生堵塞, 同时必须要对入口速度和入口固相体积分数进行限制. 根据前期研究分析可得, 入口固相体积分数取为0.10~0.30时既可以保证输送足够多的水合物, 同时管道中又不至于发生堵塞. 考虑中型天然气井的产气量为
$1.0 \times {10^5}\;{{{{\text{m}}^3}} / {\text{d}}}$ , 如若取管道直径为400 mm, 固体体积分数为0.12, 根据此时的最优工况条件, 入口混合物的速度要大于$2.93{\text{ }}{{\text{m}} / {\text{s}}}$ , 颗粒直径要小于13 mm才能满足要求. 确定了各个参数的取值范围后, 然后再计算分解平衡高度的大小以确定分离装置的安装位置. 如果取入口速度为$4{\text{ }}{{\text{m}} / {\text{s}}}$ , 颗粒直径为6 mm, 此时分解平衡高度的值为117 m, 如果天然气水合物样品的埋深在100 m左右, 此时就可考虑将分离装置安装在海床的位置.此外, 在水合物分解过程中和颗粒分离过程中存在着压力腔体或者管道内压力的波动以及引起的振动, 同时较大的内外压差, 使得结构物对静动力承载、抵抗疲劳损伤等环境加剧; 管道内外流动下的稳定性问题, 内部是气、水、固体颗粒的多相流动, 而外部是海水的绕流, 在绕流涡激振动以及内部非稳态脉动流动的作用下管道的动力学响应预测及智能调控是必须解决的关键问题, 也是深海采矿、油气开采等多相输送的共性问题.
3. 地层安全
海洋水合物沉积层具有两个特征: 一是海床具有一定的坡度(3°~15°), 二是深海浅软、欠固结地层[11]. 地层沉陷、滑塌等使得机械−热采的设备不能正常工作, 而且还要考虑地层中海水入侵的影响. 机械−热开采安全的问题是如何最大限度地开挖地层, 既防止大范围的滑塌, 又要避免局部地层的沉陷或破坏[14].
井筒降压、注热等开采方案关心的安全问题有天然气水合物小范围分解对储层变形及井筒结构安全的影响; 大规模开采不当引起的地层塌陷、滑坡、甲烷泄漏以及灾害链的发生等. 机械−热联合开采方法可以借鉴其他开采方案的安全性评价方法以及相关的判别条件. 但挖掘采空过程涉及强烈的机械扰动与振动、机械能向热能转化而加热相变、采空区的扩大而产生严重塌陷或者土体破坏. 因此, 需要具体分析采空区塌陷或破坏的临界尺寸, 进行隔段挖掘采空, 尤其关注深海海底储层内的采空区支护、土体的回填方面的技术, 以形成经济有效的安全防护措施.
3.1 地层变形分析
根据现有模拟结果, 土层的水平位移和最大剪应力会随着水合物分解范围的增大而增大, 土体的水平位移和最大剪应力的最大值以及分布集中与突变现象均发生在水合物已分解与未分解的水平范围的界面附近[51-52].
3.1.1 水合物分解后地层变形[51]
以水合物分解区域土层软化(抗剪强度、变形模量)为原来的1/10为例, 随着水合物分解区的扩大, 地层表面的沉陷区逐渐扩大, 如图10. 考察水合物分解区为50 m, 100 m, 150 m, 200 m, 250 m, 300 m, 400 m, 500 m, 700 m, 在三维情况下, 影响区以近似漏斗形向外扩展, 越靠近上部和中心, 沉降越大. 以水合物分解区域200 m情况下的位移云图和地表面沉陷变形结果来进行说明.
图11给出了在不同分解范围下在覆盖层表面所产生的沉降影响区以及各个位置的沉降量. 可以看到, 每种工况下最大沉降发生在分解区中心位置, 沉降范围和最大值均随分解范围而扩大.
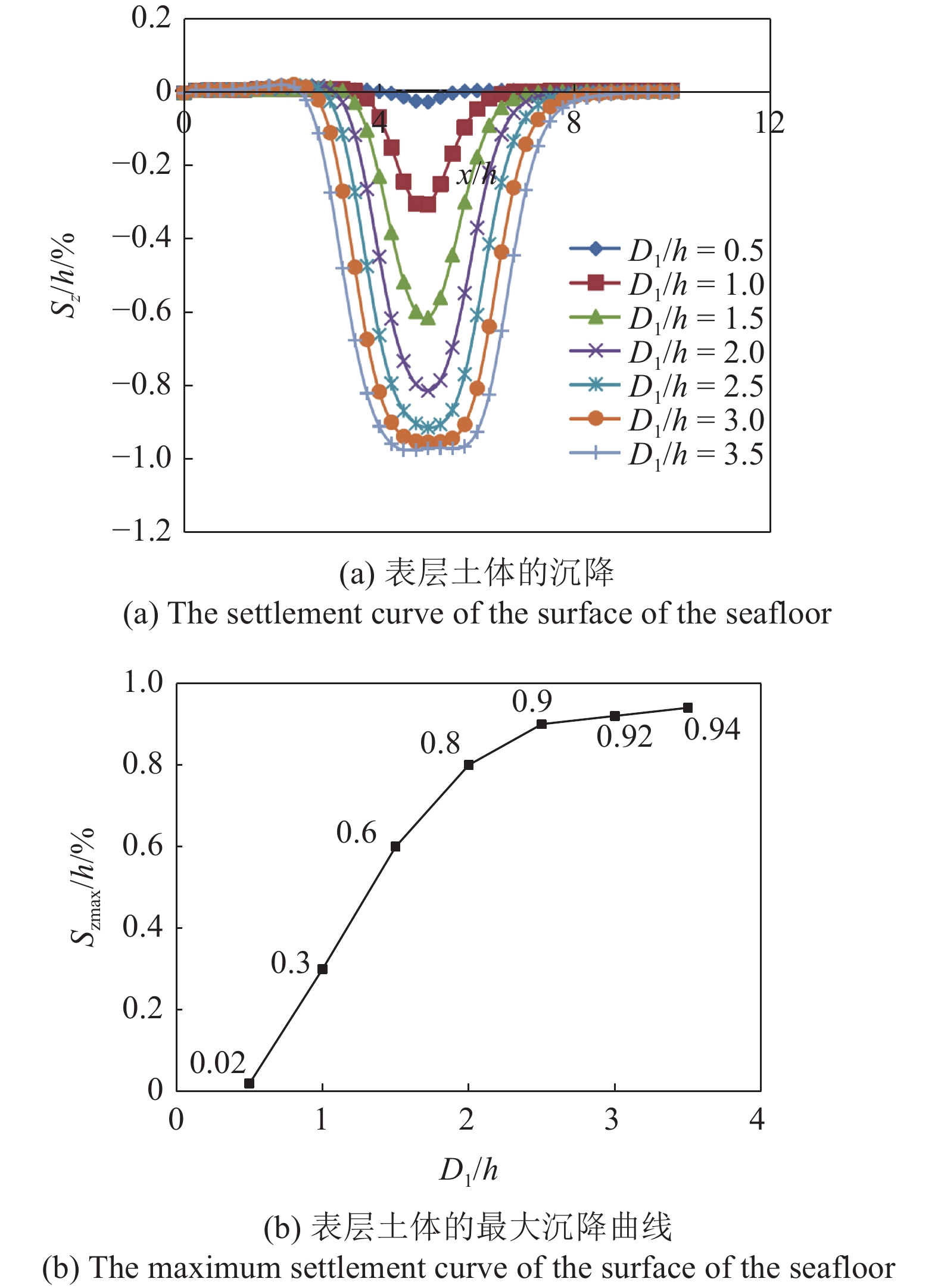
将水合物分解后表层土体沉降量达到10 cm及以上的区域视为影响区域, 则可得到在不同分解范围时, 在覆盖层表面的影响范围, 由图12可以看出, 影响范围与分解范围的差值随着分解范围的增加趋于一个稳定值, 且基本保持不变. 另外, 表层的最大沉降在
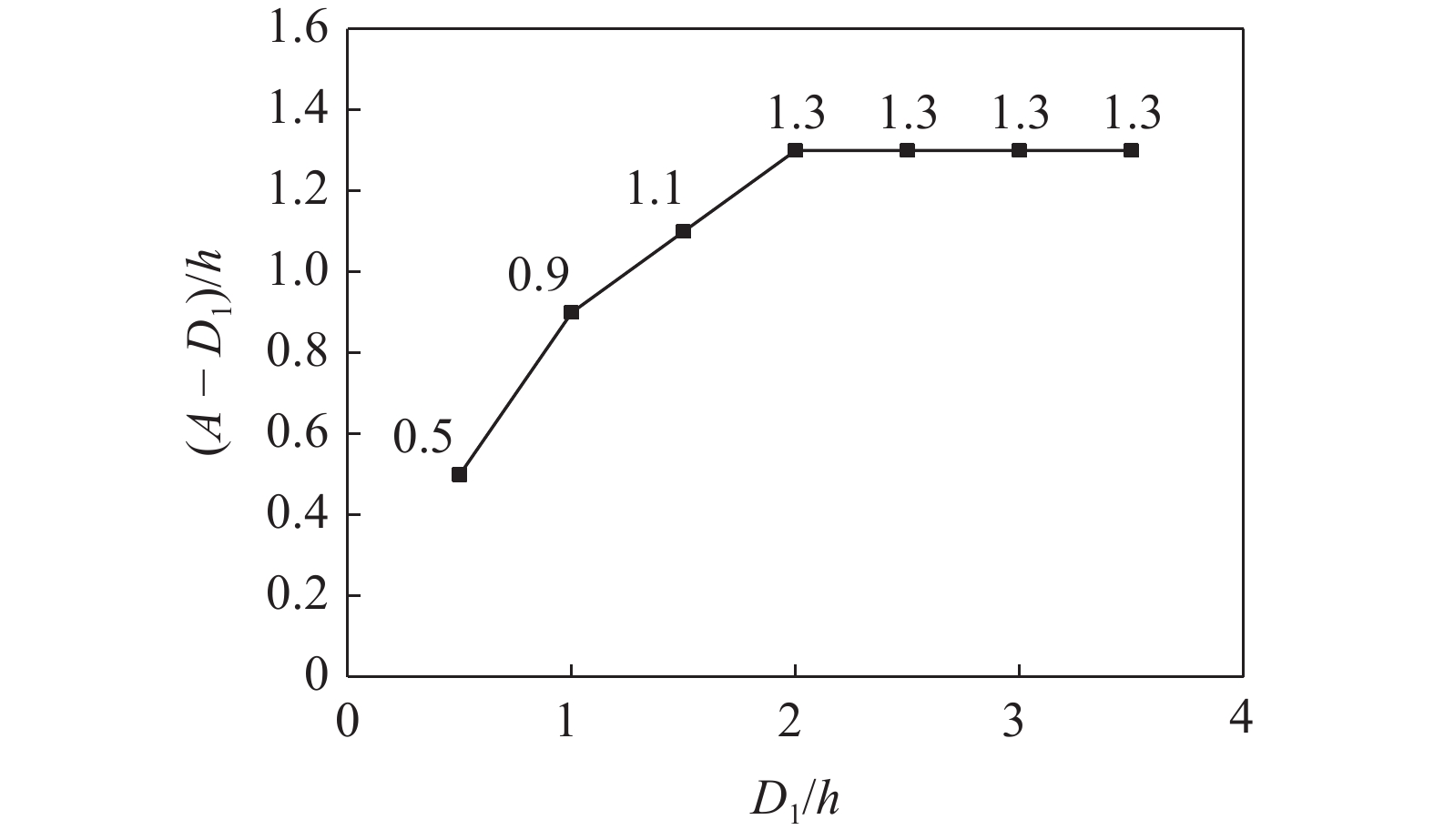
$ {{{D_1}} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{{D_1}} {h \leqslant 1}}} \right. } {h \leqslant 1}} $ 的范围内随着分解范围的增加而呈线性增加, 然后随着分解范围的增加, 表层的最大沉降逐渐趋于稳定值. 土体的变形趋势为“单峰”形式, 即水合物分解以后表层土体沉降最大的位置发生在分解区域的中心处, 往两边逐渐减小. 这是由于分解区域内的土体由于分解后强度降低而对上覆土层的支撑作用减弱以及分解区域以外的地层此时地应力得以释放, 使得土体在自重作用下发生沉降并有水平向的位移.以下为分解200 m时的水平向位移分布情况, 计算过程中, 在分解范围内以及分解边界以外监测了几个竖向截面的水平位移, 如图13. 具体监测的截面位置为x = 300 m, x = 400 m, x = 450 m, x = 500 m, x = 550 m, x = 600 m, x = 700 m截面. 根据监测截面的值作出各个截面的水平向位移. 在分解中心垂直截面(x = 500 m)以上和以下的区域有着不同的水平位移变化趋势. 在分解中心以下的区域土层上部有沿x正向(即沿坡向向上)的水平位移, 且在上部离分解中心越远水平位移越大. 而在下部则出现沿x负向(即沿坡向向下)的水平位移, 水平位移最大的位置出现在覆盖层和水合物层的交界面处. 而在分解中心截面和分解上边界之间的区域则是出现向下的水平位移. 出现以上位移现象的原因是在水合物发生分解的情况下, 水合物分解区域地层变软, 在分解影响区范围内的土体沿分解中心处以漏斗状形式发生位移, 分解中心以下的表层土体有沿坡向向上的水平位移, 而在分解中心以上表层土体有沿坡向向下的水平位移. 底部土层土体的水平位移情况则是由于覆盖层影响区内土体下沉, 把水合物分解区土体向两侧挤压而形成.
3.1.2 水合物地层开挖后地层变形[14, 52]
根据巷道软围岩的变形理论, 对水合物地层开挖后, 地层的沉陷进行估算.
临界支撑压力
$$ {p_{cr}} = \frac{{2{p_0} - {\sigma _{cm}}}}{{1 + k}} $$ (25) 其中,
$k = \dfrac{{1 + \sin \varphi }}{{1 - \sin \varphi }}$ ,${\sigma _{cm}} = \dfrac{{2 c\cos \varphi }}{{1 - \sin \varphi }}$ ,$c,\varphi $ 为黏聚力和内摩擦角.考虑塑性变形, 塑性变形的半径为
$$ {r_p} = {r_0}{\left\{ {\frac{{2\left[ {{p_0}(1 + k) + {\sigma _{cm}}} \right]}}{{(1 + k)\left[ {(k - 1){p_i} + {\sigma _{cm}}} \right]}}} \right\}^{\tfrac{1}{{k - 1}}}} $$ (26) 变形量计算公式为
$$ {u_{ip}} = \frac{{{r_0}(1 + v)}}{E}\left[ {2(1 - v)({p_0} - {p_{cr}}){{\left( {\frac{{{r_p}}}{{{r_0}}}} \right)}^2} - (1 - 2v)({p_0} - {p_i})} \right] $$ (27) 以南海的上覆层和水合物层的基本力学参数为依据, 计算在水合物地层开挖一个近似直径5 m的巷道, 考虑平面应变问题, 这个区域的最大变形量可达到18 cm.
以南海试采区海底土层倾角为3°的情况为例, 考虑采空区海底顶面土体最大竖向位移. 采空区为半径3 m × 高10 m时, 水合物采空区紧邻上部土层的竖向位移最大, 约为6 cm; 竖向位移沿着远离中心水平方向逐渐减小, 在水合物储层采空区顶部投影为圆形, 主要影响区半径为6.0 m. 当采空范围达到12.5 m × 20 m时, 土层变形急剧增加, 最大竖向位移达到30 cm以上. 竖向位移主要发生在采空区上部区域, 水平位移呈现向采空区内挤压的趋势.
从数值计算和理论评估来看, 水合物地层开挖后, 地层沉陷是必须考虑的不安全因素之一. 在上部有1000多米的海水, 上覆层较浅, 且强度不高的情况下, 水合物地层如何开挖, 是否进行支护等需要深入开展分析.
3.2 滑塌分析[51, 53-56]
图14是基于土层分层的滑塌模型. 水合物分解前, 土层是稳定的. 当水合物分解后, 土层中出现超静孔压, 孔隙流体向分层处流动, 如上覆土层与水合物层之间, 导致该处地层的抗剪强度大大降低. 水合物分解区域上方的局部土层重量绝大部分由孔隙流体压力承载, 当水合物分解范围达到临界值
${l_{cr}}$ 后, 地层发生剪切破坏, 于是滑塌发生了. 假定土层剪切破坏服从摩尔库仑强度准则$$ \tau = \sigma \tan \varphi + c $$ (28) 由主应力形式表示如下
$$ {\sigma _1} = {\sigma _3}{\tan ^2}\left( {{\text{π} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {\text{π} 2}} \right. } 2} + {\varphi \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {\varphi 2}} \right. } 2}} \right) + 2c\tan \left( {{\text{π} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {\text{π} 2}} \right. } 2} + {\varphi \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {\varphi 2}} \right. } 2}} \right) $$ (29) 根据沿斜坡方向的朗肯土压力公式与静力学平衡, 可得到关系式
$$ {\rho _{s2}}g{l_{cr}}\sin \alpha = {\rho _{s2}}g{h_2}{\tan ^2}\left( {{\text{π} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {\text{π} 2}} \right. } 2} + {\varphi \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {\varphi 2}} \right. } 2}} \right) + 2c\tan \left( {{\text{π} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {\text{π} 2}} \right. } 2} + {\varphi \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {\varphi 2}} \right. } 2}} \right) $$ (30) 从而推导得到临界长度
$$ {l_{cr}} = \frac{{{\rho _{s2}}g{h_2}{{\tan }^2}\left( {{\text{π} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {\text{π} 2}} \right. } 2} + {\varphi \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {\varphi 2}} \right. } 2}} \right) + 2c\tan \left( {{\text{π} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {\text{π} 2}} \right. } 2} + {\varphi \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {\varphi 2}} \right. } 2}} \right)}}{{{\rho _{s2}}g\sin \alpha }} $$ (31) 上式可以由离心机实验数据得到验证. 计离心机实验中上覆土层的总滑动量为土层表面的总裂缝宽度. 总滑动量
$\Delta d$ 等于滑动体部分在重力沿坡面方向分量作用下的变形, 即$$ \Delta d = \int_0^{{l_{cr}}} {\frac{{\sigma \left( x \right)}}{{{E_{s2}}}}} {\rm{d}}x = \frac{{{\rho _{s2}}g\sin \alpha }}{{2{E_{s2}}}}l_{cr}^2 $$ (32) 其中,
${\rho _{s{\text{2}}}}$ 为上覆土层密度,${h_{\text{2}}}$ 为上覆土层厚度, 上覆土层压缩模量${E_{s2}}$ 为16 MPa.$c$ 和$\phi $ 分别表示黏聚力和内摩擦角.经过计算, 裂缝的总长度与预测长度、沿着斜坡方向的滑动值分别为6 cm, 5.5 cm和6 cm, 基本一致, 证实该模型是有效的.
陈旭东等[51]针对水合物分解导致海床滑塌, 采用圆弧滑极限平衡方法进行了分析, 主要计算不同分解区长度下坡体的安全系数, 以安全系数小于1为坡体不稳定的判据, 对应的水合物分解区即为临界长度.
首先是考虑厚度比(覆盖层厚度与水合物层厚度之比)为1的情况下的临界分解长度. 计算了水合物与覆盖层厚度均为200 m、分解区长度分别为1000 m, 1100 m, 1200 m三个工况, 计算出相对应的坡体安全系数, 见表1.
表 1 不同分解长度下的安全系数Table 1. Safety factor at different dissociation lengthsDissociation length/overburden thickness Safety factor of initial sliding surface Safety factor of critical sliding surface 10 1.498 1.046 11 1.498 1.044 12 1.498 0.931 可以看出, 在厚底比为1的工况下, 当分解的长度达到
${{{D_1}} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{{D_1}} {h = 12}}} \right. } {h = 12}}$ 时, 坡体的安全系数为0.931 < 1, 坡体不稳定, 发生滑动, 故此时分解的临界长度为${{{D_1}} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{{D_1}} {h = 12}}} \right. } {h = 12}}$ . 在该工况下的数值计算结果为$ {{{D_1}} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{{D_1}} {h = 13}}} \right. } {h = 13}} $ . 误差为7.8%. 当然这里的计算结果与覆盖层和水合物层的其他参数如强度值、坡角等因素也有关系. 对于其他的坡体, 临界长度应该有不同的值.当坡体在水合物分解, 同时伴随地震载荷的情况下更易发生滑塌破坏. 在厚度比
${h \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {h H}} \right. } H} = 1$ , 分解长度比(分解区长度与覆盖层厚度之比)${{{D_1}} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{{D_1}} {h = 10}}} \right. } {h = 10}}$ 的情况下, 地震载荷为7级和8级时的安全系数和无地震时的结果对比见表2. 可以看出, 在厚度比为1, 分解范围达到${{{D_1}} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{{D_1}} {h = 10}}} \right. } {h = 10}}$ , 当存在地震载荷时, 坡体的安全系数变小. 也就是说, 当受到地震载荷作用时, 坡体变得比无地震载荷作用时更易破坏.表 2 不同地震等级下的安全系数Table 2. Safety factors at different earthquake levelsEarthquake
gradeSafety factor of initial
sliding surfaceSafety factor of critical
sliding surfacenone 1.498 1.046 7 1.283 1.002 8 1.142 0.896 坡角对安全系数有显著的影响, 尤其在坡角小于10°的情况下. 安全系数还与滑动前海床的精确形状密切相关. 基于无限长坡体的分析结果与基于常规圆弧滑方法分析得到的安全系数区别较大. 一般采用无限长坡体分析方法得到的结果可能离实际较大, 因为该方法忽略了滑动体的重量及惯性, 以及侧壁的强度和阻力. 这一点需要在实际工程应用时注意.
3.3 安全防护[14]
考虑软岩巷道的支护原则, 比如在小型盾构机挖掘过程中, 喷射混凝土, 及时封闭挖掘区周边, 实行密贴支护, 一方面为防止周边土体大变形及强度破坏, 另一方面是为了封闭隔水, 使周边土体与支护共同支承围岩压力; 采用锚喷网支护, 允许适当变形适应软岩大变形的特点, 同时形成支护与周边土体一体化的支承圈维持巷道和支护的稳定; 实行二次支护, 在锚喷网作为一次支护控制巷道变形稳定后进行二次支护, 一、二次支护共同支承围岩应力; 对破碎区域进行注浆加固, 提高支承圈的强度及自承力. 为了降低高额的支护费用, 考虑进行分区隔段开挖, 或者开挖到一定尺度的水合物地层后进行加固处理, 同时形成一个开采、安全性实时评估、加固三者结合的安全预警与应急的开采体系.
4. 结论与展望
4.1 结论
我国水合物资源量可观, 而单纯依赖渗流原理的传统油气开采方案难以实现水合物高效、安全、绿色的商业化开发. 本文针对郑哲敏先生提出的机械−热联合水合物开采新方法的研究进行了综述, 包括该方法提出的背景、内涵以及其中关键工程科学问题的研究进展.
机械−热开采水合物是基于对流传热提高效率的原理和管道多相输送技术而提出的新方法, 相比于其他现有技术, 本质特色在于可以充分利用表层海水的无穷无尽热量和对流传热的优势, 同时可有效控制地层安全, 考虑利用开采气体膨胀作用降低管道提升的能耗. 海底水合物地层挖掘粉碎设备与形式, 如带螺旋输送的钻头破碎、喷嘴射流破碎等, 在现场试验中初步地得到了验证.
基于传热分析, 利用传统管道将海水输送到水合物地层, 海水温度还能保持在15 °C以上, 比水合物分解所需温度可高出5 °C左右, 充足的海水供给可节省加热带来的巨额费用. 以南海水合物区日平均水合物沉积物挖掘量为73.2 m3/d, 开采时间为20年, 前2年为投资建设期的设计方案, 第6年由亏损转入盈利, 在资金投入与产出方面是可行的.
目前已构建了综合考虑多相流动、传热传质和水合物的分解等物理过程的含水合物分解的气液固欧拉三相流三维数学模型, 揭示了多相流动非稳态特征及主要控制因素, 发现了管道输送水合物完全分解平衡高度, 同时得到输送的最优工况可通过管道输送的安全性、产气量和分解平衡高度三个方面来进行考虑, 即在管道不发生堵塞风险的前提下同时满足产气量以及分解平衡高度的约束条件.
机械−热开采地层安全的问题是如何最大限度的开挖地层, 但需要防止大范围的滑塌, 且避免局部地层的沉陷或破坏, 针对井筒降压、注热等开采方案的滑塌临界条件和地层变形的研究结果可借鉴, 但需要具体分析采空区塌陷或破坏的临界尺寸分析, 还要考虑采掘振动、相变等影响, 尤其要关注在采空区支护、土体的回填方面如何高效经济.
4.2 展望
机械−热联合开采涉及力学与热学、物理、化学、海洋学以及机械工程、石油工程等多个学科的交叉融合, 具有丰富的内涵, 比如含相变对流传热、管道多相流、地层与结构稳定性、多组分分离、气体膨胀做功利用率、智能绿色协同控制技术等, 新的研究成果将引领深海油气开发、深海金属矿产开发、深海环境安全、深部地层裂缝网络支撑剂规模化输送技术、化工领域的流化床反应器等领域的进步, 属于未来可拓展的工程科学领域研究范畴.
该方法将在经济、安全以及能量效率利用上具有优势, 实现示范应用及未来商业化, 需要确保产气量的长期性、可持续性以及环境污染和地质灾害的可控. 随着我国深海三步曲的深入, 快速地推动着深海资源开发的科学理论和技术装备形成, 该方法的工程技术和装备问题会逐步得到解决, 比如深海储层内安全、高效作业以及储层支护等.
致谢
在郑哲敏先生逝世一周年之际, 谨以此文缅怀先生!感谢先生对我们天然气水合物研究团队一直以来的指导; 感谢谈庆明研究员、刘大有研究员、曾晓辉研究员、晋国栋研究员、许晶禹研究员、王一伟研究员、陈伟民研究员、樊菁研究员等在研究中的讨论和帮助; 感谢李家春院士对研究的关心和指导.
-
表 1 不同分解长度下的安全系数
Table 1 Safety factor at different dissociation lengths
Dissociation length/overburden thickness Safety factor of initial sliding surface Safety factor of critical sliding surface 10 1.498 1.046 11 1.498 1.044 12 1.498 0.931 表 2 不同地震等级下的安全系数
Table 2 Safety factors at different earthquake levels
Earthquake
gradeSafety factor of initial
sliding surfaceSafety factor of critical
sliding surfacenone 1.498 1.046 7 1.283 1.002 8 1.142 0.896 -
[1] Sloan ED. Clathrate Hydrates of Natural Gas, 2nd ed. New York: Marcel Dekker, 1998
[2] Koh CA. Towards a fundamental understanding of natural gas hydrates. Chemical Society Reviews, 2002, 31: 157-167 doi: 10.1039/b008672j
[3] 魏纳, 白睿玲, 周守为, 等. 碳达峰目标下中国深海天然气水合物开发战略. 天然气工业, 2022, 42(2): 156-165 doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2022.02.017 Wei Na, Bai Ruiling, Zhou Shouwei, et al. China’s deepwater gas hydrate development strategies under the goal of carbon peak. Natural Gas Industry, 2022, 42(2): 156-165 (in Chinese) doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2022.02.017
[4] 鲁晓兵, 张旭辉, 王平康, 等. 天然气水合物成藏动力学研究进展. 中国科学: 物理学力学天文学, 2019, 49: 034605 doi: 10.1360/SSPMA2018-00362 Lu Xiaobing, Zhang Xuhui, Wang Pingkang, et al. Advances of formation dynamics of natural gas hydrate. Sci Sin-Phys Mech Astron, 2019, 49: 034605 (in Chinese) doi: 10.1360/SSPMA2018-00362
[5] 祝有海, 庞守吉, 王平康, 等. 中国天然气水合物资源潜力及试开采进展. 沉积与特提斯地质, 2021, 41(4): 524-535 doi: 10.19826/j.cnki.1009-3850.2021.12001 Zhu Youhai, Pang Shouji, Wang Pingkang, et al. A review of the resource potentials and test productions of natural gas hydrates in China. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 2021, 41(4): 524-535 (in Chinese) doi: 10.19826/j.cnki.1009-3850.2021.12001
[6] 龚建明, 王红霞, 陈建文, 等. 天然气水合物在沉积地层中的分布模式. 海洋地质动态, 2004, 20(6): 6-8 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2722.2004.06.003 Gong Jianming, Wang Hongxia, Chen Jianwen, et al. Geophysical recognition technique for gas hydrate. Marine Geology Letters, 2004, 20(6): 6-8 (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2722.2004.06.003
[7] 金春爽, 汪集旸, 张光学. 南海天然气水合物稳定带的影响因素. 矿床地质, 2005, 24(4): 388-397 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2005.04.004 Jin Chunshuang, Wang Jiyang, Zhang Guangxue. Factors affecting natural gas hydrate stability zone in the South China Sea. Mineral Deposits, 2005, 24(4): 388-397 (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2005.04.004
[8] Ye YG, Liu CL. Natural Gas Hydrates: Experimental Techniques and Their Application. Verlag Berlin Heidelberg: Springer, 2013: 10-13
[9] Boswell R, Collett TS. The gas hydrates resource pyramid. Fire in the ice, Methane hydrate newsletter. US Department of Energy, Office of Fossil Energy, National Energy Technology Laboratory, 2006: 5-7
[10] 自然资源部. 我国海域天然气水合物预测资源量约800亿吨油当量. 中国矿产资源报告, 2018 Ministry of Natural Resources, PRC. The predicted resource of natural gas hydrate in China's sea area is about 80 billion tons of oil equivalent. China Mineral Resources, 2018 (in Chinese)
[11] 鲁晓兵, 张旭辉, 王淑云. 天然气水合物开采相关的安全性研究进展. 中国科学: 物理学力学天文学, 2019, 49: 034602 doi: 10.1360/SSPMA2018-00213 Lu Xiaobing, Zhang Xuhui, Wang Shuyun. Advances on the safety related with natural gas hydrate exploitation. Sci Sin-Phys Mech Astron, 2019, 49: 034602 (in Chinese) doi: 10.1360/SSPMA2018-00213
[12] 戴兰宏. 工程科学前沿的拓荒者—郑哲敏. 力学进展, 2013, 43(3): 265-294 doi: 10.6052/1000-0992-13-033 Dai Lanhong. A pioneer in the frontier of engineering science—Zhe-Min Zheng. Advances in Mechanics, 2013, 43(3): 265-294 (in Chinese) doi: 10.6052/1000-0992-13-033
[13] 郑哲敏. 关于天然气水合物开发工程科学研究的一点认识. 中国科学: 物理学力学天文学, 2019, 49: 034601 Zheng Zhemin. Special issue on the exploitation and safety control of natural gas hydrate. Science China Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy, 2019, 49: 034601 (in Chinese)
[14] 鲁晓兵, 张旭辉. 机械−热开采水合物可行性论证. 中国科学院力学研究所科技报告, 2012 Lu Xiaobing, Zhang Xuhui. Feasibility study on mechanical-thermal hydrate recovery method. Scientific Report in Institute of Mechanics. Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2012 (in Chinese)
[15] 张旭辉, 鲁晓兵, 刘乐乐. 天然气水合物开采方法研究进展. 地球物理学进展, 2014, 29(2): 858-869 doi: 10.6038/pg20140252 Zhang Xuhui, Lu Xiaobing, Liu Lele. Advances in natural gas hydrate recovery methods. Progress in Geophysics, 2014, 29(2): 858-869 (in Chinese) doi: 10.6038/pg20140252
[16] 张旭辉, 鲁晓兵. 一种新的海洋浅层水合物开采法—机械-热联合法. 力学学报, 2016, 48(5): 1238-1246 doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-15-112 Zhang Xuhui, Lu Xiaobing. A new exploitation method for gas hydrate in shallow stratum: mechanical-thermal method. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2016, 48(5): 1238-1246 (in Chinese) doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-15-112
[17] 张旭辉, 鲁晓兵, 李鹏. 天然气水合物开采方法的研究综述. 中国科学: 物理学力学天文学, 2019, 49: 034604 Zhang Xuhui, Lu Xiaobing, Li Peng. A comprehensive review in natural gas hydrate recovery methods. Science China Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy, 2019, 49: 034604, (in Chinese)
[18] 赵金洲, 李海涛, 张烈辉, 等. 海洋天然气水合物固态流化开采大型物理模拟实验. 天然气工业, 2018, 38(10): 76-83 doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2018.10.011 Zhao Jinzhou, Li Haitao, Zhang Liehui, et al. The first global physical simulation experimental systems for the exploitation of marine natural gas hydrates through solid fluidization. Natural Gas Industry, 2018, 38(10): 76-83 (in Chinese) doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2018.10.011
[19] 周守为, 陈伟, 李清平, 等. 深水浅层非成岩天然气水合物固态流化试采技术研究及进展. 中国海上油气, 2017, 29(4): 1-8 doi: 10.11935/j.issn.1673-1506.2017.04.001 Zhou Shouwei, Chen Wei, Li Qqingping, et al. Research on the solid fluidization well testing and production for shallow non-daigenetic natural gas hydrate in deep water area. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2017, 29(4): 1-8 (in Chinese) doi: 10.11935/j.issn.1673-1506.2017.04.001
[20] 张晟, 梁晶, 张斌. 油气田经济产量研究综述. 改革与战略, 2010, 26(1): 182-186 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-736X.2010.01.052 Zhang Sheng, Liang Jing, Zhang Bin. Reviews on economic production of gas and oil fields. Reformation & Strategy, 2010, 26(1): 182-186 (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-736X.2010.01.052
[21] 贾承造. 美国SEC油气储量评估方法. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2004 Jia Chengzao. SEC Estimation Approach for Oil & Gas Reserves. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2004 (in Chinese)
[22] 刘亚平. 天然气水合物藏降压开发方案基础研究. [博士论文]. 青岛: 中国石油大学(华东), 2009 Liu Yaping. Fundamental studies on natural gas hydrate reservoir development program by depressurization. [PhD Thesis]. Qingdao: China University of Petroleum (East China), 2009 (in Chinese)
[23] 刘晓宇, 樊恮狮, 梁德青, 等. 水合物气资源经济性评估模型. 天然气地球科学, 2007, 18(4): 601-605 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1926.2007.04.025 Liu Xiaoyu, Fan Shuanshi, Liang Deqing, et al. Economic evaluation model of natural gas hydrate resource. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2007, 18(4): 601-605 (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1926.2007.04.025
[24] 中国石油天然气总公司计划局, 中国石油天然气总公司规划设计总院. 石油工业建设项目经济评价方法与参数. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 1994 Planning Bureau of CNPC, Programming and Design Institute of CNPC. Economic Evaluation Approaches and Parameters of Petroleum Industry Building Projects. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 1994 (in Chinese)
[25] Sean WY, Sato T, Yamasaki A, et al. CFD and experimental study on methane hydrate dissociation Part I. Dissociation under water flow. AIChE Journal, 2007, 53: 262-274
[26] 郑荣荣, 左江伟, 路大勇, 等. 流动体系水合物生成/分解特性研究综述. 当代化工, 2020, 49(6): 1166-1174 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0460.2020.06.039 Zheng Rongrong, Zuo Jiangwei, Lu Dayong, et al. Review of Study on Kinetic Characteristics of Hydrate Formation/Decomposition in Flow Systems. Contemporary Chemical Industry, 2020, 49(6): 1166-1174 (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0460.2020.06.039
[27] Kim HC, Bishnoi PR, Heidemann PA, et al. Kinetics of methane hydrate decomposition. Chemical Engineering Science, 1987, 42(7): 1645-1653 doi: 10.1016/0009-2509(87)80169-0
[28] Yin Z, Chong ZR, Tan HK, et al. Reviews of gas hydrate dissociation kinetic models for energy recovery. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2016, 35: 1362-1387 doi: 10.1016/j.jngse.2016.04.050
[29] Jamaluddin AKM, Kalogerakis N, Bishnoi PR. Modelling of decomposition of a synthetic core of methane gas hydrate by coupling intrinsic kinetics with heat transfer rates. The Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 1989, 67(6): 948-954
[30] Sun CY, Chen GJ. Methane hydrate dissociation above 0℃ and below 0℃. Fluid Phase Equilibria, 2006, 242: 123-128 doi: 10.1016/j.fluid.2006.01.025
[31] Oyama H, Konno Y, Masuda Y, et al. Dependence of depressurization induced dissociation of methane hydrate bearing laboratory cores on heat transfer. Energy & Fuels, 2009, 23(10): 4995-5002
[32] Yang SHB, Babu P, Chua SFS, et al. Carbon dioxide hydrate kinetics in porous media with and without salts. Applied Energy, 2016, 162: 1131-1140 doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2014.11.052
[33] Misyura SY, Donskoy IG. Dissociation kinetics of methane hydrate and CO2 hydrate for different granular composition. Fuel, 2020, 262: 116614 doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2019.116614
[34] 付强, 魏纳, 孟英峰, 等. 深水钻井天然气水合物井筒多相流动模型及敏感性分析. 中国海上油气, 2016, 28(4): 107-113 Fu Qiang, Wei Na, Meng Yingfeng, et al. Mode of wellbore multiphase flow and its sensitivity analysis during drilling in deep water natural gas hydrate reservoirs. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2016, 28(4): 107-113 (in Chinese)
[35] Liu ZY, Yang MJ, Zhang HQ, et al. A high-pressure visual flow loop for hydrate blockage detection and observation. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2019, 90: 074102 doi: 10.1063/1.5088993
[36] 李鹏. 垂直管道中含天然气水合物相变的气液固多相流动. [博士论文]. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2019 Li Peng. Gas-liquid-solid flow with gas hydrate dissociation in a vertical pipe. [PhD Thesis]. Beijing: University of China Academy of Sciences, 2019 (in Chinese)
[37] Li P, Zhang XH, Lu XB. Dissociation behaviors of CO2 hydrate-bearing sediment particle during settling in water. Energies, 2018, 11(11): 2896 doi: 10.3390/en11112896
[38] Li P, Liu DN, Zhang XH, et al. Effect of bubbles produced from hydarte-bearing particle dissociation on particle motion in water. Energy & Fuels, 2021, 35: 1371-1380
[39] Wei N, Sun WT, Meng YF. Multiphase non equilibrium pipe flow behaviors in the solid fluidization exploitation of marine natural gas hydrate reservoir. Energy Science & Engineering, 2018, 6(6): 760-782
[40] 黄鑫, 蔡明杰, 毛良杰, 等. 南海固态流化开采天然气水合物设计参数优化. 科学技术与工程, 2020, 20(33): 13647-13653 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2020.33.019 Huang Xin, Cai Mingjie, Mao Liangjie, et al. Optimization of design parameters of solid-fluidization exploitation of natural gas hydrate in the South China Sea. Science Technology and Engineering, 2020, 20(33): 13647-13653 (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2020.33.019
[41] 徐海良, 孔维阳, 杨放琼. 天然气水合物在水力提升管道中的分解特性. 天然气工业, 2018, 38(7): 129-137 doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2018.07.018 Xu Hailing, Kong Weiyang, Yang Fangqiong. Decomposition characteristics of natural gas hydrates in hydraulic lifting pipelines. Natural Gas Industry, 2018, 38(7): 129-137 (in Chinese) doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2018.07.018
[42] Chen W, Xu HL, Kong WY, et al. Study on three-phase flow characteristics of natural gas hydrate pipeline transmission. Ocean Engineering, 2020, 214: 107727 doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2020.107727
[43] Wang ZY, Sun BJ. Annular multiphase flow behavior during deep water drilling and the effect of hydrate phase transition. Petroleum Science, 2009, 6: 57-63 doi: 10.1007/s12182-009-0010-3
[44] 刘艳军, 唐孝蓉, 胡坤. 天然气水合物浆体分解对其在垂直管中流动特性影响的研究. 化学通报, 2018, 81(3): 267-273 doi: 10.14159/j.cnki.0441-3776.2018.03.012 Liu Yanjun, Tang Xiaorong, Hu Kun. Study on Flow Characteristics of Natural Gas Hydrate Slurry with Decomposition in Vertical Tube. Chemistry Bulletin, 2018, 81(3): 267-273 (in Chinese) doi: 10.14159/j.cnki.0441-3776.2018.03.012
[45] Pan H, Chen XZ, Liang XF, et al. CFD simulations of gas–liquid–solid flow in fluidized bed reactors—A review. Powder Technology, 2016, 299: 235-258 doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2016.05.024
[46] 李长俊, 黄婷, 贾文龙. 深水天然气水合物及其管道输送技术. 科学通报, 2016, 61: 2449-2462 Li Changjun, Huang Ting, Jia Wenlong. A review of natural gas hydrates and its pipeline transportation technologies in deep water. Science Bulletin, 2016, 61: 2449-2462 (in Chinese)
[47] 王海秀, 练章华, 王树立. 基于OLGA的海底管道水合物的生成和影响因素分析. 海洋开发与管理, 2021, 2: 87-92 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9857.2021.06.015 Wang Haixiu, Lian Zhanghua, Wang Shuli. The hydrate fromation and its influencing factors in submarine pipelines by using OLGA. Ocean Development and Management, 2021, 2: 87-92 (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9857.2021.06.015
[48] 韦雪蕾, 刘宝玉, 潘振, 等. 水平管道水合物浆液流动特性的数值模拟. 化学工程, 2018, 46(3): 41-46 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9954.2018.03.009 Wei Xuelei, Liu Baoyu, Pan Zhen, et al. Numerical simulation on hydrate slurry flow properties in horizontal pipeline. Chemical Engineering, 2018, 46(3): 41-46 (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9954.2018.03.009
[49] Li P, Zhang XH, Lu XB. Three-dimensional Eulerian modeling of gas–liquid–solid flow with gas hydrate dissociation in a vertical pipe. Chemical Engineering Science, 2019, 196: 145-165 doi: 10.1016/j.ces.2018.10.053
[50] Li P, Zhang XH, Lu XB. Dissociation equilibrium height and friction coefficient in pipeline transportation of gas hydrate-bearing sediment particles. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2020: 103470
[51] 陈旭东. 天然气水合物分解对地层及地层中结构安全性影响研究. [硕士论文]. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2015 Chen Xudong. Study on the safety of stratum and structures with gas hydrate dissociation. [Master Thesis]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2015 (in Chinese)
[52] 王晶. 水合物分解引起井口周围土层变形与破坏的研究. [硕士论文]. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2018 Wang Jing. Study of deformation and failture caused by hydrate decomposition on wellhead soil layer. [Master Thesis]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2018 (in Chinese)
[53] Lu L, Zhang XH, Lu XB. Numerical study on the stratum's responses due to natural gas hydrate dissociation. Ships and Offshore Structures, 2017, 12(5-6): 775-780
[54] 张旭辉, 胡光海, 鲁晓兵. 天然气水合物分解对地层稳定性影响的离心机实验模拟. 实验力学, 2012, 27(3): 301-310 Zhang Xuhui, Hu Guanghai, Lu Xiaobing. Centrifuge experimental simulation of the effect of gas hydrate dissociation on the seabed stability. Journal of Experimental Mechanics, 2012, 27(3): 301-310 (in Chinese)
[55] Zhang XH, Lu XB, Shi YH, et al. Centrifuge experimental study on instability of seabed stratum caused by gas hydrate dissociation. Ocean Engineering, 2015, 105(1): 1-9
[56] Zhang XH, Lu XB, Chen XD, et al. Mechanism of soil stratum instability induced by hydrate dissociation. Ocean Engineering, 2016, 122: 74-83 doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2016.06.015



 下载:
下载: