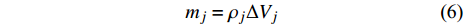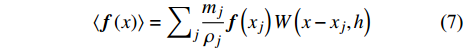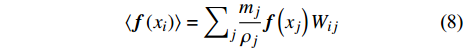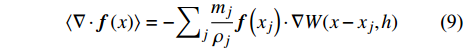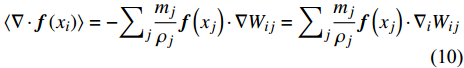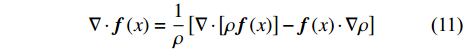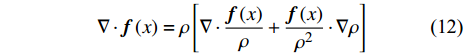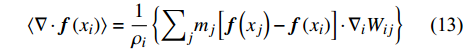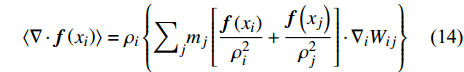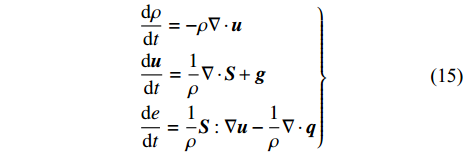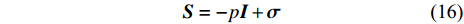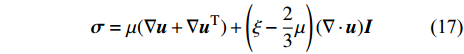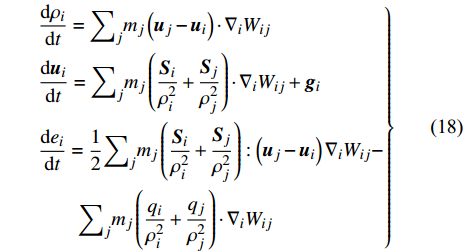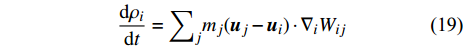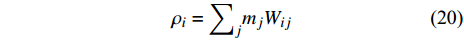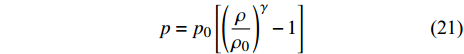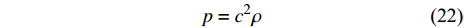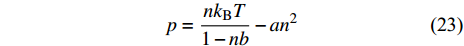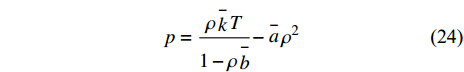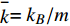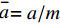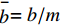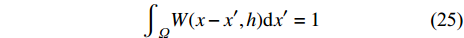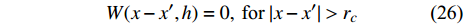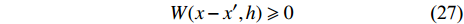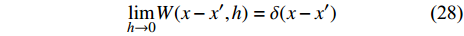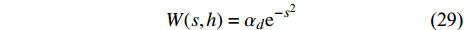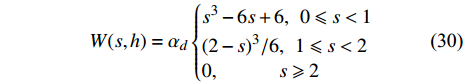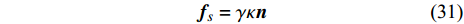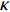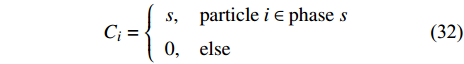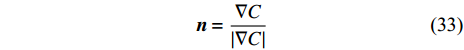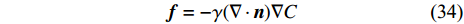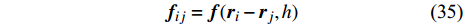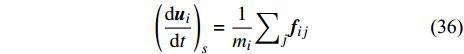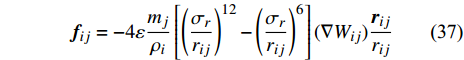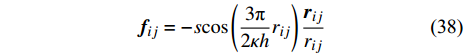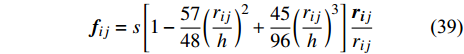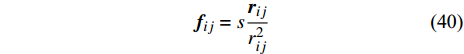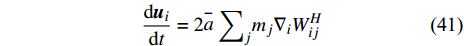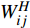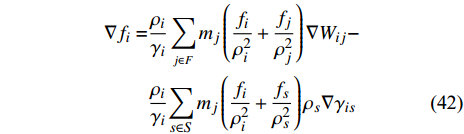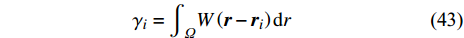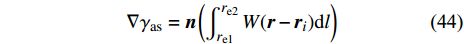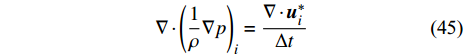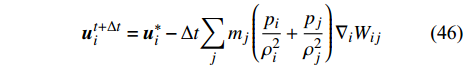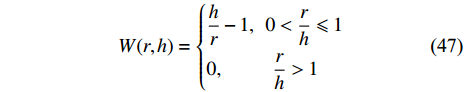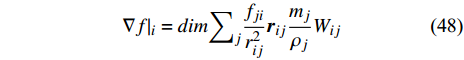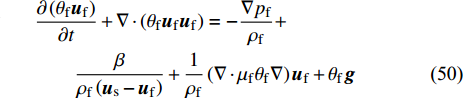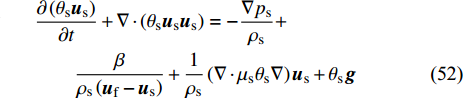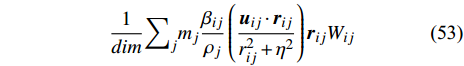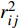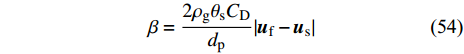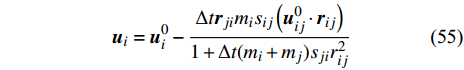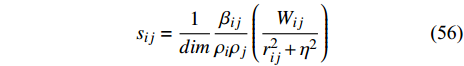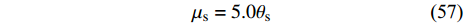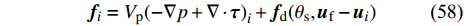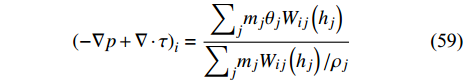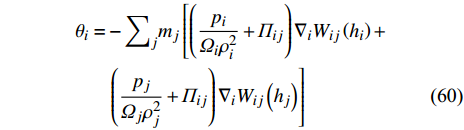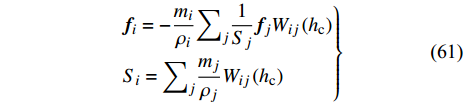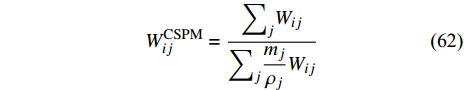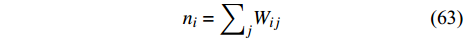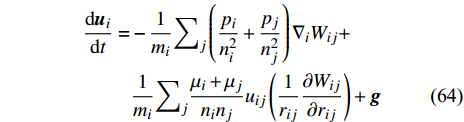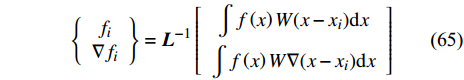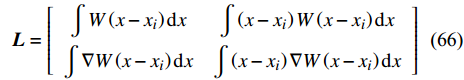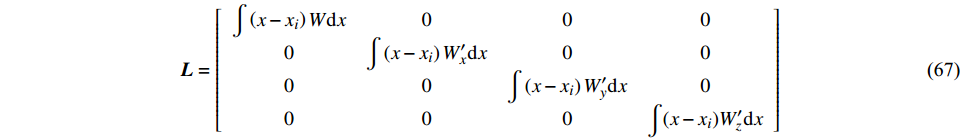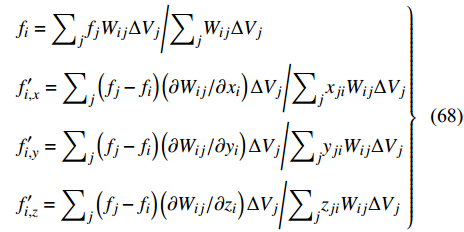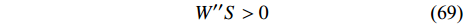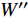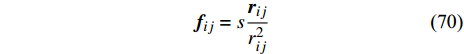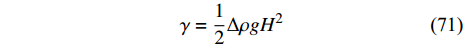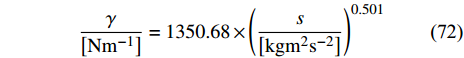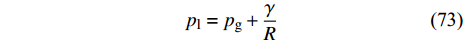A REVIEW OF SMOOTHED PARTICLE HYDRODYNAMICS FAMILY METHODS FOR MULTIPHASE FLOW
-
摘要: 光滑粒子流体动力学(smoothed particle hydrodynamics, SPH)具有粒子方法的无网格和全拉格朗日特征, 适用于具有界面大变形、不连续性和多物理场的多相流的高精度模拟. SPH方法模拟多相流已有大量报道, 具体的实现方式也大不相同. 本文首先阐述了采用SPH方法模拟流体的基本控制方程, 以及求解过程中需要考虑的流体压力求解、表面张力、固体边界等问题. 整理和总结了基于SPH方法进行多相流模拟的主要实现方式: (1)双流体模型的拉格朗日求解器: 两相离散为两组独立SPH粒子, 并用显式相间作用耦合两相; (2)多相SPH方法: SPH方法对多相流模拟的自然延伸, 相间作用由SPH参数隐式描述; (3) SPH与其他离散方法的耦合: 差异较大的两相各自采用不同离散方法, 发挥不同拉格朗日方法的优点; (4) SPH和基于网格方法的耦合: 网格方法处理简单的单相流动主体, 获得精度和效率间的平衡. 另外, 还在模拟参数物理化等方面论述了与SPH方法模拟多相流相关的一些改进和修正方法, 并在最后讨论和建议了提高多相流SPH模拟效率和精度的措施.Abstract: With meshfree and fully Lagrangian features of particle methods, smoothed particle hydrodynamics (SPH) is suitable to achieve high-accurate simulations of multiphase flows with large interfacial deformations, discontinuities, and multi-physics. Multiphase flow simulations with SPH methods have been reported abundantly and the specific implementations are much different. In this review, the basic SPH method and issues about fluid pressure, surface tension and solid boundary are discussed. And various implementations of SPH for multiphase flow simulation are mainly summarized as: (1) Lagrangian solver for the two-fluid model (TFM): The two phases are discreterized into two independent groups of SPH particles and coupled by the explicit interphase interaction; (2) multiphase SPH: The multiphase SPH method is considered as the natural extension of SPH method on multiphase flow simulation, and the interphase interaction is implicitly described by SPH parameters; (3) coupling of SPH and other discrete methods: The two phases with large differences each adopt different discrete methods to give play to the advantages of different Lagrangian methods; and (4) coupling of SPH and grid-based methods: The grid method handles the simple main-flow to obtain the balance between accuracy and efficiency. Also, some issues associated with SPH simulations of multiphase flows, such as the physicalization of simulation parameters and the improvement of accuracy and efficiency, are suggested as requiring attention.
-
Keywords:
- meshfree /
- smoothed particle hydrodynamics /
- multiphase flow /
- surface tension /
- kernel function
-
引 言
多相流广泛存在于自然界和工业应用中. 对多相流进行高精度和高效率的建模和模拟非常重要. 然而, 其中流动形态和界面跟踪的复杂性限制了基于网格的传统方法模拟多相流能力, 尤其对于存在界面大变形、不连续性和多物理过程的多相流动. 而无网格方法可以很好地处理网格方法遇到的上述问题. 在过去几十年发展起来的无网格方法中, 光滑粒子流体动力学方法(smoothed particle hydrodynamics, SPH)是众所周知并被广泛应用的其中一种.
SPH方法由Gingold和Monaghan[1]以及Lucy[2]于1977年发明, 最初用于模拟天体物理学中的非轴对称现象. 它已获得极大发展并成为模拟流体运动的标准方法之一[3]. 已有包含各种综述的大量文献[3-20](相关文献的数量极其巨大, Google Scholar可查询到近10万个结果)论述了SPH 方法各方面及在各领域中的应用情况, 如界面流动、流变学、流动不稳定性、多相流、破损、弹性和断裂力学、爆炸力学、波传播和热传导等.
从纯粹的拉格朗日法角度来看, SPH方法具有以下主要优点[7, 14]:
1)易于处理大变形和快速移动的自由表面;
2)自发捕获和跟踪间断面, 而这是使用基于网格的方法难以实现的;
3)能有效模拟耦合多物理场的多相流;
4) SPH粒子大小可灵活调节, 对应不同的数值精度要求;
5)二维和三维SPH模拟均易于实现并具有良好的并行计算可扩展性.
上述特性确保了SPH方法特别适用于基于网格的方法很难或者无法完成的多相流高精度模拟. 许多研究人员已应用 SPH 方法模拟多相流, 这些应用中SPH的实现方式有很大不同. 最常见的是多相SPH方法[21-29], 其中两种流体分别采用SPH方法求解. 此外, SPH方法还可被视为拉格朗日求解器求解表征两相流动的双流体模型(two-fluid model, TFM)[30-32]. SPH方法也可以与其他离散方法结合使用, 多用于含固体颗粒的多相流动模拟. 为了降低计算成本, 基于网格的欧拉求解器耦合到 SPH 方法中, 处理不存在相界面的流动主体部分. 一些研究人员还发展了各种修正方法来提高SPH方法在多相流模拟中的准确性和稳定性.
尽管众多文献涵盖了 SPH方法模拟各种多相流动, 也有一些综述文章论述了SPH 方法用于多相流动模拟的各类模型, 但大多仅涉及多相流模拟的某类 SPH 方法实现, 很少总结SPH方法在多相流模拟中的不同实现方式. 本文将归纳和比较这些不同SPH方法实现方式, 并对相应适用体系进行建议.
本文组织如下: 第1节简单介绍SPH方法; 第2节介绍模拟多相流的其他SPH类方法; 第3节总结和比较SPH方法在多相流模拟中的各种实现方式; 第4节论述SPH方法的各种改进措施; 最后在第5节总结全文, 并展望提高SPH方法模拟多相流精度和效率的多种方式.
1. SPH方法
SPH方法是一种典型的拉格朗日粒子方法, 它用带有特定物理性质(例如密度、黏度、质量、速度和温度)的粒子集合来表示流体[8, 10, 15]. 粒子的运动和性质变化由质量、动量和能量守恒方程控制. 它们的数值求解则由核近似和粒子插值的权重积分获得.
1.1 SPH方法的基本原理
简而言之, SPH的基本思想[8]可概括如下: 用一组带有物理性质的粒子来离散化问题域, 并将流体的控制方程转变为具有各种边界条件的常微分方程; 然后, 采用核函数插值近似的权重积分获得数值解. SPH方法的关键是插值近似, 包括核近似和粒子近似.
1.1.1 核近似
问题域Ω中点x的连续光滑函数值f (x)定义为[8]
$$ {\boldsymbol{f}}\left(x\right)={\int }_{\varOmega }{\boldsymbol{f}}\left({x}'\right)\delta \left(x-{x}'\right){\rm{d}}{x}' $$ (1) 其中δ(x − x′)为狄拉克δ函数
$$ \delta \left(x-{x}'\right)=\left\{\begin{array}{l}\infty ,\; \;\; x={x}'\\ 0,\;\;\; x\ne {x}'\end{array}\right. $$ (2) 为了消除由δ函数引入的无限值, 引入光滑核函数来逼近δ函数, 则该函数值表达为[8, 12]
$$ \langle {\boldsymbol{f}}\left(x\right)\rangle ={\int }_{\varOmega }{\boldsymbol{f}}\left({x}'\right)W(x-{x}',h)\mathrm{d}{x}' $$ (3) 其中W(x − x′, h)为核函数, 光滑长度h用于衡量权重积分的影响区域.
函数导数由核函数近似表达为
$$ \langle \nabla \cdot {\boldsymbol{f}}\left(x\right)\rangle ={\int }_{\varOmega }[\nabla \cdot {\boldsymbol{f}}({x}'\left)\right]W(x-{x}',h)\mathrm{d}{x}' $$ (4) 根据高斯积分定理, 上式可改写为
$$ \langle \nabla \cdot {\boldsymbol{f}}\left(x\right)\rangle =-{\int }_{\varOmega }{\boldsymbol{f}}\left({x}'\right)\cdot \nabla W(x-{x}',h)\mathrm{d}{x}' $$ (5) 1.1.2 粒子近似
问题域Ω被离散化为一组粒子(如图1所示), 粒子j处代表的空间体积即粒子j的体积为ΔVj. 若粒子j的密度为ρj, 则其质量mj为
$$ {m}_{j}={\rho }_{j}\Delta {V}_{j} $$ (6) SPH核近似的积分公式表示为[8]
$$ \left\langle {\boldsymbol{f}}\left(x\right) \right\rangle ={\sum }_{j}\frac{{m}_{j}}{{\rho }_{j}}{\boldsymbol{f}}\left({x}_{j}\right)W\left(x-{x}_{j}, h\right) $$ (7) 函数在粒子i处的值为
$$ \langle {\boldsymbol{f}}\left({x}_{i}\right)\rangle ={\sum }_{j}\frac{{m}_{j}}{{\rho }_{j}}{\boldsymbol{f}}\left({x}_{j}\right){W}_{ij} $$ (8) 这里Wij=W(xi − xj, h). 函数导数的粒子近似表达为
$$ \langle \nabla \cdot {\boldsymbol{f}}\left(x\right)\rangle =-{\sum }_{j}\frac{{m}_{j}}{{\rho }_{j}}{\boldsymbol{f}}\left({x}_{j}\right)\cdot \nabla W(x-{x}_{j},h) $$ (9) 其在粒子i处的值为
$$ \langle \nabla \cdot {\boldsymbol{f}}\left({x}_{i}\right)\rangle =-{\sum }_{j}\frac{{m}_{j}}{{\rho }_{j}}{\boldsymbol{f}}\left({x}_{j}\right)\cdot \nabla {W}_{ij}={\sum }_{j}\frac{{m}_{j}}{{\rho }_{j}}{\boldsymbol{f}}\left({x}_{j}\right)\cdot {\nabla }_{i}{W}_{ij} $$ (10) $$ \nabla \cdot {\boldsymbol{f}}\left(x\right)=\frac{1}{\rho }\left[\nabla \cdot \left[\rho {\boldsymbol{f}}\left(x\right)\right]-{\boldsymbol{f}}\left(x\right)\cdot \nabla \rho \right] $$ (11) $$ \nabla \cdot {\boldsymbol{f}}\left(x\right)=\rho \left[\nabla \cdot \frac{{\boldsymbol{f}}\left(x\right)}{\rho }+\frac{{\boldsymbol{f}}\left(x\right)}{{\rho }^{2}}\cdot \nabla \rho \right] $$ (12) 则粒子i处的函数导数为
$$ \langle \nabla \cdot {\boldsymbol{f}}\left({x}_{i}\right)\rangle =\frac{1}{{\rho }_{i}}\left\{{\sum }_{j}{m}_{j}\left[{\boldsymbol{f}}\left({x}_{j}\right)-{\boldsymbol{f}}\left({x}_{i}\right)\right]\cdot {\nabla }_{i}{W}_{ij}\right\} $$ (13) $$ \langle \nabla \cdot {\boldsymbol{f}}\left({x}_{i}\right)\rangle ={\rho }_{i}\left\{{\sum }_{j}{m}_{j}\left[\frac{{\boldsymbol{f}}\left({x}_{i}\right)}{{\rho }_{i}^{2}}+\frac{{\boldsymbol{f}}\left({x}_{j}\right)}{{\rho }_{j}^{2}}\right]\cdot {\nabla }_{i}{W}_{ij}\right\} $$ (14) 这样, 函数的取值及其导数值可以通过离散粒子的加权平均得到.
1.2 控制方程的离散化
流体运动由守恒方程控制, 即连续方程、动量方程(纳维−斯托克斯方程)和能量方程, 它们以下列形式表示
$$\left. \begin{aligned} & \frac{\mathrm{d}\rho }{\mathrm{d}t}=-\rho \nabla \cdot \boldsymbol{u}\\& \frac{\mathrm{d}\boldsymbol{u}}{\mathrm{d}t}=\frac{1}{\rho }\nabla \cdot \boldsymbol{S}+\boldsymbol{g}\\& \frac{\mathrm{d}e}{\mathrm{d}t}=\frac{1}{\rho }\boldsymbol{S}:\nabla \boldsymbol{u}-\frac{1}{\rho }\nabla \cdot {\boldsymbol{q}} \end{aligned} \right\} $$ (15) 其中u为速度, ρ为密度, S为应力张量, g为单位质量体积力, e为比内能, q为热通量. 应力张量S采用显式形式
$$ \boldsymbol{S}=-p\boldsymbol{I}+\boldsymbol{\sigma } $$ (16) 这里I表示单位张量, p为内压, 剪切应力σ表达为
$$ \boldsymbol{\sigma }=\mu (\nabla \boldsymbol{u}+\nabla {\boldsymbol{u}}^{\mathrm{T}})+\left(\xi -\frac{2}{3}\mu \right)(\nabla \cdot \boldsymbol{u})\boldsymbol{I} $$ (17) 其中μ和ξ分别为剪切黏度系数和体积黏度系数.
$$ \left. \begin{aligned} & \frac{\mathrm{d}{\rho }_{i}}{\mathrm{d}t}={\sum }_{j}{m}_{j}\left({\boldsymbol{u}}_{j}-{\boldsymbol{u}}_{i}\right)\cdot {\nabla }_{i}{W}_{ij}\\& \frac{\mathrm{d}{\boldsymbol{u}}_{i}}{\mathrm{d}t}={\sum }_{j}{m}_{j}\left(\frac{{\boldsymbol{S}}_{i}}{{\rho }_{i}^{2}}+\frac{{\boldsymbol{S}}_{j}}{{\rho }_{j}^{2}}\right)\cdot {\nabla }_{i}{W}_{ij}+{\boldsymbol{g}}_{i}\\& \frac{\mathrm{d}{e}_{i}}{\mathrm{d}t}=\frac{1}{2}{\sum }_{j}{m}_{j}\left(\frac{{\boldsymbol{S}}_{i}}{{\rho }_{i}^{2}}+\frac{{{\boldsymbol{S}}}_{j}}{{\rho }_{j}^{2}}\right):\left({\boldsymbol{u}}_{j}-{\boldsymbol{u}}_{i}\right){\nabla }_{i}{W}_{ij}-\\& \qquad{\sum }_{j}{m}_{j}\left(\frac{{q}_{i}}{{\rho }_{i}^{2}}+\frac{{q}_{j}}{{\rho }_{j}^{2}}\right)\cdot {\nabla }_{i}{W}_{ij} \end{aligned}\right\} $$ (18) 在SPH方法中, 计算粒子密度有两种形式, 其中一种利用了密度的导数
$$ \frac{\mathrm{d}{\rho }_{i}}{\mathrm{d}t}={\sum }_{j}{m}_{j}({{{\boldsymbol{u}}}}_{j}-{{{\boldsymbol{u}}}}_{i})\cdot {\nabla }_{i}{W}_{ij} $$ (19) 另一种则将粒子密度表达为其他粒子的权重总和
$$ {\rho }_{i}={\sum }_{j}{m}_{j}{W}_{ij} $$ (20) 需要注意的是, 由于动量方程中的压力表达式未知, 连续性方程和动量方程并不封闭. 流体的压力一般由状态方程(equation of state, EOS)获得. 对于不可压缩SPH, 则由投影方法求解压力泊松方程来耦合速度和压力.
1.3 状态方程
在SPH方法中, 流体的状态方程是有效计算动量方程中压力项的重要因素. 早期的SPH模拟[34]使用了 Batchelor状态方程[35]
$$ p={p}_{0}\left[{\left(\frac{\rho }{{\rho }_{0}}\right)}^{\gamma }-1\right] $$ (21) 其中γ是一个常数, 取值范围一般从1到7; 下标0表示参考量. 它也是弱可压缩SPH中最常用的状态方程. 对于较大的γ, 压力对密度的高敏感性可能导致密度波动较大时压力估算偏差极大.
$$ p={c}^{2}\rho $$ (22) 其中c是流体声速; 它是平衡真实流体近似值和时间演化效率的重要因素.
对于范德华(vdW)流体, 状态方程为[38]
$$ p=\frac{n{k}_{{\rm{B}}}T}{1-nb}-a{n}^{2} $$ (23) 或
$$ p=\frac{\rho\stackrel-{k}T}{1-\rho \stackrel-{b}}-\stackrel-{a}{\rho }^{2} $$ (24) 其中n是数密度, T是温度, kB是玻尔兹曼常数, a和b分别是表达内聚作用和分子大小的系数;
$ \stackrel{-}{k}={k}_{B}/m $ ,$ \stackrel{-}{a}=a/m $ ,$ \stackrel{-}{b}=b/m $ , 其中m为粒子质量. 状态方程第二项是形成稳定液滴表面的内聚作用. 范德华状态方程也被称为内聚压力模型.1.4 核函数
SPH方法的核心问题之一是如何有效地执行准确和稳定的近似操作. 用于核近似和粒子近似的光滑核函数决定了插值方式和加权积分.
许多研究人员对光滑核进行了研究, 并提出了多种核函数. 光滑核函数一般需要满足如下要求[3, 8-9, 15]:
(1)在支持域上满足正则化条件(归一性)
$$ {\int }_{\varOmega }W(x-{x}',h)\mathrm{d}{x}'=1 $$ (25) (2)紧致性
$$ W(x-{x}',h)=0,\;\text{for}\;|x-{x}'|>{r}_{c} $$ (26) 式中rc表示光滑核函数有效作用距离.
(3)非负性
$$ W(x-{x}',h)\geqslant 0 $$ (27) (4)当光滑长度趋于零时, 光滑核函数满足狄拉克δ函数(δ函数性)
$$ \underset{h\to 0}{\mathrm{l}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{m}}W(x-{x}',h)=\delta (x-{x}') $$ (28) (5)递减、偶对称以及充分光滑性质.
理论上, 任何满足上述要求的函数都可以作为SPH方法的光滑核函数. Liu等[9, 39]讨论了它的一般构造方法. 一个常用的核函数是最初由 Gingold和Monaghan[1]提出的高斯函数
$$ W(s,h)={\alpha }_{d}{\mathrm{e}}^{-{s}^{2}} $$ (29) 使用最广泛的是分段样条函数, 如三次样条函数[36, 40]
$$ W(s,h)={\alpha }_{d}\left\{ \begin{aligned} & {s}^{3}-6s+6 ,\;\; 0\leqslant s<1\\& {(2-s)}^{3}/6, \;\; 1\leqslant s<2\\& 0, \qquad\quad s\geqslant 2 \end{aligned}\right. $$ (30) 其中s=|x − x′|/h, αd是与维度d相关的归一化因子. 有关典型光滑核函数的更多细节可参见已有的综述文献[8-9, 15].
1.5 表面张力
存在于两相界面处的表面张力是多相流的重要特性, 特别是对于气液流、微流动流和表面流, 它是影响流动行为的主要因素. 表面张力的准确数值表达对于多相流动建模至关重要. 从分子相互作用的角度来看, 表面张力源于界面上分子间力的不对称性[38], 见图2所示.
在SPH方法中, 主要有三类模型描述表面张力, 即连续表面力(continuum surface force, CSF)模型、粒子间力(inter-particle force, IPF)模型和内聚压力模型(cohesive pressure model, CPM). 有时, CPM 被视为广义的IPF模型.
1.5.1 CSF模型
CSF模型由Brackbill等[41]首先提出, 它是一种宏观力模型, 表面张力被描述为两相之间的偏向分子相互作用而两相流体之间的分界面被视为有限厚度的过渡区域. 表面张力的力密度定义为与表面的局部曲率成正比[37, 42-45]并表达为
$$ {{\boldsymbol{f}}}_{s}=\gamma \kappa \boldsymbol{n} $$ (31) 其中γ是表面张力系数,
$\kappa $ 是界面的局部曲率, n是界面的单位法向量.$${C_i} = \left\{ {\begin{array}{*{20}{l}} {s,}&{{\rm{particle}}\;i \in {\rm{phase}}\;s}\\ {0,}&{{\rm{else}}} \end{array}} \right.$$ (32) 然后将界面定义为具有非零色函数梯度的有限过渡带. 界面的法向量由下式计算
$$ \boldsymbol{n}=\frac{\nabla C}{\left|\nabla C\right|} $$ (33) 最后将表面张力转化为体积力
$$ \boldsymbol{f}=-\gamma (\nabla \cdot \boldsymbol{n})\nabla C $$ (34) 1.5.2 IPF模型
IPF 模型中, 表面张力由界面处SPH粒子的对力隐式表达. 当界面过渡区内的两个粒子i和j分别属于不同相时, IPF通常表达为
$$ {\boldsymbol{f}}_{ij}=\boldsymbol{f}({\boldsymbol{r}}_{i}-{\boldsymbol{r}}_{j},h) $$ (35) 与其他相粒子相互作用的附加力将导致由表面张力产生的净加速度
$$ {\left(\frac{{\rm{d}}{\boldsymbol{u}}_{i}}{{\rm{d}}t}\right)}_{s}=\frac{1}{{m}_{i}}{\sum }_{j}{\boldsymbol{f}}_{ij} $$ (36) 文献中常用的IPF模型包括Lennard−Jones力模型[46]
$$ {\boldsymbol{f}}_{ij}=-4\varepsilon\frac{{m}_{j}}{{\rho }_{i}} \left[{\left(\frac{{\sigma }_{r}}{{r}_{ij}}\right)}^{12}-{\left(\frac{{\sigma }_{r}}{{r}_{ij}}\right)}^{6}\right](\nabla {W}_{ij})\frac{{\boldsymbol{r}}_{ij}}{{r}_{ij}} $$ (37) 余弦力模型[27]
$$ {\boldsymbol{f}}_{ij}=-s\mathrm{c}\mathrm{o}\mathrm{s}\left(\frac{3{\text{π}} }{2\kappa h}{r}_{ij}\right)\frac{{\boldsymbol{r}}_{ij}}{{r}_{ij}} $$ (38) 三次多项式力模型[47]
$$ {\boldsymbol{f}}_{ij}=s\left[1-\frac{57}{48}{\left(\frac{{r}_{ij}}{h}\right)}^{2}+\frac{45}{96}{\left(\frac{{r}_{ij}}{h}\right)}^{3}\right]\frac{{\boldsymbol{r}}_{\boldsymbol{i}j}}{{r}_{ij}} $$ (39) 及简单的斥力模型[29]
$$ {\boldsymbol{f}}_{ij}=s\frac{{\boldsymbol{r}}_{ij}}{{r}_{ij}^{2}} $$ (40) 更多的IPF模型见于Wang等[15]的综述.
1.5.3 CPM
CPM可以被视为广义 IPF模型, 其中界面粒子上的附加力由内聚的范德华状态方程隐式确定. 假设内聚压力的相互作用范围超过其他力的相互作用范围[48]; 因此, 内部的粒子内聚压力项被平衡导致净力为零, 而界面区域的粒子内聚压力项不平衡由范德华状态方程中的吸引项(
$ \stackrel{-}{a}{\rho }^{2} $ )产生表面张力. 界面区域内粒子的净加速度为[33, 48]$$ \frac{{\rm{d}}{\boldsymbol{u}}_{i}}{{\rm{d}}t}=2\stackrel-{a}{\sum }_{j}{m}_{j}{\nabla }_{i}{W}_{ij}^{H} $$ (41) 其中
${W}_{ij}^{H} $ =W(ri−rj, H)是光滑长度为H ≥ 2h的核函数.1.6 固体边壁
与其他离散方法一样, SPH方法中固壁边界条件的实现并不像基于网格的方法那样直接. SPH方法中, 实施固壁边界条件的目的是防止流体粒子穿透固壁, 并在光滑近似被截断时在边界处进行加权插值, 从而实现自由滑移、非滑移或部分滑移边界条件. 离散方法(包括SPH方法)中的固壁边界处理方式原则上可以大致分为两类, 即粒子表示法和几何表示法.
1.6.1 粒子表示法
在粒子表示法中, 固体边壁由固定粒子的集合表示, 在流体粒子和边界粒子之间施加附加力以产生指定的边界条件. 根据不同的粒子生成方式, 固壁的粒子表示法又有边界粒子模型[34]、镜像粒子模型[49]和动态粒子模型[8, 50]等3种典型模型.
在边界粒子模型中, 固体虚拟粒子位于边界上, 如图3所示. 固体粒子施加到流体粒子上的排斥力用于防止流体非物理渗入固壁. 研究人员提出了各种排斥力模型来改进和修正边界力计算[13, 15, 34].
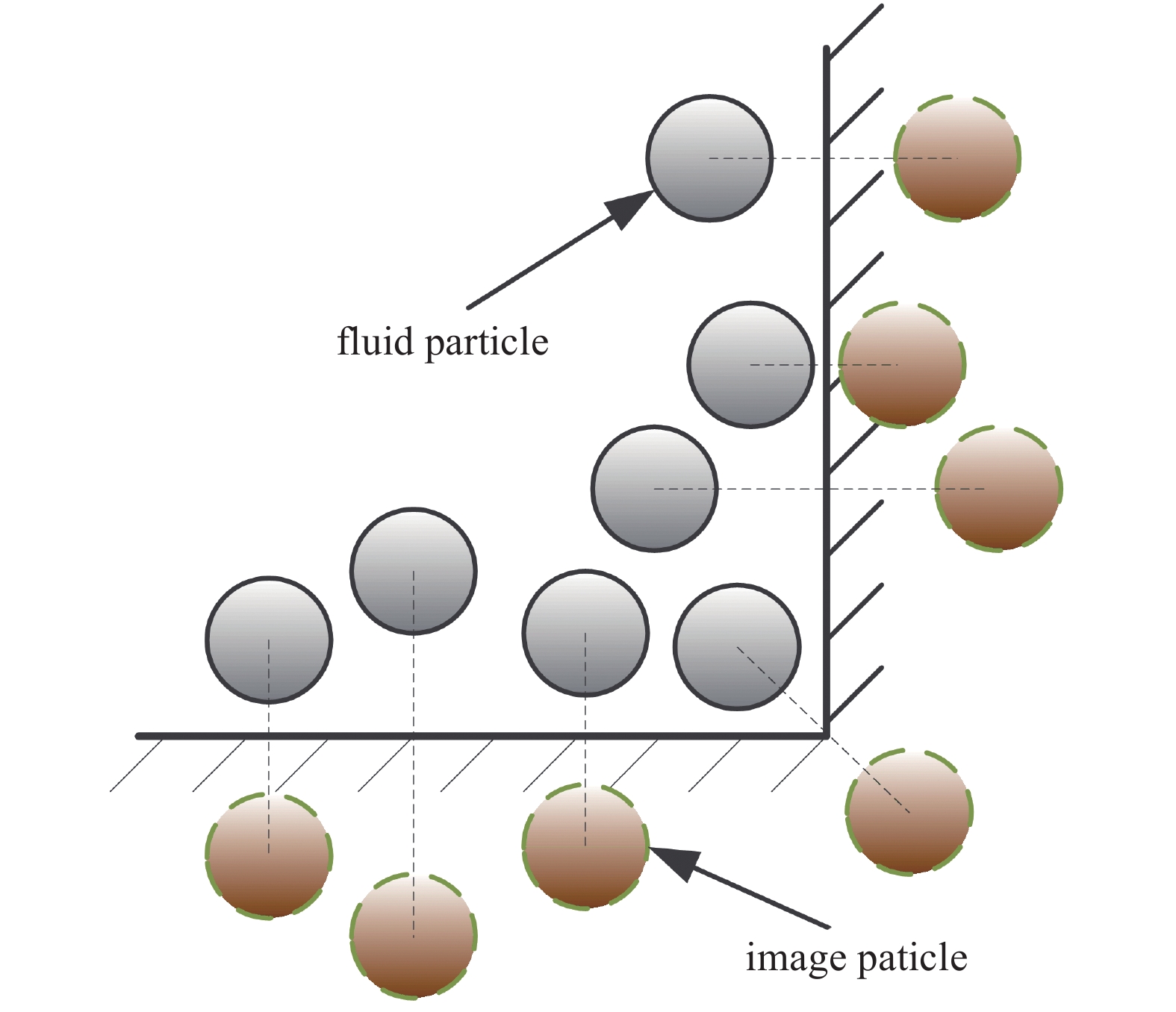
镜像粒子模型也被称为鬼粒子模型, 其中镜像粒子为流体粒子在固壁中的镜像[49, 51], 如图4所示. 镜像粒子的位置和速度与流体粒子切向对称, 而其他属性与流体粒子相同. 因此, 镜像粒子信息会在每个时间步中动态重新生成.
在动态粒子模型(图5所示)中, 固体边壁由边界内的一组固定粒子表示[8, 50, 52]. 边界粒子的位置不随时间变化而但其他属性通过靠近边界的流体粒子线性外推获得. 这些边界内粒子提供了动态的边界条件.
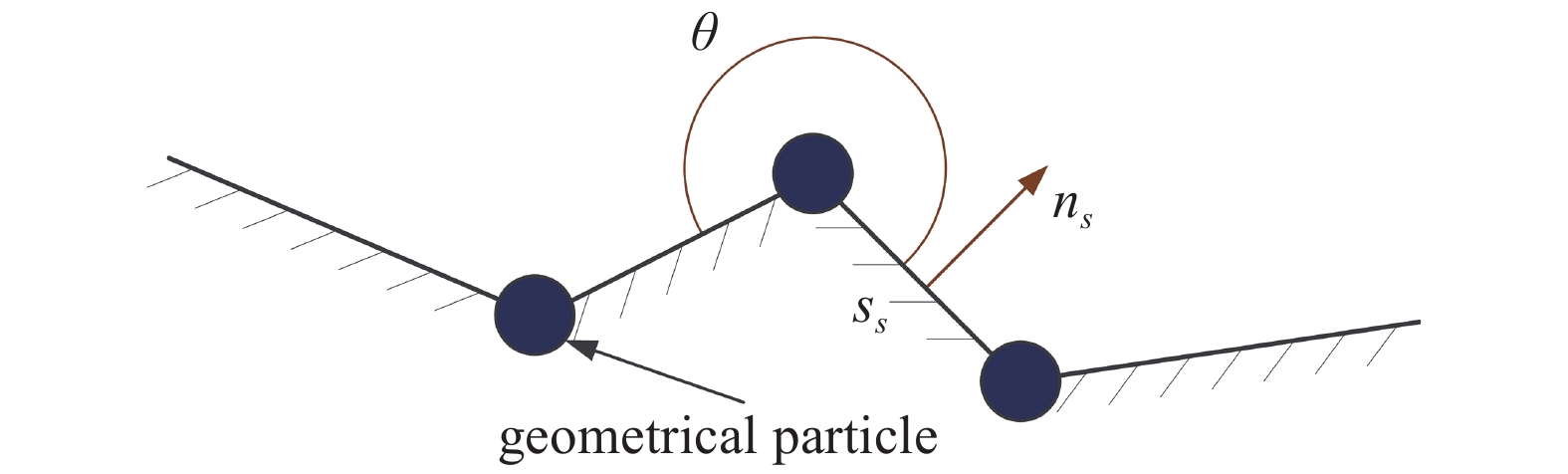
1.6.2 几何表示法
几何表示法引入半解析模型[53-55]. 在半解析模型中(图6所示), 边界属性(如线段和向内法线)由几何代表性粒子重新定义[53]. 引入重整化因子来重建靠近边界的流体粒子的控制方程. 梯度算子则被表达为[53]
$$ \begin{split} \nabla {f}_{i}=&\frac{{\rho }_{i}}{{\gamma }_{i}}\sum\limits_{_{j \in F}} {{m_j}} \left(\frac{{f}_{i}}{{\rho }_{i}^{2}}+\frac{{f}_{j}}{{\rho }_{j}^{2}}\right)\nabla {W}_{ij}-\\& \frac{{{\rho }}_{{i}}}{{{\gamma }}_{{i}}}{\sum \limits_{{s}\in {S}}{{m}}_{{j}}}\left(\frac{{{f}}_{{i}}}{{{\rho }}_{{i}}^{2}}+\frac{{{f}}_{{s}}}{{{\rho }}_{{s}}^{2}}\right){{\rho }}_{{s}}\nabla {{\gamma }}_{{i}{s}} \end{split} $$ (42) 上述算子中的修正参数定义为
$$ {\gamma }_{i}={\int }_{\varOmega }W\left(\boldsymbol{r}-{\boldsymbol{r}}_{i}\right){\rm{d}}r\qquad $$ (43) $$ \nabla {\gamma _{{\rm{as}}}} = {\boldsymbol{n}}\left( {\displaystyle\int_{{r_{{\rm{e1}}}}}^{{r_{{\rm{e2}}}}} {W({\boldsymbol{r}} - {{\boldsymbol{r}}_i}){\rm{d}}l} } \right)$$ (44) 2. 多相流模拟其他SPH类方法
2.1 不可压缩SPH
在常规SPH方法中, 由描述压力和密度之间关系的状态方程表达动量方程中的压力项. 因此, 流体被认为是可压缩的而没有速度无散约束. Cummins和Rudman[56]用投影方法求解压力泊松方程, 解决了SPH方法中的速度无散问题, 从而建立不可压缩SPH (incompressible SPH, ISPH)方法.
中间速度场u*是在没有压力梯度项的情况下在时间上向前积分动量方程计算得到. 压力泊松方程基于中间速度场获得并求解获得达到不可压缩条件的压力场
$$ \nabla \cdot {\left(\frac{1}{\rho }\nabla p\right)}_{i}=\frac{\nabla \cdot {\boldsymbol{u}}_{i}^{*}}{\Delta t} $$ (45) 继而用压力场校正速度场以实现速度无散条件
$$ {\boldsymbol{u}}_{i}^{t+\Delta t}={\boldsymbol{u}}_{i}^{*}-\Delta t{\sum\limits_{j}{m}_{j} }\left(\frac{{p}_{i}}{{\rho }_{i}^{2}}+\frac{{p}_{j}}{{\rho }_{j}^{2}}\right){\nabla }_{i}{W}_{ij} $$ (46) Ellero等[57]引入动态约束使流体粒子体积恒定以实现不可压缩性. Hu和Adams[58]将投影方法成功应用于多相流建立多相ISPH. Szewc等[59]比较了ISPH方法中基于网格的泊松求解器和基于粒子的泊松求解器. Cornelis等[60]提出了隐式ISPH用于水流的真实渲染. Aly[61]应用ISPH方法模拟了方管和方腔中的自然对流. Lind等使用 ISPH方法模拟了自由表面流动[42]和空气中液滴变形过程[62].
2.2 移动粒子半隐式法
Koshizuka[63]针对核材料流体力学问题提出了另一种基于拉格朗日的无网格方法——移动粒子半隐式法(moving particle semi-implicit, MPS). 随着进一步的发展, MPS已被广泛用于处理各类问题, 如溃坝[64]、破波[65]、气液两相流[66-67]和自由表面流[68]. Khayyer和Gotoh[69]以及Kondo和Koshizuka[70]修正MPS中压力项, 消除了非物理高频数值振荡.
MPS具有与其他粒子方法相似的特征, 控制方程中各项公式与SPH方法非常相似. ISPH和MPS都采用类似的半隐式数值方法来求解不可压缩流, 它们之间的主要区别在于光滑核函数[71-72]. 在MPS中, 经常使用如下非常近程的光滑核函数[63]
$$ W(r,h)=\left\{ \begin{aligned} & \frac{h}{r}-1, \;\; 0<\frac{r}{h}\leqslant 1\\& 0,\;\;\qquad\frac{r}{h}>1 \end{aligned}\right. $$ (47) 它的值在r = 0时趋于无穷以避免粒子聚集, 而ISPH中r = 0 时的光滑核函数值为一有限值.
2.3 宏观拟颗粒方法
宏观拟颗粒方法(macro-scale pseudo-particle method, MaPPM)是SPH方法的另一种变体, 由 Ge和Li[73-74]提出用于颗粒−流体系统高精度模拟. 在MaPPM中, 各点处的导数计算被该点与其相邻点的有限差分加权平均计算取代
$$ \nabla f{|}_{i}=dim{\sum }_{j}\frac{{f}_{ji}}{{r}_{ij}^{2}}{\boldsymbol{r}}_{ij}\frac{{m}_{j}}{{\rho }_{j}}{W}_{ij} $$ (48) 式中, dim表示体系的维度, 如是二维, dim = 2; 如是三维, 则dim = 3.
这种替换带来了两个主要好处: (1)在对多相流进行模拟和分析时, 可以保持导数的简单加权平均性质; (2)可采用不可导函数作为光滑核函数.
Zhou等[29]在MaPPM中建立了表面张力IPF模型, 研究液滴变形和流体在固壁上的润湿行为. Ma等[75]用“冻结粒子”簇表达固体颗粒, 应用MaPPM对包含1024个颗粒的气固悬浮系统进行了高分辨率直接数值模拟, 并研究了气固系统动态多尺度结构. Xiong等[76-77]用MaPPM模拟研究了有数十万个固体颗粒的流体−颗粒流化过程.
3. SPH模拟多相流的多种实现方式
总结SPH模拟多相流的各文献可发现, SPH模拟多相流的实现方式大致可分为4类: (1)双流体模型的拉格朗日求解器; (2)多相SPH方法; (3) SPH与其他离散方法耦合; (4) SPH和基于网格的方法耦合.
3.1 TFM的拉格朗日求解器
类似于SPH在单相流中的应用, SPH方法也可以作为TFM的拉格朗日求解器模拟两相流动.
TFM[30-32]作为具有不同界面或分散相(气泡或固体颗粒)两相流的连续方法描述. 各相均分别由一套质量、动量和能量守恒方程单独描述. 由两相方程中的相间作用项来耦合相间质量、动量和能量传递.
对于流固两相流, 各相控制方程表达为下列方式[30]
流体相
$$ \frac{\partial {\theta }_{{\rm{f}}}}{\partial t}+\nabla \cdot \left({\theta }_{{\rm{f}}}{{\boldsymbol{u}}}_{{\rm{f}}}\right)=0 $$ (49) $$ \begin{split} & \frac{\partial \left({\theta }_{{\rm{f}}}{\boldsymbol{u}}_{{\rm{f}}}\right)}{\partial t}+\nabla \cdot \left({\theta }_{{\rm{f}}}{\boldsymbol{u}}_{{\rm{f}}}{\boldsymbol{u}}_{{\rm{f}}}\right)= -\frac{\nabla {p}_{{\rm{f}}}}{{\rho }_{{\rm{f}}}}+\\ & \qquad \frac{\beta }{{\rho }_{{\rm{f}}}\left({\boldsymbol{u}}_{{\rm{s}}}-{\boldsymbol{u}}_{{\rm{f}}}\right)}+\frac{1}{{\rho }_{{\rm{f}}}}\left(\nabla \cdot {\mu }_{{\rm{f}}}{\theta }_{{\rm{f}}}\nabla \right){\boldsymbol{u}}_{{\rm{f}}}+{\theta }_{{\rm{f}}}{\boldsymbol{g}} \end{split} $$ (50) 固体相
$$ \frac{\partial {\theta }_{{\rm{s}}}}{\partial t}+\nabla \cdot \left({\theta }_{{\rm{s}}}{\boldsymbol{u}}_{{\rm{s}}}\right)=0 $$ (51) $$ \begin{split} & \frac{\partial \left({\theta }_{{\rm{s}}}{\boldsymbol{u}}_{{\rm{s}}}\right)}{\partial t}+\nabla \cdot \left({\theta }_{{\rm{s}}}{\boldsymbol{u}}_{{\rm{s}}}{\boldsymbol{u}}_{{\rm{s}}}\right)= -\frac{\nabla {p}_{{\rm{s}}}}{{\rho }_{{\rm{s}}}}+\\& \qquad \frac{\beta }{{\rho }_{{\rm{s}}}\left({\boldsymbol{u}}_{{\rm{f}}}-{\boldsymbol{u}}_{{\rm{s}}}\right)}+\frac{1}{{\rho }_{{\rm{s}}}}\left(\nabla \cdot {\mu }_{{\rm{s}}}{\theta }_{{\rm{s}}}\nabla \right){\boldsymbol{u}}_{{\rm{s}}}+{\theta }_{{\rm{s}}}{\boldsymbol{g}} \end{split} $$ (52) 其中θ是各相体积分数, β是阻力系数, 下标f和s分别表示液相和固相. 两组方程之间的约束条件是θf+θs=1和0 ≤ θf, θs ≤ 1. 耦合两相的相互作用由动量方程中的曳力项来表示.
与SPH方法求解单相流动类似, 将两相离散为两组独立SPH粒子, 用于构建TFM 的拉格朗日求解器. 而两相SPH粒子的分布自然满足约束条件θf+θs=1和0 ≤ θf, θs ≤ 1; 与其他方法类似, 解决两相问题的关键是相间相互作用及其离散表示.
Monaghan和Kocharyan[12]用SPH方法求解了含尘两相流动. 动量方程中的相间相互作用项被离散化为曳力核函数计算
$$ \frac{1}{dim}{\sum }_{j}{m}_{j}\frac{{\beta }_{ij}}{{\rho }_{j}}\left(\frac{{\boldsymbol{u}}_{ij}\cdot {\boldsymbol{r}}_{ij}}{{r}_{ij}^{2}+{\eta }^{2}}\right){\boldsymbol{r}}_{ij}{W}_{ij} $$ (53) 其中η2是防止
${r}_{ij}^{2} $ =0时出现奇点的约为 ~0.001h2的剪切常数. 曳力系数β与表示空气和尘埃的SPH粒子属性相关, 并表达为$$ \beta =\frac{2{\rho }_{{\rm{g}}}{\theta }_{{\rm{s}}}{C}_{{\rm{D}}}}{{d}_{{\rm{p}}}}|{\boldsymbol{u}}_{{\rm{f}}}-{\boldsymbol{u}}_{{\rm{s}}}| $$ (54) 其中dp是尘埃直径, CD是与颗粒雷诺数Rep=ρgμg|uf−us|/dp有关的标准阻力系数. 两个SPH粒子沿中心线动量和角动量保持守恒.
Monaghan[78]发展了一种隐式曳力模型, 以提高 SPH计算的准确性和稳定性. 粒子i的速度基于曳力引起的减速度更新
$$ {\boldsymbol{u}}_{i}={\boldsymbol{u}}_{i}^{0}-\frac{\Delta t{\boldsymbol{r}}_{ji}{m}_{i}{s}_{ij}\left({\boldsymbol{u}}_{ij}^{0}\cdot {\boldsymbol{r}}_{ij}\right)}{1+\Delta t({m}_{i}+{m}_{j}){s}_{ji}{r}_{ij}^{2}} $$ (55) 其中上标0表示应用曳力项前的初始值, Δt为时间步长, 系数sij为
$$ {s}_{ij}=\frac{1}{dim}\frac{{\beta }_{ij}}{{\rho }_{i}{\rho }_{j}}\left(\frac{{W}_{ij}}{{r}_{ij}^{2}+{\eta }^{2}}\right) $$ (56) Laibe和Price[79]采用可变光滑长度的曳力核函数中来进行气体−粉尘混合物的模拟. Xiong等[76]在液固悬浮体系模拟中引入了与固体体积分数相关的固相黏度系数计算式,
$$ {\mu }_{{\rm{s}}}=5.0{\theta }_{{\rm{s}}} $$ (57) 3.2 多相SPH方法
SPH方法在流动模拟中显示出巨大的潜力,研究人员扩展SPH方法用于多相流模拟, 建立多相 SPH方法[15, 21-29]. 在多相SPH方法中, 两个不同的相被离散成两组具有不同属性的SPH 粒子, 并且相间相互作用由不同的SPH参数隐式描述. 它是 SPH模拟两相流的最常用方法. 与TFM的拉格朗日求解器不同, 多相SPH方法采用隐式相互作用来耦合两相, 并将固体/气泡视为SPH粒子的集合.
多相SPH方法是SPH方法用于多相流模拟的自然延伸. 它包含SPH 方法在单相流模拟中的特点和优势, 并引入了各种两相相互作用(如表面张力)模型来完成多相流模拟, 可精细准确地描述界面行为.
3.2.1 液−液体系
液−液体系的模拟是多相SPH较早期及较常见的应用. 液−液系统中两种流体的特性, 例如密度和黏度, 通常相差不大.
瑞利−泰勒(Rayleigh−Taylor, R-T)不稳定性是在具有不同性质的两种液体之间界面上发展和演变的不稳定性. Cummins和Rudman[56]引入人工表面张力首次用多相SPH方法进行 R-T不稳定性模拟. Tartakovsky和Meakin[27]发展了基于数密度的多相SPH, 消除了两种流体之间的人工表面张力, 模拟得到更真实的界面行为和R-T 不稳定性. Hu和Adams[58]发展多相投影方法模拟了不可压不互溶液−液两相流动; 还发展基于恒定密度的 SPH 投影方法, 并采用CSF表面张力模型模拟了R-T不稳定性[80].
开尔文−亥姆霍兹(Kelvin–Helmholtz, K-H)不稳定性是不同水平速度的两种平行流体间的另一种不稳定性现象. Shadloo和Yildiz[81]应用多相SPH方法模拟研究了两种不可压不互溶液体的K-H不稳定性.
Shao[82] 在界面处应用压力连续性条件, 用多相SPH方法解耦求解液液两相. Tong和Browne[28]采用基于恒定密度的SPH投影方法研究两种流体之间的传热和界面处的Marangoni力效应.
3.2.2 气−液体系
相比于液−液体系, 气−液体系中两相密度比会高得多, 可以达到数百或数千量级. 处理高密度比是 SPH方法模拟气液体系的一个挑战. 常规SPH方法还无法成功处理密度比高于10的两相流体[83]. SPH方法进行气液体系模拟的另一个困难是消除高密度比下表面张力导致的压力变化.
Colagrossi和Landrini[83]发展了多相SPH方法中两相界面表征的校正方法, 并模拟了带空气环境的溃坝过程. Das和Das[84]采用CSF模型和核函数近似校正方式发展多相SPH方法, 成功模拟了水池中气体从气孔注入和气泡演化的过程.
Szewc等[26, 85]采用密度校正和表面张力CSF模型发展多相ISPH, 模拟了两相密度比为1000的液体中气泡上升变化过程, 并获得了气−液体系中气泡曳力系数与雷诺数的关系. Lind等[62]采用多相 ISPH方法模拟了密度比为1000的气体中液−滴变形过程.
孙鹏楠等[86]应用粒子平移技术(particle shifting technique, PST)[87-88]改善CSF模型计算时的界面失稳, 成功模拟了气泡在水中上浮及破碎过程.
3.2.3 液−固体系
在应用多相SPH方法模拟的液−固体系时, 固体常被处理为流动的边界或性质截然不同的刚体SPH粒子.
Akinci等[89]提出了一种在多相 SPH方法中通过流体力双向耦合流体和刚性物体的方法, 实现了船只通过桥梁和舰艇在波涛汹涌的大海中航行的模拟.
Tofighi等[90]将固体表达为具有极高黏度的 SPH 粒子的集合, 用于模拟流体中刚体的运动过程. Fourtakas和Rogers[91]提出了一个液−固体系多相SPH模型, 该模型结合了液体和固体之间黏附效应涉及的屈服变形、剪切和悬浮等作用, 用于易蚀坝溃裂过程的模拟.
3.2.4 气−固体系
Ma等[75]采用MaPPM方法实现气固悬浮体系的高分辨率直接数值模拟. 在MaPPM中, 固体颗粒视作一组“冻结的SPH粒子”. Xiong等[76-77]采用MaPPM 对气固流态化进行了大规模直接数值模拟, 以亚网格的精度模拟了多达30 240个固体颗粒和超过10亿个流体SPH粒子, 该模拟基于并行GPU完成.
3.3 耦合SPH和其他离散方法
在多相流模拟中, SPH方法通常适合求解连续相或变形较大的相. SPH很容易与其他离散方法耦合来模拟流体−固体系统或流体中的可变形物体. 在耦合方法中, SPH和其他离散方法相结合, 在其特定的适用领域中获益. 这种耦合将SPH方法的应用扩展到具有不同特性的多相流; 此外, 也将不同拉格朗日方法的优点结合到此类模拟中.
对于流体−颗粒体系, 应用离散元方法(discrete element method, DEM)跟踪每个固体颗粒的运动是很自然的做法. SPH粒子和DEM粒子的相互作用(曳力和浮力)表达为接触的两相粒子之间物理量差值的函数. SPH和DEM的耦合以亚颗粒的精度实现了流体−颗粒悬浮体系的直接数值模拟.
Potapov等[92]建立SPH-DEM耦合方法, 模拟研究了圆柱绕流和两平行剪切板之间的流−固体系二维流动. Huang和Nydal[93]结合SPH和DEM研究固体颗粒在顶盖驱动方腔流中的运动过程. Robinson等[25]应用SPH-DEM方法模拟了三维液柱中的颗粒沉降, 流体对固体颗粒的作用力表示为
$$ {\boldsymbol{f}}_{i}={V}_{{\rm{p}}}{(-\nabla p+\nabla \cdot \boldsymbol{\tau })}_{i}+{\boldsymbol{f}}_{{\rm{d}}}({\theta }_{{\rm{s}}},{\boldsymbol{u}}_{{\rm{f}}}-{\boldsymbol{u}}_{{{i}}}) $$ (58) 其中Vp是颗粒的体积, fd为流体作用在颗粒上的曳力, 其取决于局部的固相体积分数θs和流体−固体颗粒之间的滑移速度uslip=uf−ui. 压力梯度和应力张量采用SPH 插值方法计算
$$ {\left(-\nabla p+\nabla \cdot \tau \right)}_{i}=\frac{{\displaystyle\sum }_{j}{m}_{j}{\theta }_{j}{W}_{ij}\left({h}_{j}\right)}{{\displaystyle\sum }_{j}{m}_{j}{W}_{ij}\left({h}_{j}\right)/{\rho }_{j}} \qquad$$ (59) $$ \begin{split} {\theta }_{i}= &-{\sum }_{j}{m}_{j}\left[\left(\frac{{p}_{i}}{{{\varOmega }}_{i}{\rho }_{i}^{2}}+{{\varPi }}_{ij}\right){\nabla }_{i}{W}_{ij}\left({h}_{i}\right)+\right.\\&\left. \left(\frac{{p}_{j}}{{{\varOmega }}_{j}{\rho }_{j}^{2}}+{{\varPi }}_{ij}\right){\nabla }_{i}{W}_{ij}\left({h}_{j}\right)\right] \end{split} $$ (60) SPH粒子上的相间力由每个DEM粒子贡献量的加权平均得到
$$ \left.\begin{aligned} & {\boldsymbol{f}}_{i}=-\frac{{m}_{i}}{{\rho }_{i}}{\sum }_{j}\frac{1}{{S}_{j}}{\boldsymbol{f}}_{j}{W}_{ij}\left({h}_{{\rm{c}}}\right)\\& {S}_{i}={\sum }_{j}\frac{{m}_{j}}{{\rho }_{j}}{W}_{ij}\left({h}_{{\rm{c}}}\right) \end{aligned}\right\} $$ (61) El Shamy和Sizkow[94]将SPH方法和DEM方法耦合用于评估动态激励下饱和颗粒土壤的液化过程. Robb等[95]耦合SPH-DEM方法模拟了不规则浮冰接近静止覆盖物和上游浮冰在障碍物上积聚等过程, 建立浮冰动力学研究的定量工程工具. Liu等[96]和Ji等[97]在基于多面体单元的DEM模型中引入闵可夫斯基加和操作简化不规则固体颗粒间的碰撞作用计算, 并耦合SPH方法建立了液固多相流动模拟方法, 成功模拟了包含石块运动的溃坝过程以及石块落水过程.
Polwaththe-Gallage等[98]使用基于DEM的弹簧网络模型来表示红细胞的黏弹性细胞膜, 并采用 SPH方法对细胞内外的流体进行建模. 耦合模型用于模拟毛细血管中细胞的变形和运动, 并研究了细胞间相互作用对细胞运动的影响.
最近, 陈飞国和葛蔚[99]将表征气体运动的拟颗粒模型(pseudo-particle model, PPM)[100-101]和光滑粒子流体动力学耦合, 对液滴破碎和油膜雾化等气液流动过程进行了高精度模拟. 与多相SPH方法中仅用不同参数区分气液两相的方式不同, PPM-SPH耦合方法中由截然不同的模型表达气液两相, 更能反映两相行为差异.
3.4 耦合SPH和基于网格的方法
SPH方法在流体流动模拟中非常成功, 特别是在界面流动、大变形流动和多相流动中. 然而, 为了获得高精度模拟结果, 需要采用大量的计算粒子表示流体, 对计算要求极高. 而对于单相的流动主体, 完全的拉格朗日求解并不必需也不高效. 基于上述认识, 将SPH方法和基于网格的方法耦合可以获得精度和效率间的平衡. 这些耦合方法的关键为重叠区域中两类方法的衔接处理.
Marrone等[102]发展SPH和有限体积CFD (computational fluid dynamics)的耦合方法, 模拟了存在变形和破碎的自由表面流. 流动主体部分采用结构化网格求解, 变形较大的部分采用SPH方法求解. Napoli等[103]考虑了CFD和SPH重叠区域的物性匹配, 提高了SPH-CFD耦合方法模拟的准确性. Deng等[104]将SPH和有限体积CFD耦合用于求解气固流动双流体模型. 分散的固体颗粒进行类似流体的连续处理, 并由基于GPU的SPH计算求解; 而流体运动模拟则采用有限体积CFD在Ansys FLUENT软件中实施.
Feng等[105]耦合SPH和有限元方法(finite element method, FEM)模拟了磨料水射流切割的单次加速过程. Zhang等[106]在 SPH 中加入了大涡模拟(large eddy simulation, LES)表征湍流效应, 并使用有限元虚拟边界法描述固体颗粒, 模拟了流体中颗粒沉降过程, 验证了SPH改进方法用于多相流模拟研究的能力.
SPH-FEM耦合模型常用于研究流−固耦合问题, SPH的引入降低了流体−固壁间耦合处理复杂性[107], 而FEM可以提高复杂固壁的处理能力以及计算准确性和稳定性[108-109]. Long等[110]在SPH-FEM耦合模型中加入共轭传热计算, 用于解决热流构耦合问题.
4. 多相流 SPH 方法的其他讨论
4.1 近似修正方法
4.1.1 核近似修正
Chen等[111]提出了一种修正光滑粒子方法 (corrective smoothed-particle method, CSPM), 通过提高核近似的精度来解决张力不稳定性问题
$$ {W}_{ij}^{{\rm{CSPM}}}=\frac{{\displaystyle\sum }_{j}{W}_{ij}}{{\displaystyle\sum }_{j}\dfrac{{m}_{j}}{{\rho }_{j}}{W}_{ij}} $$ (62) CSPM 已成功用于固壁边界[111]和两相界面处[28, 84]的流体改进求解.
4.1.2 粒子近似修正
在多相体系中直接应用质量密度表达式可能会引起人工表面张力并扭曲界面处的密度计算[83]. Tartakovsky和Meakin[112]提出使用粒子数密度来消除不同相属性对密度计算的影响, 从而避免人工表面张力. 粒子数密度计算公式为
$$ {n}_{i}={\sum }_{j}{W}_{ij} $$ (63) 这样, 动量方程可以表达为
$$ \begin{split} \frac{{\rm{d}}{\boldsymbol{u}}_{i}}{{\rm{d}}t}=&-\frac{1}{{m}_{i}}{\sum }_{j}\left(\frac{{p}_{i}}{{n}_{i}^{2}}+\frac{{p}_{j}}{{n}_{j}^{2}}\right){\nabla }_{i}{W}_{ij}+\\& \frac{1}{{m}_{i}}{\sum }_{j}\frac{{\mu }_{i}+{\mu }_{j}}{{n}_{i}{n}_{j}}{{u}}_{ij}\left(\frac{1}{{r}_{ij}}\frac{\partial {W}_{ij}}{\partial {r}_{ij}}\right)+\boldsymbol{g} \end{split} $$ (64) 此外, 这种粒子数密度近似方法适用于高密度比的多相流动模拟.
4.1.3 一致性修正
SPH近似表达中的一致性(Cn一致性)表示为可由SPH方法精确再现多项式的阶数[113]. 它受光滑核函数、光滑长度、边界条件和粒子分布等因素影响. 通常, 传统SPH方法可认为恢复到一阶一致性(C1一致性). 但是对于具有不均匀粒子分布、光滑长度与颗粒间距不同或边界(固壁边界或相界面)处, 传统SPH方法甚至不能完全满足零阶(C0)一致性[114].
Liu和Liu[36, 114]提出了有限粒子法(finite particle method, FPM)来提高SPH方法的一致性. 在FPM中, 场函数f(x)及其导数的近似值修正为[113]
$$ \left\{\begin{array}{c}{f}_{i}\\ \nabla {f}_{i}\end{array}\right\}={\boldsymbol{L}}^{-1}\left[\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle\int f\left(x\right)W(x-{x}_{i}){\rm{d}}x\\ \displaystyle\int f\left(x\right)W\nabla (x-{x}_{i}){\rm{d}}x\end{array}\right] $$ (65) 其中修正矩阵L为
$$ \boldsymbol{L}=\left[\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle\int W\left(x-{x}_{i}\right)\mathrm{d}x& \displaystyle\int \left(x-{x}_{i}\right)W\left(x-{x}_{i}\right)\mathrm{d}x\\ \displaystyle\int \nabla W\left(x-{x}_{i}\right)\mathrm{d}x& \displaystyle\int \left(x-{x}_{i}\right)\nabla W\left(x-{x}_{i}\right)\mathrm{d}x\end{array}\right] $$ (66) 对于遇到边界缺陷和粒子分布敏感性问题的情况, FPM大大提高了SPH方法的一致性. 但对于粒子分布高度无序的情况, 由于病态校正矩阵导致数值求解不稳定, FPM 模拟可能也会崩溃[115]. 合理假设粒子自我导向的贡献在光滑核函数的导数中占主导地位, Zhang等[106]将修正矩阵简化为如下对角矩阵建立解耦有限粒子法(decoupled finite particle method, DFPM)
$$ \boldsymbol{L}=\left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} \displaystyle\int \left(x-{x}_{i}\right)W\mathrm{d}x & 0&0&0\\ 0& \displaystyle\int \left(x-{x}_{i}\right){W}_{x}'\mathrm{d}x&0&0\\ 0& 0&\displaystyle\int \left(x-{x}_{i}\right){W}_{y}'\mathrm{d}x&0\\ 0&0&0&\displaystyle\int (x-{x}_{i}){W}_{z}'\mathrm{d}x \end{array}} \right] $$ (67) 因此, f(x)及其导数的粒子近似为
$$\left. \begin{aligned} & {f}_{i}={\sum }_{j}{f}_{j}{W}_{ij}\Delta {V}_{j}\Biggr/{\sum }_{j}{W}_{ij}\Delta {V}_{j}\\& {f}_{i,x}'={\sum }_{j}\left({f}_{j}-{f}_{i}\right)\left(\partial {W}_{ij}/\partial {x}_{i}\right)\Delta {V}_{j}\Biggr/{\sum }_{j}{x}_{ji}{W}_{ij}\Delta {V}_{j}\\& {f}_{i,y}'={\sum }_{j}\left({f}_{j}-{f}_{i}\right)\left(\partial {W}_{ij}/\partial {y}_{i}\right)\Delta {V}_{j}\Biggr/{\sum }_{j}{y}_{ji}{W}_{ij}\Delta {V}_{j}\\& {f}_{i,z}'={\sum }_{j}\left({f}_{j}-{f}_{i}\right)\left(\partial {W}_{ij}/\partial {z}_{i}\right)\Delta {V}_{j}\Biggr/{\sum }_{j}{z}_{ji}{W}_{ij}\Delta {V}_{j} \end{aligned}\right\} $$ (68) 4.2 张力不稳定性
张力不稳定性是应用SPH方法时一个众所周知的问题, 它会导致粒子过密聚集或粒子被炸开[33]. 张力不稳定性在SPH模拟中时常被观察到, 一直是早期SPH研究[116]的关注焦点. 即使压力为正值, 张力不稳定性仍会发生. Swegle等[117]和Monaghan[118]给出了应力状态稳定性或不稳定性的判据; 应力不稳定增长的条件为
$$ {W}''S>0 $$ (69) 这里
${W}'' $ 是光滑核函数的二阶导数, S是应力状态. 该条件表明, 核函数对SPH方法的稳定模拟至关重要. 核函数的二阶导数在整个支持域中应该满足非负性. 同时, 建议采用双曲型核函数来消除张力不稳定性[39].4.3 高雷诺数流动
众所周知, 与其他粒子方法类似, 传统SPH 方法不适合模拟高雷诺数下的流动, 这是由于高涡度条件下会发生张力不稳定性以及在负压条件下会产生非真实的粒子空缺[119].
Sun等[119-120]在δ-SPH方法[121]中实施张力不稳定性控制(tensile instability control, TIC)和粒子平移技术[87-88]建立δ+-SPH方法. 在δ+-SPH方法中, 连续性方程引入了一个额外的数值扩散项, 并将粒子平移重构粒子分布. δ+-SPH方法克服了SPH方法难以模拟高雷诺数流动的局限性.
4.4 表面张力系数
如前面小节里所述, SPH方法中两相界面处的表面张力主要由CSF, IPF或CPM等模型表达. CSF模型直接用实际表面张力系数来表达宏观表面张力. 然而, 对于IPF和CPM模型, 表面张力系数隐含在模型参数中, 其理论关系式尚未获得[27].
Zhou等[29]采用如下IPF模型表征两不互溶液体间的表面张力作用
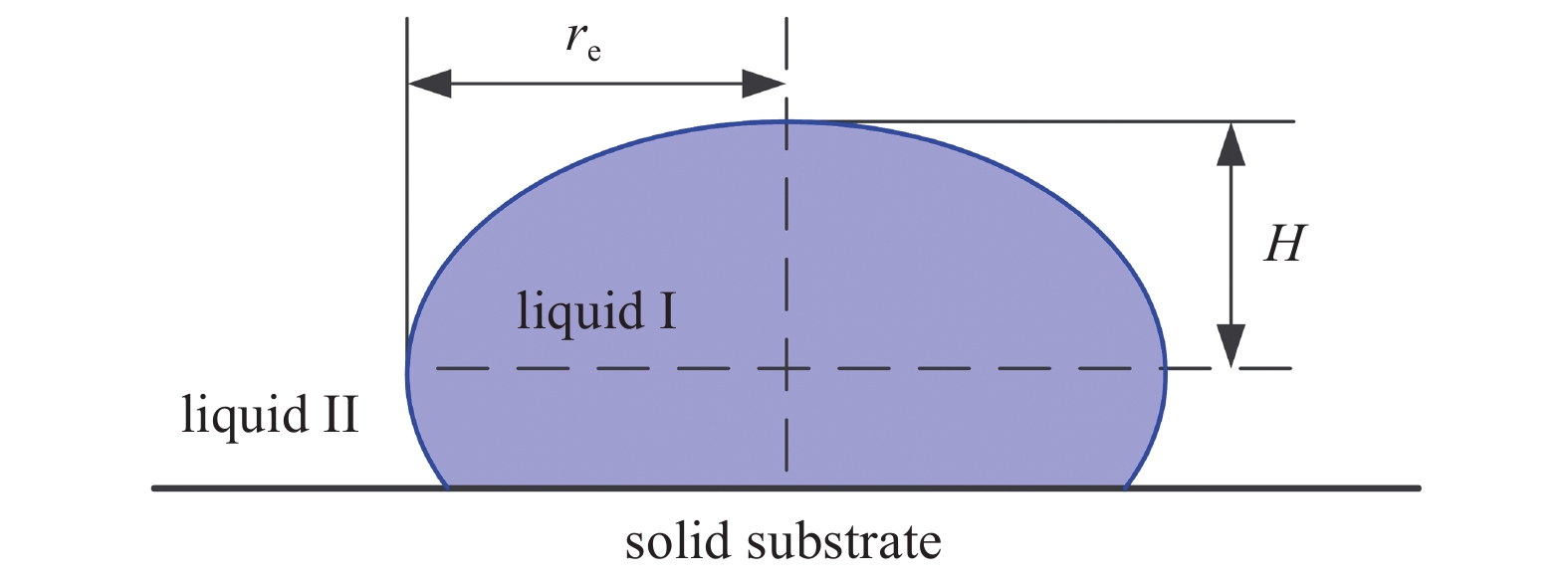
$$ {\boldsymbol{f}}_{ij}=s\frac{{\boldsymbol{r}}_{ij}}{{r}_{ij}^{2}} $$ (70) 研究了不同参数s下固体基质上液滴在液体中的变形情况. 两相表面张力系数γ则可由躺滴法根据下式计算得到
$$ \gamma =\frac{1}{2}\Delta \rho g{H}^{2} $$ (71) 其中Δρ是两种液体之间的密度差, H是液滴的半高(见图7). 模型系数s和物理表面张力系数γ之间的关系表达如下[29]
$$ \frac{\gamma }{\left[\mathrm{N}{\mathrm{m}}^{-1}\right]}=1350.68\times {\left(\frac{s}{\left[\mathrm{k}\mathrm{g}{\mathrm{m}}^{2}{\mathrm{s}}^{-2}\right]}\right)}^{0.501} $$ (72) Xu等[122]和Yang等[33]应用CPM模型模拟了不同半径的黏性液滴的粒子分布情况, 而表面张力系数γ可基于拉普拉斯方程计算得到
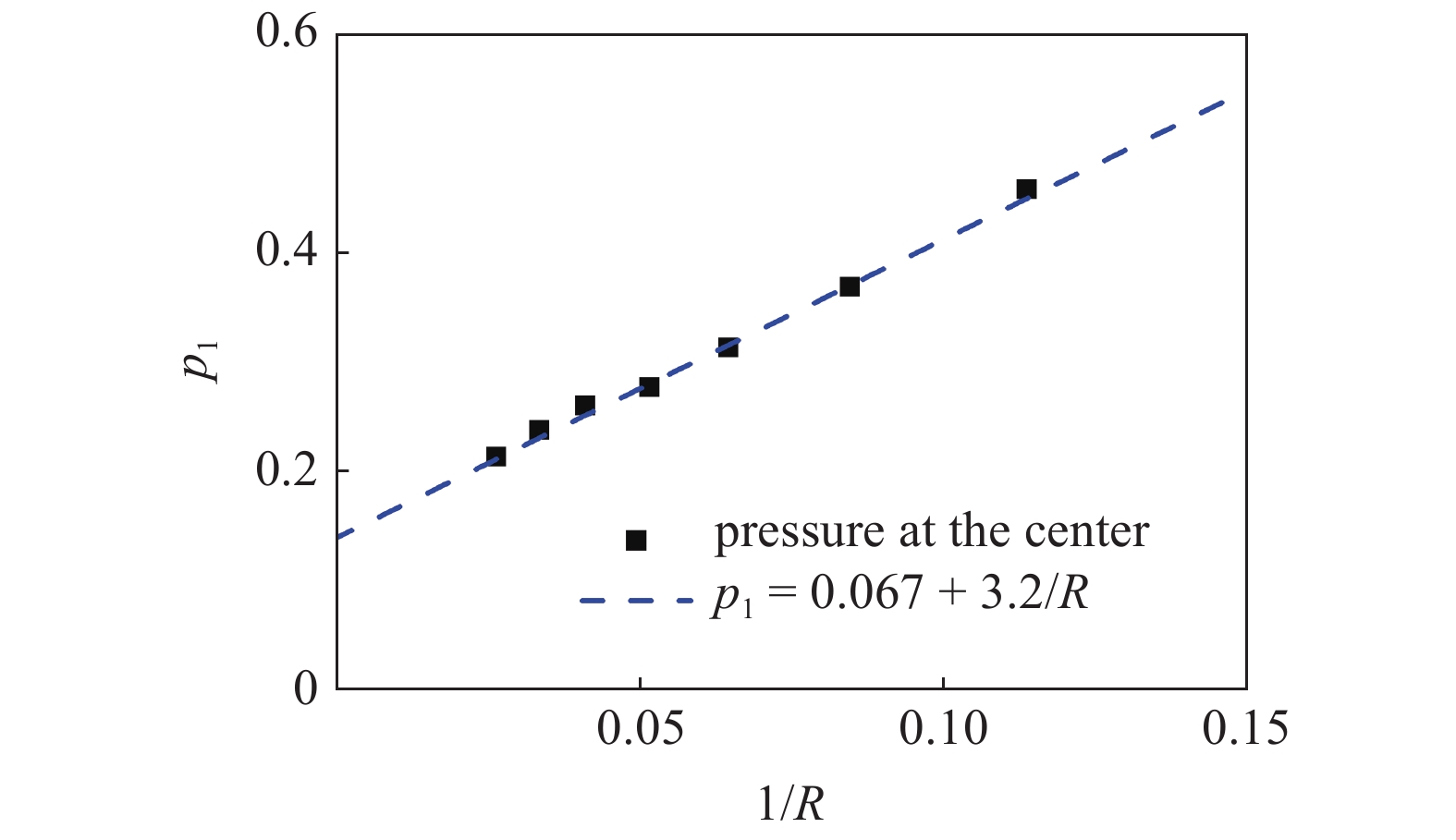
$$ {p}_{{\rm{l}}}={p}_{{\rm{g}}}+\frac{\gamma }{R} $$ (73) 其中pl是液滴中心压力, pg是远离液滴的蒸汽压, R是液滴的半径. 液滴中心压力则根据液滴中心粒子密度由范德华状态方程计算得到, 不同半径的液滴中心压力与1/R线性拟合得到的斜率即为表面张力系数, 如图8所示.
5. 结 论
作为无网格方法的代表, SPH在过去的几十年中发展迅速, 并在许多研究领域得到了广泛的应用. 由于其天然的拉格朗日特征, SPH方法具有处理界面、大变形、不连续性和多物理场的能力, 在多相流的模拟研究中显示出巨大的潜力. 许多研究者在SPH方法模拟多相流方面已获得众多成果. 本工作试图从实现方式的异同归类这些多相流SPH模拟研究.
(1)鉴于SPH方法成功应用于单相流动模拟, 作为TFM的完全拉格朗日求解器则是SPH方法模拟多相流的直接方法. 该方式需要多相系统各相耦合项以及建模参数(例如压力和黏度)的显式表达式.
(2)多相SPH方法则对每个相分别SPH建模, 并且自然地将具有不同参数的两个相耦合. 多相 SPH方法是SPH方法中应用最多的多相流模拟方法, 已成功应用于各种不同体系的研究.
(3) SPH方法还能与其他离散方法(如分子动力学、耗散粒子动力学和离散单元法)相耦合模拟各类多相流. 耦合方法保持了每相对应的不同离散方法的特征和优势.
(4)此外, 为了降低使用大量SPH 粒子进行多相流模拟的计算成本, 还可以使用基于网格的方法求解较为简单的主体流动, 而仅在界面处应用SPH方法. 欧拉−拉格朗日耦合方法为多相流模拟提供了准确性和效率之间的折衷方案, 并显示出模拟实际多相流体系的巨大潜力.
然而, 为了提高多相流 SPH 模拟的准确性和效率, 仍有一些问题需要解决. 例如, (1) SPH 参数与流体物性之间的关系. 不同的加权核函数会导致不同的有效物性[123-124]. 为了稳定模拟, 还引入了如人工黏度[125]等人工参数. 因此, 模型参数和实际物性的校准会随着不同核函数、光滑长度和近似方式而有所差异. (2)计算成本高的解决方案. SPH 方法虽然适用于模拟具有大变形和分明相界面的流动, 但其计算成本非常高, 尤其是模拟多相流. 一种解决方案是实现大规模并行计算[22, 77, 91, 126-127]以及基于GPU等加速计算技术[128-134]; 另一种方案是减少不必要的计算, 如耦合其他离散方法表达分散体, 耦合基于网格方法模拟连续相主体平缓流动等. (3)实验验证和增强模拟. 有许多实验验证了SPH 模拟, 例如溃坝[64, 135]和气−液雾化[22]. 此外, SPH方法还广泛应用于计算机视觉用于显示真实的流体行为[60, 136]. 实验、模拟和视觉技术的结合可能会激励在计算机上进行现实中困难或无法实现的增强虚拟实验.
-
[1] Gingold RA, Monaghan JJ. Smoothed particle hydrodynamics: theory and application to non-spherical stars. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 1977, 181: 375-389 doi: 10.1093/mnras/181.3.375
[2] Lucy LB. A numerical approach to the testing of the fission hypothesis. Astronomical Journal, 1977, 82(12): 1013-1024
[3] Monaghan JJ. Smoothed particle hydrodynamics. Reports on Progress in Physics, 2005, 68(8): 1703-1759 doi: 10.1088/0034-4885/68/8/R01
[4] Cleary PW, Prakash M, Ha J, et al. Smooth particle hydrodynamics: status and future potential. Progress in Computational Fluid Dynamics, 2007, 7(2-4): 70-90
[5] Gotoh H, Khayyer A. On the state-of-the-art of particle methods for coastal and ocean engineering. Coastal Engineering Journal, 2018, 60(1): 79-103 doi: 10.1080/21664250.2018.1436243
[6] Koumoutsakos P. Multiscale flow simulations using particles. Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics, 2005, 37: 457-487 doi: 10.1146/annurev.fluid.37.061903.175753
[7] Li SF, Liu WK. Meshfree and particle methods and their applications. Applied Mechanics Reviews, 2002, 55(1): 1-34 doi: 10.1115/1.1431547
[8] Liu GR, Liu MB. Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics: A Meshfree Particle Method. World Scientific, 2003.
[9] Liu MB, Liu GR. Smoothed particle hydrodynamics (SPH): An overview and recent developments. Archives of Computational Methods in Engineering, 2010, 17(1): 25-76 doi: 10.1007/s11831-010-9040-7
[10] Monaghan JJ. Smoothed particle hydrodynamics. Annual Reviews in Astronomy and Astrophysics, 1992, 30(1): 543-574 doi: 10.1146/annurev.aa.30.090192.002551
[11] Monaghan JJ. Smoothed particle hydrodynamics and its diverse applications. Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics, 2011, 44(1): 323-346
[12] Monaghan JJ, Kocharyan A. SPH simulation of multi-phase flow. Computer Physics Communications, 1995, 87(1): 225-235
[13] Shadloo MS, Oger G, Le Touzé D. Smoothed particle hydrodynamics method for fluid flows, towards industrial applications: Motivations, current state, and challenges. Computers & Fluids, 2016, 136: 11-34
[14] Violeau D, Rogers BD. Smoothed particle hydrodynamics (SPH) for free-surface flows: past, present and future. Journal of Hydraulic Research, 2016, 54(1): 1-26 doi: 10.1080/00221686.2015.1119209
[15] Wang ZB, Chen R, Wang H, et al. An overview of smoothed particle hydrodynamics for simulating multiphase flow. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 2016, 40(23): 9625-9655
[16] Ye T, Pan DY, Huang C, et al. Smoothed particle hydrodynamics (SPH) for complex fluid flows: Recent developments in methodology and applications. Physics of Fluids, 2019, 31(1): 11301 doi: 10.1063/1.5068697
[17] Khairi MAW, Rozainy MR, Ikhsan J. Smoothed particle hydrodynamics simulation for debris flow: a review. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 2020, 864: 12045 doi: 10.1088/1757-899X/864/1/012045
[18] Moreira AB, Leroy A, Violeau D, et al. Overview of large-scale smoothed particle hydrodynamics modeling of dam hydraulics. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2020, 146(2): 3119001 doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)HY.1943-7900.0001658
[19] Lind SJ, Rogers BD, Stansby PK. Review of smoothed particle hydrodynamics: towards converged Lagrangian flow modelling. Proceedings of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 2020, 2241(476): 20190801
[20] Yang PY, Huang C, Zhang ZL, et al. Simulating natural convection with high rayleigh numbers using the smoothed particle hydrodynamics method. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2021, 166: 120758 doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2020.120758
[21] Breinlinger T, Polfer P, Hashibon A, et al. Surface tension and wetting effects with smoothed particle hydrodynamics. Journal of Computational Physics, 2013, 243: 14-27 doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2013.02.038
[22] Koch R, Braun S, Wieth L, et al. Prediction of primary atomization using smoothed particle hydrodynamics. European Journal of Mechanics B Fluids, 2017, 61: 271-278 doi: 10.1016/j.euromechflu.2016.10.007
[23] Li L, Shen LM, Nguyen GD, et al. A smoothed particle hydrodynamics framework for modelling multiphase interactions at meso-scale. Computational Mechanics, 2018, 62(5): 1071-1085 doi: 10.1007/s00466-018-1551-3
[24] Ray M, Yang XF, Kong S, et al. High-fidelity simulation of drop collision and vapor–liquid equilibrium of van der Waals fluids. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, 2017, 36(2): 2385-2392 doi: 10.1016/j.proci.2016.06.018
[25] Robinson M, Ramaioli M, Luding S. Fluid-particle flow simulations using two-way-coupled mesoscale SPH-DEM and validation. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 2014, 59: 121-134 doi: 10.1016/j.ijmultiphaseflow.2013.11.003
[26] Szewc K, Pozorski J, Minier JP. Simulations of single bubbles rising through viscous liquids using smoothed particle hydrodynamics. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 2013, 50: 98-105 doi: 10.1016/j.ijmultiphaseflow.2012.11.004
[27] Tartakovsky A, Meakin P. Modeling of surface tension and contact angles with smoothed particle hydrodynamics. Physical Review E, 2005, 72(2): 26301
[28] Tong MM, Browne DJ. An incompressible multi-phase smoothed particle hydrodynamics (SPH) method for modelling thermocapillary flow. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2014, 73: 284-292 doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2014.01.064
[29] Zhou GZ, GeW, Li JH. A revised surface tension model for macro-scale particle methods. Powder Technology, 2008, 183(1): 21-26 doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2007.11.024
[30] Gidaspow D. Multiphase Flow and Fluidization: Continuum and Kinetic Theory Descriptions. San Diego: Academic Press, 1994.
[31] Ishii M, Mishima K. Two-fluid model and hydrodynamic constitutive relations. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 1984, 82(2): 107-126
[32] Stewart HB. Stability of two-phase flow calculation using two-fluid models. Journal of Computational Physics, 1979, 33(2): 259-270 doi: 10.1016/0021-9991(79)90020-2
[33] Yang XF, Liu MB, Peng SL. Smoothed particle hydrodynamics modeling of viscous liquid drop without tensile instability. Computers & Fluids, 2014, 92: 199-208
[34] Monaghan JJ. Simulating free surface flows with SPH. Journal of Computational Physics, 1994, 110(2): 399-406 doi: 10.1006/jcph.1994.1034
[35] Batchelor GK. An Introduction to Fluid Dynamics. Cambridge University Press, 1967.
[36] Liu MB, Liu GR. Meshfree particle simulation of micro channel flows with surface tension. Computational Mechanics, 2005, 35(5): 332-341 doi: 10.1007/s00466-004-0620-y
[37] Morris JP. Simulating surface tension with smoothed particle hydrodynamics. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Fluids, 2000, 33(3): 333-353 doi: 10.1002/1097-0363(20000615)33:3<333::AID-FLD11>3.0.CO;2-7
[38] Silbey RJ, Alberty RA, Bawendi MG. Physical Chemistry. Wiley, 2004: 944
[39] Liu MB, Liu GR, Lam KY. Constructing smoothing functions in smoothed particle hydrodynamics with applications. Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics, 2003, 155(2): 263-284 doi: 10.1016/S0377-0427(02)00869-5
[40] Monaghan JJ, Pongracic H. Artificial viscosity for particle methods. Applied Numerical Mathematics, 1985, 1(3): 187-194 doi: 10.1016/0168-9274(85)90015-7
[41] Brackbill JU, Kothe DB, Zemach C. A continuum method for modeling surface tension. Journal of Computational Physics, 1992, 100(2): 335-354 doi: 10.1016/0021-9991(92)90240-Y
[42] Lind SJ, Xu R, Stansby PK, et al. Incompressible smoothed particle hydrodynamics for free-surface flows: A generalised diffusion-based algorithm for stability and validations for impulsive flows and propagating waves. Journal of Computational Physics, 2012, 231(4): 1499-1523 doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2011.10.027
[43] Nomura K, Koshizuka S, Oka Y, et al. Numerical analysis of droplet breakup behavior using particle method. Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 2001, 38(12): 1057-1064 doi: 10.1080/18811248.2001.9715136
[44] Zhang MY. Simulation of surface tension in 2D and 3D with smoothed particle hydrodynamics method. Journal of Computational Physics, 2010, 229(19): 7238-7259 doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2010.06.010
[45] Liu WB, Ma DJ, Zhang MY, et al. A new surface tension formulation in smoothed particle hydrodynamics for free-surface flows. Journal of Computational Physics, 2021, 439: 110203 doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2021.110203
[46] Zhang MY, Zhang H, Zheng LL. Simulation of droplet spreading, splashing and solidification using smoothed particle hydrodynamics method. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2008, 51(13): 3410-3419
[47] 苏铁熊, 马理强, 刘谋斌等. 基于光滑粒子动力学方法的液滴冲击固壁面问题数值模拟. 物理学报, 2013, 62(6): 64702-64707 (Su Tiexiong, Ma Liqiang, Liu Moubin, et al. A numerical analysis of drop impact on solid surfaces by using smoothed particle hydrodynamics method. Acta Physica Sinica, 2013, 62(6): 64702-64707 (in Chinese) doi: 10.7498/aps.62.064702 [48] Nugent S, Posch HA. Liquid drops and surface tension with smoothed particle applied mechanics. Physical Review E, 2000, 62(4): 4968-4975 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.62.4968
[49] Morris JP, Fox PJ, Zhu Y. Modeling Low reynolds number incompressible flows using SPH. Journal of Computational Physics, 1997, 136(1): 214-226 doi: 10.1006/jcph.1997.5776
[50] Gong K, Liu H, Wang BL. Water entry of a wedge based on SPH Model with an improved boundary treatment. Journal of Hydrodynamics, 2009, 21(6): 750-757 doi: 10.1016/S1001-6058(08)60209-7
[51] Bierbrauer F, Bollada PC, Phillips TN. A consistent reflected image particle approach to the treatment of boundary conditions in smoothed particle hydrodynamics. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2009, 198(41): 3400-3410
[52] Gómez-Gesteira M, Dalrymple RA. Using a three-dimensional smoothed particle hydrodynamics method for wave impact on a tall structure. Journal of Waterway, Port, Coastal, and Ocean Engineering, 2004, 130(2): 63-69 doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-950X(2004)130:2(63)
[53] Ferrand M, Laurence DR, Rogers BD, et al. Unified semi-analytical wall boundary conditions for inviscid, laminar or turbulent flows in the meshless SPH method. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Fluids, 2012, 71(4): 446-472
[54] Kulasegaram S, Bonet J, Lewis RW, et al. A variational formulation based contact algorithm for rigid boundaries in two-dimensional SPH applications. Computational Mechanics, 2004, 33(4): 316-325 doi: 10.1007/s00466-003-0534-0
[55] Mayrhofer A, Ferrand M, Kassiotis C, et al. Unified semi-analytical wall boundary conditions in SPH: analytical extension to 3-D. Numerical Algorithms, 2015, 68(1): 15-34 doi: 10.1007/s11075-014-9835-y
[56] Cummins SJ, Rudman M. An SPH projection method. Journal of Computational Physics, 1999, 152(2): 584-607 doi: 10.1006/jcph.1999.6246
[57] Ellero M, Serrano M, Español P. Incompressible smoothed particle hydrodynamics. Journal of Computational Physics, 2007, 226(2): 1731-1752 doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2007.06.019
[58] Hu XY, Adams NA. An incompressible multi-phase SPH method. Journal of Computational Physics, 2007, 227(1): 264-278 doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2007.07.013
[59] Szewc K, Pozorski J, Minier JP. Analysis of the incompressibility constraint in the smoothed particle hydrodynamics method. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 2012, 92(4): 343-369 doi: 10.1002/nme.4339
[60] Cornelis J, Ihmsen M, Peer A, et al. IISPH-FLIP for incompressible fluids. Computer Graphics Forum, 2014, 33(2): 255-262 doi: 10.1111/cgf.12324
[61] Aly AM. Modeling of multi-phase flows and natural convection in a square cavity using an incompressible smoothed particle hydrodynamics. International Journal of Numerical Methods for Heat & Fluid Flow, 2015, 25(3): 513-533
[62] Lind SJ, Stansby PK, Rogers BD. Incompressible–compressible flows with a transient discontinuous interface using smoothed particle hydrodynamics (SPH). Journal of Computational Physics, 2016, 309: 129-147 doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2015.12.005
[63] Koshizuka S. A particle method for incompressible viscous flow with fluid fragmentation. Computational Fluid Dynamics Journal, 1995, 4(1): 29-46
[64] Koshizuka S, Oka Y. Moving-particle semi-implicit method for fragmentation of incompressible fluid. Nuclear Science and Engineering, 1996, 123(3): 421-434 doi: 10.13182/NSE96-A24205
[65] Koshizuka S, Nobe A, Oka Y. Numerical analysis of breaking waves using the moving particle semi-implicit method. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Fluids, 1998, 26(7): 751-769 doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0363(19980415)26:7<751::AID-FLD671>3.0.CO;2-C
[66] Yoon HY, Koshizuka S, Oka Y. A Mesh-free numerical method for direct simulation of gas-liquid phase interface. Nuclear Science and Engineering, 1999, 133(2): 192-200 doi: 10.13182/NSE99-A2081
[67] Yoon HY, Koshizuka S, Oka Y. Direct calculation of bubble growth, departure, and rise in nucleate pool boiling. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 2001, 27(2): 277-298 doi: 10.1016/S0301-9322(00)00023-9
[68] Ataie-Ashtiani B, Farhadi L. A stable moving-particle semi-implicit method for free surface flows. Fluid Dynamics Research, 2006, 38(4): 241-256 doi: 10.1016/j.fluiddyn.2005.12.002
[69] Khayyer A, Gotoh H. Modified moving particle semi-implicit methods for the prediction of 2D wave impact pressure. Coastal Engineering, 2009, 56(4): 419-440 doi: 10.1016/j.coastaleng.2008.10.004
[70] Kondo M, Koshizuka S. Improvement of stability in moving particle semi-implicit method. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Fluids, 2011, 65(6): 638-654 doi: 10.1002/fld.2207
[71] Shao SD, Gotoh H. Turbulence particle models for tracking free surfaces. Journal of Hydraulic Research, 2005, 43(3): 276-289 doi: 10.1080/00221680509500122
[72] 张凯, 孙中国, 席光. 移动粒子半隐式法核函数特征对压力求解稳定性的影响. 西安交通大学学报, 2019, 53(9): 1-6 (Zhang Kai, Sun Zhongguo, Xi Guang. Influence of the kernel function characteristics on the stability of pressure solution of moving particle semi-implicit method. Journal of Xi'an Jiaotong University, 2019, 53(9): 1-6 (in Chinese) [73] Ge W, Li JH. Macro-scale pseudo-particle modeling for particle-fluid systems. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2001, 46(18): 1503-1507 doi: 10.1007/BF02900568
[74] Ge W, Li JH. Simulation of particle–fluid systems with macro-scale pseudo-particle modeling. Powder Technology, 2003, 137(1): 99-108
[75] Ma JS, Ge W, Wang XW, et al. High-resolution simulation of gas–solid suspension using macro-scale particle methods. Chemical Engineering Science, 2006, 61(21): 7096-7106 doi: 10.1016/j.ces.2006.07.042
[76] Xiong QG, Deng LJ, Wang W, et al. SPH method for two-fluid modeling of particle–fluid fluidization. Chemical Engineering Science, 2011, 66(9): 1859-1865 doi: 10.1016/j.ces.2011.01.033
[77] Xiong QG, Li B, Chen FG, et al. Direct numerical simulation of sub-grid structures in gas-solid flow−GPU implementation of macro-scale pseudo-particle modeling. Chemical Engineering Science, 2010, 65(19): 5356-5365 doi: 10.1016/j.ces.2010.06.035
[78] Monaghan JJ. Implicit SPH drag and dusty gas dynamics. Journal of Computational Physics, 1997, 138(2): 801-820 doi: 10.1006/jcph.1997.5846
[79] Laibe G, Price DJ. Dusty gas with smoothed particle hydrodynamics—I. Algorithm and Test Suite. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2012, 420(3): 2345-2364 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2966.2011.20202.x
[80] Hu XY, Adams NA. A constant-density approach for incompressible multi-phase SPH. Journal of Computational Physics, 2009, 228(6): 2082-2091 doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2008.11.027
[81] Shadloo MS, Yildiz M. Numerical modeling of Kelvin–Helmholtz instability using smoothed particle hydrodynamics. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 2011, 87(10): 988-1006 doi: 10.1002/nme.3149
[82] Shao SD. Incompressible smoothed particle hydrodynamics simulation of multifluid flows. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Fluids, 2012, 69(11): 1715-1735 doi: 10.1002/fld.2660
[83] Colagrossi A, Landrini M. Numerical simulation of interfacial flows by smoothed particle hydrodynamics. Journal of Computational Physics, 2003, 191(2): 448-475 doi: 10.1016/S0021-9991(03)00324-3
[84] Das AK, Das PK. Bubble evolution through submerged orifice using smoothed particle hydrodynamics: Basic formulation and model validation. Chemical Engineering Science, 2009, 64(10): 2281-2290 doi: 10.1016/j.ces.2009.01.053
[85] Szewc K, Tanière A, Pozorski J, et al. A study on application of smoothed particle hydrodynamics to multi-phase flows. International Journal of Nonlinear Sciences and Numerical Simulation, 2012, 13(6): 383
[86] 孙鹏楠, 李云波, 明付仁. 自由上浮气泡运动特性的光滑粒子流体动力学模拟. 物理学报, 2015, 64(17): 207-221 (Sun Pengnan, Li Yunbo, Ming Furen. Numerical simulation on the motion characteristics of freely rising bubbles using smoothed particle hydrodynamics method. Acta Physica Sinica, 2015, 64(17): 207-221 (in Chinese) [87] 王平平, 张阿漫, 孟子飞. 一种改进的适用于多相流SPH模拟的粒子位移修正算法. 科学通报, 2020, 65(8): 729-739 (Wang Pingping, Zhang Aman, Meng Zifei. An improved particle shifting algorithm for multiphase flows in SPH method. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2020, 65(8): 729-739 (in Chinese) doi: 10.1360/TB-2019-0540 [88] Akbari H. An improved particle shifting technique for incompressible smoothed particle hydrodynamics methods. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Fluids, 2019, 90(12): 603-631 doi: 10.1002/fld.4737
[89] Akinci N, Ihmsen M, Akinci G, et al. Versatile rigid-fluid coupling for incompressible SPH. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2012, 31(4): 1-8
[90] Tofighi N, Ozbulut M, Rahmat A, et al. An incompressible smoothed particle hydrodynamics method for the motion of rigid bodies in fluids. Journal of Computational Physics, 2015, 297: 207-220 doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2015.05.015
[91] Fourtakas G, Rogers BD. Modelling multi-phase liquid-sediment scour and resuspension induced by rapid flows using Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics (SPH) accelerated with a Graphics Processing Unit (GPU). Advances in Water Resources, 2016, 92: 186-199 doi: 10.1016/j.advwatres.2016.04.009
[92] Potapov AV, Hunt ML, Campbell CS. Liquid–solid flows using smoothed particle hydrodynamics and the discrete element method. Powder Technology, 2001, 116(2): 204-213
[93] Huang YJ, Nydal OJ. Coupling of discrete-element method and smoothed particle hydrodynamics for liquid-solid flows. Theoretical and Applied Mechanics Letters, 2012, 2(1): 12002 doi: 10.1063/2.1201202
[94] El Shamy U, Sizkow SF. Coupled smoothed particle hydrodynamics-discrete element method simulations of soil liquefaction and its mitigation using gravel drains. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 2021, 140: 106460 doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2020.106460
[95] Robb DM, Gaskin SJ, Marongiu J. SPH-DEM model for free-surface flows containing solids applied to river ice jams. Journal of Hydraulic Research, 2016, 54(1): 27-40 doi: 10.1080/00221686.2015.1131203
[96] Liu L, Zhang P, Xie P, et al. Coupling of dilated polyhedral DEM and SPH for the simulation of rock dumping process in waters. Powder Technology, 2020, 374: 139-151 doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2020.06.095
[97] Ji SY, Chen XD, Liu L, et al. Coupled DEM-SPH method for interaction between dilated polyhedral particles and fluid. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2019, 2019: 4987801
[98] Polwaththe-Gallage H, Saha SC, Sauret E, et al. A coupled SPH-DEM approach to model the interactions between multiple red blood cells in motion in capillaries. International Journal of Mechanics and Materials in Design, 2016, 12(4): 477-494 doi: 10.1007/s10999-015-9328-8
[99] 陈飞国, 葛蔚. 耦合拟颗粒模型和光滑粒子流体动力学模拟气液流动(内部报告). 北京: 中国科学院过程工程研究所, 2021 (Chen Feiguo, Ge Wei. Numerical modeling for gas-liquid flow with pseudo-particle model and smoothed particle hydrodynamics (Internal Report). Beijing: Institute of Process Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2021 (in Chinese))
[100] Ge W, Ma JS, Zhang JY, et al. Particle methods for multi-scale simulation of complex flows. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2005, 50(11): 1057-1069 doi: 10.1360/04wb0108
[101] Ge W, Li JH. Macro-scale phenomena reproduced in microscopic systems--pseudo-particle modeling of fluidization. Chemical Engineering Science, 2003, 58(8): 1565-1585 doi: 10.1016/S0009-2509(02)00673-5
[102] Marrone S, Di Mascio A, Le Touzé D. Coupling of smoothed particle hydrodynamics with finite volume method for free-surface flows. Journal of Computational Physics, 2016, 310: 161-180 doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2015.11.059
[103] Napoli E, De Marchis M, Gianguzzi C, et al. A coupled finite volume–smoothed particle hydrodynamics method for incompressible flows. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2016, 310: 674-693 doi: 10.1016/j.cma.2016.07.034
[104] Deng LJ, Liu YN, Wang W, et al. A two-fluid smoothed particle hydrodynamics (TF-SPH) method for gas–solid fluidization. Chemical Engineering Science, 2013, 99: 89-101 doi: 10.1016/j.ces.2013.05.047
[105] Feng Y, Wang JM, Liu FH. Numerical simulation of single particle acceleration process by SPH coupled FEM for abrasive waterjet cutting. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2012, 59(1): 193-200
[106] Zhang ZL, Walayat K, Chang JZ, et al. Meshfree modeling of a fluid-particle two-phase flow with an improved SPH method. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 2018, 116(8): 530-569 doi: 10.1002/nme.5935
[107] Fourey G, Hermange C, Le Touzé D, et al. An efficient FSI coupling strategy between smoothed particle hydrodynamics and finite element methods. Computer Physics Communications, 2017, 217: 66-81 doi: 10.1016/j.cpc.2017.04.005
[108] Zhang ZC, Qiang HF, Gao WR. Coupling of smoothed particle hydrodynamics and finite element method for impact dynamics simulation. Engineering Structures, 2011, 33(1): 255-264 doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2010.10.020
[109] Long T, Huang C, Hu D, et al. Coupling edge-based smoothed finite element method with smoothed particle hydrodynamics for fluid structure interaction problems. Ocean Engineering, 2021, 225: 108772 doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2021.108772
[110] Long T, Yang PY, Liu MB. A novel coupling approach of smoothed finite element method with SPH for thermal fluid structure interaction problems. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2020, 174: 105558 doi: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2020.105558
[111] Chen JK, Beraun JE, Jih CJ. An improvement for tensile instability in smoothed particle hydrodynamics. Computational Mechanics, 1999, 23(4): 279-287 doi: 10.1007/s004660050409
[112] Tartakovsky AM, Meakin P. A smoothed particle hydrodynamics model for miscible flow in three-dimensional fractures and the two-dimensional Rayleigh-Taylor instability. Journal of Computational Physics, 2005, 207(2): 610-624 doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2005.02.001
[113] Liu MB, Xie WP, Liu GR. Modeling incompressible flows using a finite particle method. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 2005, 29(12): 1252-1270 doi: 10.1016/j.apm.2005.05.003
[114] Liu MB, Liu GR. Restoring particle consistency in smoothed particle hydrodynamics. Applied Numerical Mathematics, 2006, 56(1): 19-36 doi: 10.1016/j.apnum.2005.02.012
[115] Zhang ZL, Liu MB. A decoupled finite particle method for modeling incompressible flows with free surfaces. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 2018, 60: 606-633 doi: 10.1016/j.apm.2018.03.043
[116] Schuessler I, Schmitt D. Comments on smoothed particle hydrodynamics. Astronomy and Astrophysics, 1981, 97: 373-379
[117] Swegle JW, Hicks DL, Attaway SW. Smoothed particle hydrodynamics stability analysis. Journal of Computational Physics, 1995, 116(1): 123-134 doi: 10.1006/jcph.1995.1010
[118] Monaghan JJ. SPH without a tensile instability. Journal of Computational Physics, 2000, 159(2): 290-311 doi: 10.1006/jcph.2000.6439
[119] Sun PN, Colagrossi A, Marrone S, et al. Multi-resolution delta-plus-SPH with tensile instability control: Towards high Reynolds number flows. Computer Physics Communications, 2018, 224: 63-80 doi: 10.1016/j.cpc.2017.11.016
[120] Sun PN, Colagrossi A, Marrone S, et al. The δplus-SPH model: Simple procedures for a further improvement of the SPH scheme. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2017, 315: 25-49 doi: 10.1016/j.cma.2016.10.028
[121] Antuono M, Colagrossi A, Marrone S. Numerical diffusive terms in weakly-compressible SPH schemes. Computer Physics Communications, 2012, 183(12): 2570-2580 doi: 10.1016/j.cpc.2012.07.006
[122] Xu ZJ, Meakin P, Tartakovsky AM. Diffuse-interface model for smoothed particle hydrodynamics. Physical Review E, 2009, 79(3): 36702 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.79.036702
[123] Monaghan JJ. Smoothed particle hydrodynamic simulations of shear flow. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2006, 365(1): 199-213 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2966.2005.09704.x
[124] Tartakovsky AM, Panchenko A. Pairwise force smoothed particle hydrodynamics model for multiphase flow: Surface tension and contact line dynamics. Journal of Computational Physics, 2016, 305: 1119-1146 doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2015.08.037
[125] Monaghan JJ. On the problem of penetration in particle methods. Journal of Computational Physics, 1989, 82(1): 1-15 doi: 10.1016/0021-9991(89)90032-6
[126] Cui XD, Habashi WG, Casseau V. MPI parallelisation of 3D multiphase smoothed particle hydrodynamics. International Journal of Computational Fluid Dynamics, 2020, 34(7-8): 610-621 doi: 10.1080/10618562.2020.1785436
[127] Plimpton S, Attaway S, Hendrickson B, et al. Parallel transient dynamics simulations: Algorithms for contact detection and smoothed particle hydrodynamics. Journal of Parallel and Distributed Computing, 1998, 50(1): 104-122
[128] Morikawa D, Senadheera H, Asai M. Explicit incompressible smoothed particle hydrodynamics in a multi-GPU environment for large-scale simulations. Computational Particle Mechanics, 2021, 8(3): 493-510 doi: 10.1007/s40571-020-00347-0
[129] Schäfer CM, Wandel OJ, Burger C, et al. A versatile smoothed particle hydrodynamics code for graphic cards. Astronomy and Computing, 2020, 33: 100410 doi: 10.1016/j.ascom.2020.100410
[130] Crespo AC, Dominguez JM, Barreiro A, et al. GPUs, a new tool of acceleration in CFD: Efficiency and reliability on smoothed particle hydrodynamics methods. Plos One, 2011, 6(6): e20685 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0020685
[131] Rustico E, Bilotta G, Hérault A, et al. Advances in multi-GPU smoothed particle hydrodynamics simulations. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2014, 25(1): 43-52 doi: 10.1109/TPDS.2012.340
[132] Crespo AJC, Domínguez JM, Rogers BD, et al. DualSPHysics: Open-source parallel CFD solver based on smoothed particle hydrodynamics (SPH). Computer Physics Communications, 2015, 187: 204-216 doi: 10.1016/j.cpc.2014.10.004
[133] Valdez-Balderas D, Domínguez JM, Rogers BD, et al. Towards accelerating smoothed particle hydrodynamics simulations for free-surface flows on multi-GPU clusters. Journal of Parallel and Distributed Computing, 2013, 73(11): 1483-1493 doi: 10.1016/j.jpdc.2012.07.010
[134] Domínguez JM, Crespo AJC, Valdez-Balderas D, et al. New multi-GPU implementation for smoothed particle hydrodynamics on heterogeneous clusters. Computer Physics Communications, 2013, 184(8): 1848-1860 doi: 10.1016/j.cpc.2013.03.008
[135] Ming FR, Zhang AM, Cheng H, et al. Numerical simulation of a damaged ship cabin flooding in transversal waves with smoothed particle hydrodynamics method. Ocean Engineering, 2018, 165: 336-352 doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2018.07.048
[136] Harada T, Koshizuka S, Kawaguchi Y. Smoothed particle hydrodynamics on GPUs. Computer Graphics International, SBC Petropolis, 2007
-
期刊类型引用(16)
1. 安栋,范金颍,宋义敏,许海亮,罗廷运. 吸能液压支架立柱防冲性能模拟及试验. 煤炭科学技术. 2025(04): 393-400 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 柴泽琳,周存龙,齐浩,郭瑞,李春阳. 抛丸和抛浆对金属基体表面完整性的影响对比. 塑性工程学报. 2024(02): 97-104 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 柴泽琳,周存龙,郭瑞,姜正义. 抛浆除鳞工艺中氧化皮去除模型研究. 湖南大学学报(自然科学版). 2024(04): 114-122 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 徐义祥,杨刚,邢钰林,胡德安. 上浮气泡与自由表面相互作用的ISPH-FVM耦合方法模拟. 力学学报. 2024(05): 1261-1270 .  本站查看
本站查看
5. 赵实柱,郎翠莲. 考虑传质过程的化工反应器多相流体动力学优化. 化学工程与装备. 2024(09): 37-39 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 张康康,尹训强,徐舒桐. 池式快堆堆本体中液体晃动效应的研究进展. 世界地震工程. 2024(04): 179-189 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 王青芬,孙伟成,沈政昌,陈强,张明,段莉莉. 搅拌理论技术在选矿领域的应用及发展. 有色金属(冶炼部分). 2024(11): 76-104 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 洪寅,刘看,武毅,吴艳青,杨秀峰. 固体推进剂药浆立式混合过程SPH方法研究. 含能材料. 2024(11): 1162-1173 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 黄晓婷,孙鹏楠,吕鸿冠. 考虑气体压缩性的多相δ~+-SPH模型及应用. 中国造船. 2024(06): 235-243 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 苏杰,周长江,姜琛. 基于IS–FEM的颗粒曳力系数计算与试验验证. 力学与实践. 2023(01): 119-129 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 闫晓惠,尚孜涵,刘建卫,陈小强. 基于SPH建模仿真技术的“城市供排水工程”课程教学改革. 西部素质教育. 2023(19): 144-147 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 李辉,谢文会,吕柏呈,高巍,徐明强. 中国南海波浪作用下悬浮隧道运动响应研究. 船舶工程. 2023(09): 160-165 .  百度学术
百度学术
13. 孟子飞,张阿漫,王平平,房祥丽. 基于目标本质无振荡重构的无网格SPH方法及其应用研究. 中国科学:物理学 力学 天文学. 2022(10): 123-134 .  百度学术
百度学术
14. 姚学昊,陈丁,武立伟,黄丹. 流固耦合破坏分析的多分辨率PD-SPH方法. 力学学报. 2022(12): 3333-3343 .  本站查看
本站查看
15. 王璐,徐绯,杨扬. 完全拉格朗日SPH在冲击问题中的改进和应用. 力学学报. 2022(12): 3297-3309 .  本站查看
本站查看
29. 江红祥,赵慧贺,刘送永,李洪盛. 磨料射流冲击割缝岩石性能影响因素分析. 振动.测试与诊断. 2022(03): 564-571+621-622 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(14)



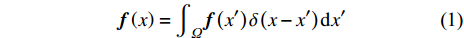
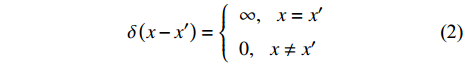
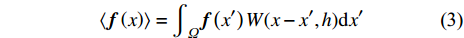
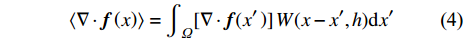
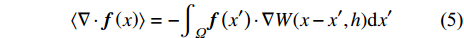

 下载:
下载: