引 言
被动隔振在工程领域中得到了广泛的应用. 被动隔振器的基本元素是刚度和阻尼[1-2]. 近年来,非线性隔振器由于具有传统线性隔振器无法比拟的特定优点而得到各国学者的关注. Ibrahim[3]对多种不同类型的非线性隔振器进行了综述. 曹登庆等[4]则总结了近年来大型柔性航天器中的动力学建模和振动控制进展. Carrella等[5]和Kovacic等[6]利用谐波平衡法对一类具有准零刚度的隔振系统的动力学特性进行了研究,其隔振带宽比线性隔振器更优. Mizuno等[7]、Zhou等[8]、Carrella等[9]、Zhu等[10]在隔振器中引入(电)磁刚度,使此类隔振器具有高静刚度和低动刚度的特点. Le等[11]则使用气动装置模拟高静态低动态刚度隔振系统,并进行了试验研究. Sun等[12-13]则对基于结构设计,针对剪刀形状的非线性隔振器和系统隔振带宽进行了研究. Araki等[14]则从理论和实验上对具有分段恒定恢复力的隔振器进行了研究. 高雪等[15]对一类分段非光滑隔振系统进行了建模研究.Lu等[16]不仅对近期的非线性被动隔振器进行了进展综述,而且还使用非线性刚度对双层隔振系统[17]进行了了理论和试验的研究.
众所周知,阻尼可以大幅减小系统共振响应,在隔振器中具有重要作用. Ruzicka和Derby[18]的专著对各种阻尼形式对隔振器的影响进行了详细论述. 有些隔振器可以在刚度和阻尼上均表现出非线性.Ravindra和Mallik[19-20]理论上研究了同时具有刚度和阻尼非线性的隔振器动力学响应和性能,给出了平方、立方阻尼对系统动力学特性的影响规律,总结了具有达芬型刚度、库仑阻尼和黏滞阻尼相结合的隔振器的性能.Thaijaroen等[21]研究了非线性橡胶阻尼隔振器的隔振性能,其摩擦建模采用光滑——非光滑模型.Yang等[22]建立了具有线性黏性阻尼、平方阻尼和干摩擦阻尼的隔振器对复杂非线性耦合隔振器进行了研究.Peng等[23-24]提出了一种反对称阻尼隔振器,并利用输出频率响应函数得到了系统的传递率,结果表明,引入非线性反对称阻尼的隔振器减小了共振响应,并且没有提高高频时的振动传递率,优于使用线性阻尼的隔振器. Peng等[25]、Kovacic等[26]分别使用谐波平衡法和平均法对立方阻尼隔振器进行了研究,结果表明立方阻尼隔振器只有在某些特殊情况下才具有优点. López等[27]在研究带摩擦阻尼的环阻尼器时,提出了一个简单的解析模型.Berger等[28]总结了动态系统仿真的摩擦建模方法.Stein等[29]采用现象学方法对振动系统与线性黏性摩擦阻尼和干摩擦阻尼耦合进行摩擦阻尼建模.Zhao等[30]提出了一种新型干摩擦阻尼器,并讨论了它在建筑减振中的作用.Tadjbakhsh等[31]同样对一类非线性摩擦阻尼器进行了研究,其中摩擦力和位移呈线性关系,这样对提高隔振效果有很大帮助.Ferri等[32-33]以及Whiteman等[34]也对类似的摩擦阻尼进行了研究,而且还引入了负黏性阻尼的概念.Tang等[35]基于线性隔振器几何布置来获取阻尼非线性,对比了两种非线性阻尼装置的性能.
本文通过采用传统摩擦阻尼器的几何非线性来实现对阻尼力的控制,使系统的摩擦阻尼变成与位移相关,当相对位移增大时,摩擦力也增大,从而使耗能变大.该隔振器的优势在于可以在共振时提供大阻尼控制共振峰,而在高频的、非共振区提供小阻尼,从而保持高频振动衰减能力.
1 摩擦阻尼和隔振系统建模
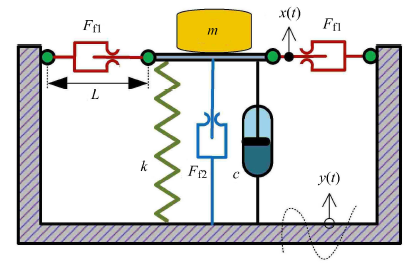
本文所用的隔振系统模型如图1所示,隔振对象的质量为M,垂向弹簧刚度系数为k,垂向线性黏性阻尼系数为c,垂向摩擦阻尼器的库伦摩擦力为常值$F_{{\rm f}2}$,在水平方向上,隔振系统还布置两个对称的摩擦阻尼器,其库伦摩擦力为$F_{{\rm f}1}$.
图 1
图 1
基于几何非线性摩擦阻尼的隔振系统原理图
Fig.1
Schematic of the vibration isolation system with geometric nonlinear friction damping
质量块与运动基座的相对位移定义为$z = x-y$,则水平摩擦阻尼器在垂直方向提供的力可以表示为
在$z / L \leqslant 0.2$情况下,阻尼力可以近似为
由方程(2)可以看出水平安装的摩擦阻尼器可以在垂直方向上提供摩擦力,在相对位移不是太大的情况下,阻尼力与相对位移成正比.
如图 1所示,如果去除水平摩擦阻尼器,系统变为经典库仑型摩擦阻尼隔振器. 基础激励作用下,系统的运动微分方程为
式中,$z = x-y$为相对位移,$y = y_0 \sin \left( {\omega t} \right)$为基础激励,方程(3)可以改写为无量纲形式
式中,$\omega _n = \sqrt {k/m}$为系统固有频率,$\zeta = c / 2\sqrt {mk}$为线性黏性阻尼比,$\lambda _1 =F_{{\rm f}2} / (Lk)$为恒定摩擦系数,$\lambda _2 = 2F_{{\rm f}1} / (kL^2)$为可变摩擦系数,$u = z / L$为无量纲相对位移,$\tilde {y}_0 = y_0 / L$为无量纲的基础激励位移,$\Omega = \omega / \omega _n$为无量纲频率比,$\tau = \omega _n t$为无量纲时间, `$'$'表示对时间$\tau$的微分.
用谐波平衡法求方程(4)的稳态响应近似解, 假设稳态响应近似解形式如下
将方程(5)代入方程(4)可得
对式(6)进行求解时,使用傅里叶展开对sgn函数进行简化,有
将式(7)代入到式(6),展开并使相同的谐波系数相等,可得
联合方程(8)和方程(9),可得
本文所关心的是摩擦阻尼,通过设定$\zeta = 0$,可以得到系统的无量纲振幅如下
相对传递率和绝对传递率是评估被动隔振器的两个非常重要的指标.相对传递率定义为质量块相对基座之间的位移幅值与输入激励幅值的比值,文中表示为$T_{\rm r} = u_0 / y_0$;绝对传递率表示被隔振对象的绝对位移相对于基础激励幅值的比,本文中绝对传递率表示为$T_{\rm a} = \left| {x\left( t \right) / y_0 } \right|$,对于本文提出的非线性隔振器,其$T_{\rm a}$表达式可以进一步写为
通过上式可得到绝对和相对位移传递率,进一步可绘制不同阻尼$\lambda _1$和$\lambda _2$下的位移传递率曲线.
2 仿真与结果
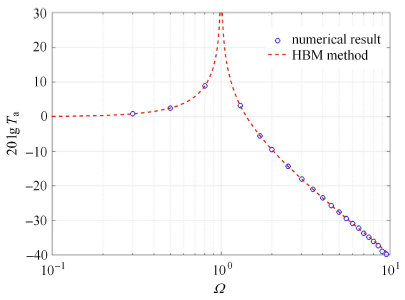
2.1 HBM解法的数值验证
图2
图2
$\lambda _1 = 0$,$\lambda _2 = 0$时谐波平衡法和数值解对比
Fig.2
Results comparison when$\lambda _1 = 0$,$\lambda _2 = 0$ for HBM and numerical method
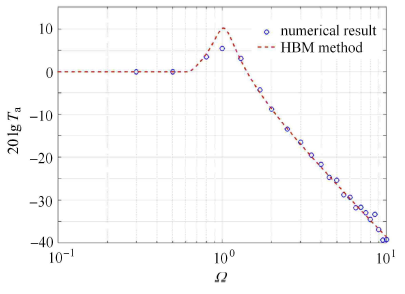
图3
图3
$\lambda _1 = 0.3$,$\lambda _2 = 0.5$时谐波平衡法和数值解对比
Fig.3
Results comparison when$\lambda _1 = 0.3$,$\lambda _2 = 0.5$ for HBM and numerical method
从图中可以看出,当线性黏性阻尼比$\zeta = 0$时,在$\lambda _1 = 0$,$\lambda _2 = 0$时,使用数值方法和谐波平衡法求解方程(4)的结果在整个振动频段完全重合;而在$\lambda _1 = 0.3$,$\lambda _2 = 0.5$时,使用数值方法求解的结果在共振区比使用谐波平衡法 略低,在低频区和高频区结果一致.这是因为,使用谐波平衡法求解时将摩擦阻尼进行了简化,在一个周期内其阻尼值偏小,因此,可以使用谐波平衡法对方程(4)进行求解.
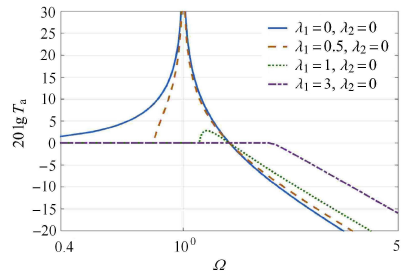
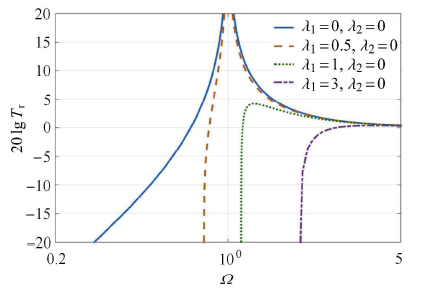
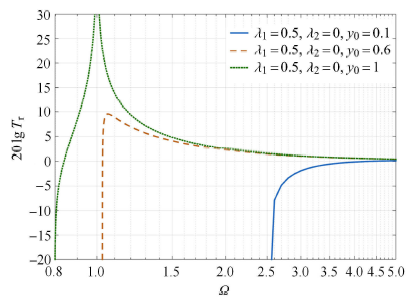
2.2 $\lambda _1$对系统传递率的影响
图4
图4
$\lambda _2 = 0$时$\lambda _1$对隔振系统绝对传递率影响图
Fig.4
Effect of$\lambda _1$ on the absolute transmissibility of the vibration isolation system when$\lambda _2 = 0$
图5
图5
$\lambda _2 = 0$时$\lambda _1$对隔振系统相对传递率影响图
Fig.5
Effect of$\lambda _1$ on the relative transmissibility of the vibration isolation system when$\lambda _2 = 0$
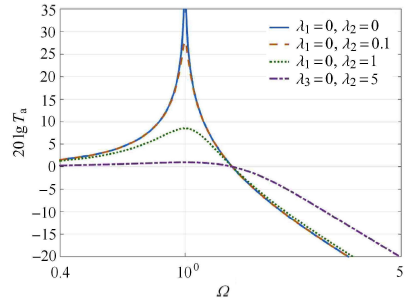
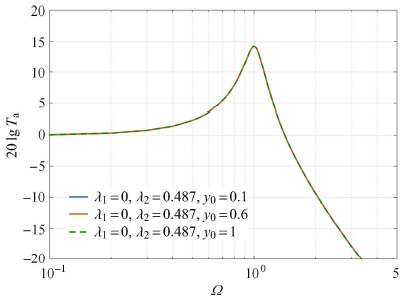
2.3$\lambda _2$对系统传递率的影响
图6
图6
$\lambda _1 = 0$时$\lambda _2$对系统绝对传递率影响图
Fig.6
Effect of$\lambda _{2}$ on the absolute transmissibility of the vibration isolation system when$\lambda _{1} = 0$
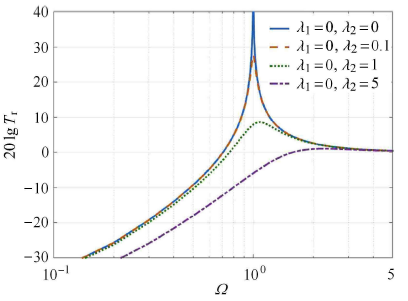
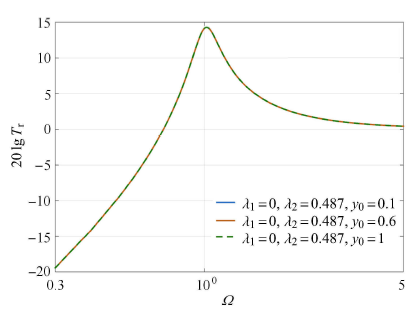
图7
图7
$\lambda _1 = 0$时$\lambda _2$对系统相对传递率影响图
Fig.7
Effect of$\lambda _{2}$ on the relative transmissibility of the vibration isolation system when$\lambda _{1} = 0$
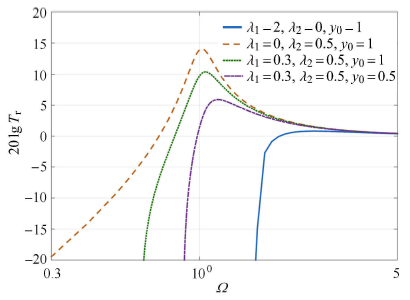
2.4 几何非线性系统和线性系统的对比
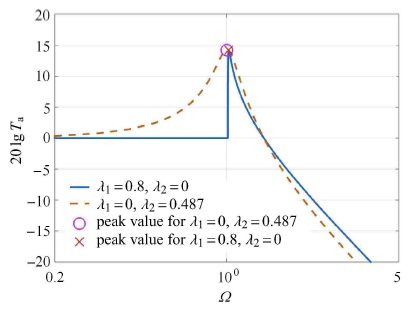
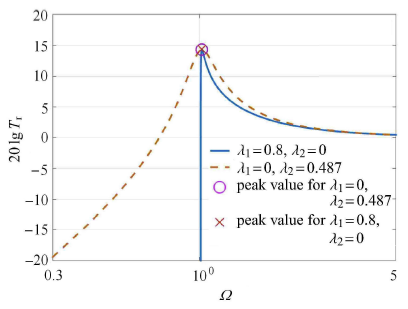
本文研究的摩擦阻尼通过几何非线性的形式布置,对于恒定摩擦力隔振系统,如果阻尼比很大,在低频振动时,隔振器相对运动可忽略,摩擦阻尼器处于"锁住"状态,而单纯几何非线性摩擦阻尼系统则可以有效避免系统"锁住".为进一步比较两种系统对系统传递率的影响,首先假设有一典型固定摩擦阻尼隔振系统,其设定$\lambda _1 =0.8$,$\lambda _2 = 0$,先获取仅有恒定摩擦阻尼隔振系统的传递率.随后,在设有一组单纯几何非线性摩擦阻尼系统,此系统的共振峰和恒定摩擦阻尼系统共振峰相等.由方程(11)可求得此时几何非线性摩擦阻尼系统的阻尼系数,有$\lambda _1 = 0$,$\lambda _2 = 0.487$,两个系统具有相同共振峰时的绝对传递率和相对传递率如图8和图9所示,可以看出与传统恒定摩擦阻尼隔振系统相比,单纯几何非线性摩擦阻尼系统不仅可以在低频段克服"锁住"状态,而且在共振峰相等的前提下,能够保持更优的高频衰减效果.
图8
图8
相同共振峰下两种系统绝对位移传递率比较
Fig.8
Comparison of the absolute transmissibility for the two kinds of vibration isolation system with the same resonance factor
图9
图9
相同共振峰下两种系统相对位移传递率比较
Fig.9
Comparison of the relative transmissibility for the two kinds of vibration isolation system with the same resonance factor
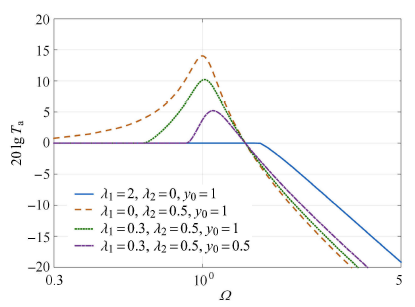
图10
图10
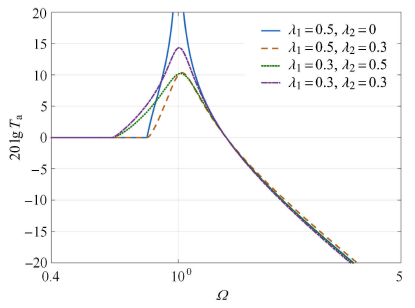
$\lambda _1$和$\lambda _2$组合参数对系统绝对传递率的影响
Fig.10
Effect of the combination of$\lambda _1$ and$\lambda _2$ on the absolute transmissibility of the nonlinear vibration isolation system
图11
图11
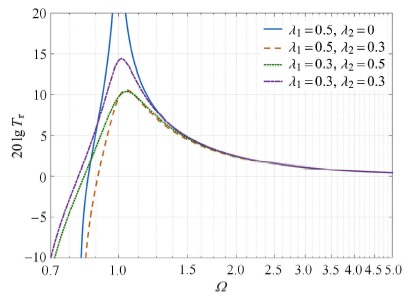
$\lambda _1$和$\lambda _2$组合参数对系统相对传递率的影响
Fig.11
Effect of the combination of$\lambda _1$ and$\lambda _2$ on the relative transmissibility of the nonlinear vibration isolation system
以恒定摩擦阻尼系统为对比标准,可得出几何非线性系统在隔振效果中的影响规律.首先,在恒定摩擦阻尼系统中引入弱非线性摩擦阻尼,不改变系统的"锁定"频率,但可显著降低共振峰值,且基本保持高频衰减效果.其次,在几何非线性摩擦阻尼系统中,增大几何非线性摩擦阻尼系数可以使得系统共振频率降低,且高频衰减效果基本保持不变.因此,在工程应用时,可以将固定摩擦阻尼和可变摩擦阻尼结合使用,这样,可以在不牺牲高频隔振效果的前提下,降低系统共振峰,抑制低频相对位移,而且避免隔振器在过大的恒定摩擦阻尼下的失效.
2.5 激励幅值对系统隔振效果影响
图12
图12
激励幅值对恒定摩擦阻尼系统绝对传递率的影响
Fig.12
Effect of the excitation amplitude on the absolute transmissibility of the constant friction vibration isolation system
图13
图13
激励幅值对恒定摩擦阻尼系统相对传递率的影响
Fig.13
Effect of the excitation amplitude on the relative transmissibility of the constant friction vibration isolation system
图14
图14
激励幅值对可变摩擦阻尼系统绝对传递率的影响
Fig.14
Effect of the excitation amplitude on the absolute transmissibility of the nonlinear friction vibration isolation system
图15
图15
激励幅值对可变摩擦阻尼系统相对传递率的影响
Fig.15
Effect of the excitation amplitude on the relative transmissibility of the nonlinear friction vibration isolation system
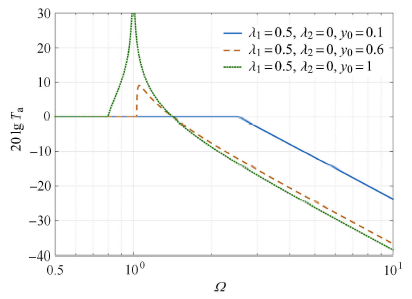
最后,为了进一步说明几何非线性摩擦阻尼的特性,先固定摩擦阻尼系数,此时隔振系统为无谐振峰隔振系统,期望的隔振效果如图16中实线所示,然而,若此时激励幅值降低,系统存在失效风险.对于同样的系统,若选择几何非线性隔振系统,可以明显避免隔振系统失效,但是需要明确的是,此时系统共振峰值增大.因此,在实际应用中,通过调整恒定摩擦阻尼系数和可变摩擦阻尼系数,这样,不仅可以在低频段克服隔振器"锁住"状态,减小谐振峰值,而且可以获得更好的高频隔振性能.
图16
图16
不同参数对系统绝对传递率的影响
Fig.16
Effect of the combination of system parameters on the absolute transmissibility of the vibration isolation system
图17
图17
不同参数对系统相对传递率的影响
Fig.17
Effect of the combination of system parameters on the relative transmissibility of the vibration isolation system
3 结 论
研究了几何非线性摩擦阻尼隔振系统的动力学特性,与传统的具有恒定摩擦力的隔振系统不同,本文通过对摩擦阻尼器的几何非线性布置,系统的摩擦阻尼与隔振系统的位移成正比,建立了系统的摩擦阻尼和受迫振动的数学模型,使用谐波平衡法求解动力学方程,获得了绝对传递率和相对传递率. 可以得出如下结论:
(1) 仅就引入几何非线性而言,变阻尼摩擦系数和恒定摩擦系数对绝对传递率和相对传递率的影响类似,即增大变摩擦阻尼系数使系统共振传递率变优而高频衰减变差;
(2) 由于变阻尼摩擦系统的摩擦力和位移相关,因此纯变阻尼摩擦系统无频率"锁定"现象,且该系统能在保持共振峰控制的同时,保持高频衰减;
(3) 与变阻尼摩擦系数相比,在小幅值激励的情况下,恒定摩擦阻尼系统对激励的隔振效果变差,隔振器应用频率范围变小,严重可导致隔振器失效;
(4)通过合理的参数选择,可以使几何非线性系统在共振传递率和高频衰减效果均优于恒定摩擦阻尼系统,同时可以显著避免因激励幅值过小时产生的"锁住"现象,提高系统的可靠性.
参考文献
Recent advances in nonlinear passive vibration isolators
The theory of nonlinear vibration isolation has witnessed significant developments due to pressing demands for the protection of structural installations, nuclear reactors, mechanical components, and sensitive instruments from earthquake ground motion, shocks, and impact loads. In view of these demands, engineers and physicists have developed different types of nonlinear vibration isolators. This article presents a comprehensive assessment of recent developments of nonlinear isolators in the absence of active control means. It does not deal with other means of linear or nonlinear vibration absorbers. It begins with the basic concept and features of nonlinear isolators and inherent nonlinear phenomena. Specific types of nonlinear isolators are then discussed, including ultra-low-frequency isolators. For vertical vibration isolation, the treatment of the Euler spring isolator is based on the post-buckling dynamic characteristics of the column elastica and axial stiffness. Exact and approximate analyses of axial stiffness of the post-buckled Euler beam are outlined. Different techniques of reducing the resonant frequency of the isolator are described. Another group is based on the Gospodnetic risch-Fay beam, which is free to slide on two supports. The restoring force of this beam resembles to a great extent the restoring roll moment of biased ships. The base isolation of buildings, bridges, and liquid storage tanks subjected to earthquake ground motion is then described. Base isolation utilizes friction elements, laminated-rubber bearings, and the friction pendulum. Nonlinear viscoelastic and composite material springs, and smart material elements are described in terms of material mechanical characteristics and the dependence of their transmissibility on temperature and excitation amplitude. The article is closed by conclusions, which highlight resolved and unresolved problems and recommendations for future research directions.
大型柔性航天器动力学与振动控制研究进展
颗粒材料在高应力环境下会发生颗粒破碎现象,颗粒破碎不仅影响颗粒材料的力学特性,同时与大量工程问题密切相关.目前的相关研究主要集中在唯象地描述颗粒破碎的演化以及破碎对力学特性的影响层面,对颗粒破碎演化路径的物理机制研究较少.本文基于热力学框架,采用细观力学中细观-宏观的均匀化方法推导了颗粒体系弹性能和破碎能量耗散,并在最大能量耗散的假设下,在热力学框架内,建立了理想化的无摩擦球体颗粒等向压缩过程的弹性-破碎模型,阐述了颗粒材料破碎演化路径细观热力学机制.由于模型的推导不依赖任何唯象的经验公式,因此模型中包含的参数均有明确的物理意义.模型预测与前人试验结果对比表明,材料的初始级配对弹性压缩模量和破碎应力的影响并不相同:不同分形维数级配对应的弹性体变模量存在极大值,而破碎应力却随着分形维数的增大单调递增;颗粒破碎的演化符合最大能量耗散原理,且颗粒材料的压缩曲线可以分为弹性-破碎-拟弹性3个机制不同的阶段.
Advances in dynamics and vibration control of large scale flexible spacecraft
颗粒材料在高应力环境下会发生颗粒破碎现象,颗粒破碎不仅影响颗粒材料的力学特性,同时与大量工程问题密切相关.目前的相关研究主要集中在唯象地描述颗粒破碎的演化以及破碎对力学特性的影响层面,对颗粒破碎演化路径的物理机制研究较少.本文基于热力学框架,采用细观力学中细观-宏观的均匀化方法推导了颗粒体系弹性能和破碎能量耗散,并在最大能量耗散的假设下,在热力学框架内,建立了理想化的无摩擦球体颗粒等向压缩过程的弹性-破碎模型,阐述了颗粒材料破碎演化路径细观热力学机制.由于模型的推导不依赖任何唯象的经验公式,因此模型中包含的参数均有明确的物理意义.模型预测与前人试验结果对比表明,材料的初始级配对弹性压缩模量和破碎应力的影响并不相同:不同分形维数级配对应的弹性体变模量存在极大值,而破碎应力却随着分形维数的增大单调递增;颗粒破碎的演化符合最大能量耗散原理,且颗粒材料的压缩曲线可以分为弹性-破碎-拟弹性3个机制不同的阶段.
Static analysis of a passive vibration isolator with quasi-zero stiffness characteristic
The frequency range over which a linear passive vibration isolator is effective, is often limited by the mount stiffness required to support a static load. This can be improved upon by employing nonlinear mounts incorporating negative stiffness elements configured in such a way that the dynamic stiffness is much less than the static stiffness. Such nonlinear mounts are used widely in practice, but rigorous analysis, and hence a clear understanding of their behaviour is not readily available in the literature. In this paper, a simple system comprising a vertical spring acting in parallel with two oblique springs is studied. It is shown that there is a unique relationship between the geometry and the stiffness of the springs that yields a system with zero dynamic stiffness at the static equilibrium position. The dynamic stiffness increases monotonically with displacement either side of the equilibrium position, and this is least severe when the oblique springs are inclined at an angle between approximately 48° and 57°. Finally, it is shown that the force–displacement characteristic of the system can be approximated by a cubic equation.
A study of a nonlinear vibration isolator with a quasi-zero stiffness characteristic
A vibration isolator consisting of a vertical linear spring and two nonlinear pre-stressed oblique springs is considered in this paper. The system has both geometrical and physical nonlinearity. Firstly, a static analysis is carried out. The softening parameter leading to quasi-zero dynamic stiffness at the equilibrium position is obtained as a function of the initial geometry, pre-stress and the stiffness of the springs. The optimal combination of the system parameters is found that maximises the displacement from the equilibrium position when the prescribed stiffness is equal to that of the vertical spring alone. It also satisfies the condition that the dynamic stiffness only changes slightly in the neighbourhood of the static equilibrium position. For these values, a dynamical analysis of the isolator under asymmetric excitation is performed to quantify the undesirable effects of the nonlinearities. It includes considering the possibilities of the appearance of period-doubling bifurcation and its development into chaotic motion. For this purpose, approximate analytical methods and numerical simulations accompanied with qualitative methods including phase plane plots, Poincar maps and Lyapunov exponents are used. Finally, the frequency at which the first period-doubling bifurcation appears is found and the effect of damping on this frequency determined.
Vibration isolation system using negative stiffness
A tunable high-static-low-dynamic stiffness vibration isolator
In this study, a novel vibration isolator is developed. The developed isolator possesses the characteristics of high-static ow-dynamic stiffness (HSLDS) and can act passively or semi-actively. The HSLDS property of the isolator is obtained by connecting a mechanical spring, in parallel with a magnetic spring that is constructed by a pair of electromagnets and a permanent magnet. The mechanical spring is a structural beam whose stiffness exhibits a hardening behavior. The stiffness of the magnetic spring can be positive or negative, depending on the polarity of the current to the electromagnets. A passive HSLDS isolator is obtained when the electromagnet current is zero. In the stiffness characterization study, the analytical model for each of the springs is established and the tuning parameters are identified. Using the stiffness models, the design optimization issues are investigated. In the experimental study, the effectiveness of the isolator for vibration isolation is tested. The analytical natural frequencies of the isolator are validated experimentally. The relationships between the displacement transmissibility and the exciting frequency are measured both under the passive mode and under the semi-active mode. The on-line tuning capability of the isolator is investigated.
On the design of a high-static-low-dynamic stiffness isolator using linear mechanical springs and magnets
The frequency range over which a linear passive vibration isolator is effective is often limited by the mount stiffness required to support a static load. This can be improved upon by incorporating a negative stiffness element in the mount such that the dynamic stiffness is much less than the static stiffness. In this case, it can be referred to as a high-static–low-dynamic stiffness (HSLDS) mount. This paper is concerned with a theoretical and experimental study of one such mount. It comprises two vertical mechanical springs between which an isolated mass is mounted. At the outer edge of each spring, there is a permanent magnet. In the experimental work reported here, the isolated mass is also a magnet arranged so that it is attracted by the other magnets. Thus, the combination of magnets acts as a negative stiffness counteracting the positive stiffness provided by the mechanical springs. Although the HSLDS suspension system will inevitably be nonlinear, it is shown that for small oscillations the mount considered here is linear. The measured transmissibility is compared with a comparable linear mass–spring–damper system to show the advantages offered by the HSLDS mount.
Vibration isolation using six degree-of-freedom quasi-zero stiffness magnetic levitation
In laboratories and high-tech manufacturing applications, passive vibration isolators are often used to isolate vibration sensitive equipment from ground-borne vibrations. However, in traditional passive isolation devices, where the payload weight is supported by elastic structures with finite stiffness, a design trade-off between the load capacity and the vibration isolation performance is unavoidable. Low stiffness springs are often required to achieve vibration isolation, whilst high stiffness is desired for supporting payload weight. In this paper, a novel design of a six degree of freedom (six-dof) vibration isolator is presented, as well as the control algorithms necessary for stabilising the passively unstable maglev system. The system applies magnetic levitation as the payload support mechanism, which realises inherent quasi-zero stiffness levitation in the vertical direction, and zero stiffness in the other five dofs. While providing near zero stiffness in multiple dofs, the design is also able to generate static magnetic forces to support the payload weight. This negates the trade-off between load capacity and vibration isolation that often exists in traditional isolator designs. The paper firstly presents the novel design concept of the isolator and associated theories, followed by the mechanical and control system designs. Experimental results are then presented to demonstrate the vibration isolation performance of the proposed system in all six directions.
Active pneumatic vibration isolation system using negative stiffness structures for a vehicle seat
In this paper, an active pneumatic vibration isolation system using negative stiffness structures (NSS) for a vehicle seat in low excitation frequencies is proposed, which is named as an active system with NSS. Here, the negative stiffness structures (NSS) are used to minimize the vibratory attraction of a vehicle seat. Owing to the time-varying and nonlinear behavior of the proposed system, it is not easy to build an accurate dynamic for model-based controller design. Thus, an adaptive intelligent backstepping controller (AIBC) is designed to manage the system operation for high-isolation effectiveness. In addition, an auxiliary control effort is also introduced to eliminate the effect of the unpredictable perturbations. Moreover, a radial basis function neural network (RBFNN) model is utilized to estimate the optimal gain of the auxiliary control effort. Final control input and the adaptive law for updating coefficients of the approximate series can be obtained step by step using a suitable Lyapunov function. Afterward, the isolation performance of the proposed system is assessed experimentally. In addition, the effectiveness of the designed controller for the proposed system is also compared with that of the traditional backstepping controller (BC). The experimental results show that the isolation effectiveness of the proposed system is better than that of the active system without NSS. Furthermore, the undesirable chattering phenomenon in control effort is quite reduced by the estimation mechanism. Finally, some concluding remarks are given at the end of the paper.
A nonlinear vibration isolator achieving high-static-low-dynamic stiffness and tunable anti-resonance frequency band
61A 2-D isolator with n-layer Scissor-Like Structure (SLS) is modeled and studied.61The system can achieve good isolation performance in two directions simultaneously.61An excellent anti-resonance frequency band can be achieved with tunable properties.61Experimental results validate the excellent nonlinear stiffness and damping performance.
Multi-direction vibration isolation with quasi-zero stiffness by employing geometrical nonlinearity
61A novel scissor-like structure is employed to construct a three-direction isolator.61The nonlinear stiffness and damping characteristics can be designed via structural parameters.61The system can achieve very excellent quasi-zero stiffness in vibration control in three directions.61The structural nonlinearity is an effective way for beneficial nonlinear stiffness/damping design.
Vertical vibration isolator having piecewise-constant restoring force
一类分段光滑隔振系统的非线性动力学设计方法
<p>分段光滑隔振系统是一类具备分段刚度或阻尼的非线性动力学系统,在振动控制领域中具有广泛代表性,诸如限位隔振系统、分级汽车悬挂等. 分段光滑的刚度或阻尼特性能够实现隔振系统的特定动力学性能及提升隔振性能,如抑制共振响应、提升共振区隔振性能等,但是亦会给隔振系统的动力学行为带来诸多不利影响. 以分段双线性分段光滑隔振系统为理论模型,系统研究了摒除不利于隔振的非线性动力学现象设计方法,包括幅值跳跃、周期运动的倍周期分岔等. 首先,利用平均法与奇异性理论给出了主共振频响曲线拓扑特征的完整拼图. 研究结果表明,参数空间分为4 个区域,其中2 个区域存在幅值跳跃,而其产生跳跃原因分别由鞍结分岔与擦边分岔所导致;基于此提出避免主共振跳跃的设计方法. 其次,建立了隔振有效区内周期运动的庞加莱映射,通过特征值分析给出了避免倍周期分岔发生的条件,证实增大阻尼可以抑制倍周期分岔的发生. 最后通过数值仿真分析了噪声对多稳态运动的影响. 研究结果发现在噪声影响下,分段光滑隔振系统的响应会在不同稳态间跃迁,非常不利于隔振. 因此,在完成跳跃与倍周期分岔的防治设计后,应采用数值仿真校验系统是否存在多稳态运动.</p>
Nonlinear dynamics design for piecewise smooth vibration isolation system
<p>分段光滑隔振系统是一类具备分段刚度或阻尼的非线性动力学系统,在振动控制领域中具有广泛代表性,诸如限位隔振系统、分级汽车悬挂等. 分段光滑的刚度或阻尼特性能够实现隔振系统的特定动力学性能及提升隔振性能,如抑制共振响应、提升共振区隔振性能等,但是亦会给隔振系统的动力学行为带来诸多不利影响. 以分段双线性分段光滑隔振系统为理论模型,系统研究了摒除不利于隔振的非线性动力学现象设计方法,包括幅值跳跃、周期运动的倍周期分岔等. 首先,利用平均法与奇异性理论给出了主共振频响曲线拓扑特征的完整拼图. 研究结果表明,参数空间分为4 个区域,其中2 个区域存在幅值跳跃,而其产生跳跃原因分别由鞍结分岔与擦边分岔所导致;基于此提出避免主共振跳跃的设计方法. 其次,建立了隔振有效区内周期运动的庞加莱映射,通过特征值分析给出了避免倍周期分岔发生的条件,证实增大阻尼可以抑制倍周期分岔的发生. 最后通过数值仿真分析了噪声对多稳态运动的影响. 研究结果发现在噪声影响下,分段光滑隔振系统的响应会在不同稳态间跃迁,非常不利于隔振. 因此,在完成跳跃与倍周期分岔的防治设计后,应采用数值仿真校验系统是否存在多稳态运动.</p>
非线性被动隔振的若干进展
工程中航空航天、船舶与海洋结构物及其上装备和精密仪器易受极端环境干扰和破坏,使得非线性隔振理论在近十年来迅猛发展;针对日益严峻的隔振和抗冲击等要求,工程师和科学家们已发展出各种不同的非线性隔振系统,包括主动、半主动、被动和复合隔振.利用非线性改善的被动隔振兼具传统被动隔振的鲁棒性和主动隔振的高效性成为振动控制领域的先进技术.本文主要综述了非线性隔振理论和应用的近十年进展,包括非线性隔振设计、建模、分析、仿真和实验.在隔振系统的构建中,既考虑了刚度非线性又考虑了阻尼非线性;动力学响应的研究中,既有确定性分析又有随机分析.首先提出了适用于非线性隔振系统改进的评价方式;其次综述了高静态低动态刚度隔振及其加强形式非线性阻尼加强和双层非线性隔振,混沌反控制技术、内共振影响、非线性能量阱应用等振动机制利用型隔振和非线性隔振功能材料.最后,对非线性隔振研究发展的热点和关键性问题进行了分析和展望.
Some recent progresses in nonlinear passive isolations of vibrations
工程中航空航天、船舶与海洋结构物及其上装备和精密仪器易受极端环境干扰和破坏,使得非线性隔振理论在近十年来迅猛发展;针对日益严峻的隔振和抗冲击等要求,工程师和科学家们已发展出各种不同的非线性隔振系统,包括主动、半主动、被动和复合隔振.利用非线性改善的被动隔振兼具传统被动隔振的鲁棒性和主动隔振的高效性成为振动控制领域的先进技术.本文主要综述了非线性隔振理论和应用的近十年进展,包括非线性隔振设计、建模、分析、仿真和实验.在隔振系统的构建中,既考虑了刚度非线性又考虑了阻尼非线性;动力学响应的研究中,既有确定性分析又有随机分析.首先提出了适用于非线性隔振系统改进的评价方式;其次综述了高静态低动态刚度隔振及其加强形式非线性阻尼加强和双层非线性隔振,混沌反控制技术、内共振影响、非线性能量阱应用等振动机制利用型隔振和非线性隔振功能材料.最后,对非线性隔振研究发展的热点和关键性问题进行了分析和展望.
Experimental investigation of a two-stage nonlinear vibration isolation system with high-static-low-dynamic stiffness
Performance of non-linear vibration isolators under harmonic excitation
Vibration isolators having non-linearity in both stiffness and damping terms are analyzed under harmonic excitations. Isolators with symmetric as well as asymmetric restoring forces are considered. The method of harmonic balance is used to obtain the steady state, harmonic response and transmissibility under both force and base excitations. The linear stability analysis of the solutions is presented. A parametric study indicating the effects of various types of damping is reported. The subharmonic and chaotic responses for the systems under investigation will be discussed in a subsequent paper.
Hard Duffing-type vibration isolator with combined coulomb and viscous damping
The steady-state, harmonic response of a vibration isolation system with a cubic, hard non-linear restoring force and combined Coulomb and viscous damping is presented. The results have been obtained by using the method of harmonic balance. It has been assumed that the motion is continuous without any stop. An anomalous jump in the response, similar to the one obtained in earlier studies on certain soft systems, is observed when the isolation system is subjected to a base excitation. Linear stability analysis is carried out to determine the status of the anomalous jump. The effect of the damping parameters on the jump in the response is investigated. Transmissibility curves are plotted for various parameter values to study the performance characteristics. The obtained results extend the previous works of Den Hartog and Ruzicka who considered a linear restoring element.
Nonlinear dynamic modelling of rubber isolators using six parameters based on parabolic spring, springpot, and smooth-slip friction element
A time-domain six-parameter model is adopted to simulate the vibration behaviour of rubber isolators over the frequency range of 0.05 25 Hz. The one-dimensional model working under constant preload and temperature is capable of producing force as a function of displacement excitation. The model consists of three components, including a nonlinear parabolic spring, a fractional-derivative-based springpot and a smooth-slip friction element. In order to obtain all required six parameters, a novel standard procedure is proposed based on a two-stage optimization method using two sets of data measured in both amplitude and frequency domains. A number of isolators with differences in shape, composition and mode of deformation are selected for study. The consistency of the proposed optimization method and the accuracy of the obtained model are verified by good agreements between measured and simulated results of stiffness and damping across the ranges of investigated displacement amplitudes and frequencies.
Dynamic transmissibility of a complex nonlinear coupling isolator
A mathematical model was developed for a complex nonlinear coupling isolator for attenuating vibration which coupled quadratic damping, viscous damping, Coulomb damping, and nonlinear spring forces. The approximate analytical solution for the dynamic transmissibility of the isolator was deduced by combining Fourier transforms and the harmonic balance method with deterministic excitation. The mathematical characteristics of the dynamic transmissibility were analyzed to illustrate the dynamic performance of the isolator. The analytical results show multiple solutions, especially the low-frequency attenuation characteristics below the resonance frequency. The results provide a theoretical basis for the design of nonlinear isolators.
The transmissibility of vibration isolators with a nonlinear antisymmetric damping characteristic
一类非线性隔振器振动传递特性分析
非线性输出频率响应函数是由Volterra级数发展而来的一个 新概念.对一类具有反对称阻尼特性的隔振器,通过该概念推导出了振动传递性与系统非线性参数之间的显式解析关系;进而系统地研究了非线性阻尼参数对隔振器 的力传递性能和位移传递性能的影响.研究结果表明,虽然非线性隔振器在受正弦信号激励下会出现高次倍频分量,但对于其传递性能的评估仍可简单地通过系统输 入和输出信号的基频分量之间的关系来衡量;另外,反对称非线性阻尼能够有效地抑制隔振器在共振区的力传递性和位移传递性,而在非共振区则基本无抑制效果. 研究结果对于具有反对称阻尼特性的隔振器的分析与设计具有重要意义.
Analysis on transmissibility for a class of nonlinear vibration isolators
非线性输出频率响应函数是由Volterra级数发展而来的一个 新概念.对一类具有反对称阻尼特性的隔振器,通过该概念推导出了振动传递性与系统非线性参数之间的显式解析关系;进而系统地研究了非线性阻尼参数对隔振器 的力传递性能和位移传递性能的影响.研究结果表明,虽然非线性隔振器在受正弦信号激励下会出现高次倍频分量,但对于其传递性能的评估仍可简单地通过系统输 入和输出信号的基频分量之间的关系来衡量;另外,反对称非线性阻尼能够有效地抑制隔振器在共振区的力传递性和位移传递性,而在非共振区则基本无抑制效果. 研究结果对于具有反对称阻尼特性的隔振器的分析与设计具有重要意义.
Study of the effects of cubic nonlinear damping on vibration isolations using Harmonic Balance Method
In the present study, Harmonic Balance Method (HBM) is applied to investigate the performance of passive vibration isolators with cubic nonlinear damping. The results reveal that introducing either cubic nonlinear damping or linear damping could significantly reduce both the displacement transmissibility and the force transmissibility of the isolators over the resonance region. However, at the non-resonance region where frequency is lower than the resonant frequency, both the linear damping and the cubic nonlinear damping have almost no effect on the isolators. At the non-resonance region with higher frequency, increasing the linear damping has almost no effects on the displacement transmissibility but could raise the force transmissibility. In addition, the influence of the cubic nonlinear damping on the isolators is dependent on the type of the disturbing force. If the strength of the disturbing force is constant and independent of the excitation frequency, then the effect of cubic nonlinear damping on both the force and displacement transmissibility would be negligible. But, when the strength of the disturbing force is dependent of the excitation frequency, increasing the cubic nonlinear damping could slightly reduce the relative displacement transmissibility and increase the absolute displacement transmissibility but could significantly increase the force transmissibility. These conclusions are of significant importance in the analysis and design of nonlinear passive vibration isolators. [All rights reserved Elsevier].
On the relative and absolute transmissibility of a vibration isolation system subjected to base excitation
//In this paper a one-degree of freedom passive vibration isolator system which is subject to harmonic base excitation is analyzed. The isolator is modeled as a parallel combination of a stiffness and damping element with cubic non-linearity. The method of averaging is used to obtain the steady-state harmonic response. A parametric analysis is conducted in order to investigate the influence of the system parameters on the relative and absolute transmissibility of the system from the viewpoint of possible improvement of the transmissibility of a system with linear viscous damping. .
Energy dissipation of a friction damper
In this paper the energy dissipated through friction is analysed for a type of friction dampers used to reduce squeal noise from railway wheels. A one degree-of-freedom system is analytically studied. First the existence and stability of a periodic solution are demonstrated and then the energy dissipated per cycle is determined as a function of the system parameters. In this way the influence of the mass, natural frequency and internal damping of the friction damper on the energy dissipation is established. It is shown that increasing the mass and reducing the natural frequency and internal damping of the friction damper maximizes the dissipated energy.
Friction modeling for dynamic system simulation
The working of friction modeling tools for dynamic system simulation were discussed. It was observed that in engineering applications, success of models in predicting experimental results depended on the frictional models. It was also observed that the success of frictional model relied on the system dynamic models. Various frictional models from the vast field of engineering models were examined and specific focus was laid on lumped-parameter system models, continuum system models and forced system models.
On dry friction modelling and simulation in kinematically excited oscillatory systems
This paper deals with the analysis and simulation of a general single degree of freedom (sdof) oscillatory system with idealised linear viscous damper and dry friction. For dry friction modelling the phenomenological macro-slip approach is employed, described in mathematical form either by the signum function approach or by the physically correct stick lip approach assuming switching phenomena on a short time scale. Both approaches are illustrated first using a steady-state harmonic acceleration excitation with constant amplitude and then a stationary random acceleration excitation, corresponding to a field-measured excitation in a vehicle. The differences in the two approaches are highlighted, indicating that the physically correct stick lip approach describes the friction phenomenon better than the standard signum approach. The signum approach is prone to false numerical oscillations completely distorting the acceleration response signal in comparison to measured suspension system response. The acceleration transmissibility response is analysed in respect to the dry friction force magnitude, employing stationary random excitation. A sdof oscillatory system without viscous damping, subjected to both stationary random acceleration and harmonic acceleration is analysed, too. It is shown that such a system can be used without serious practical problems; however, no implications on its performance from the analysis under harmonic constant amplitude acceleration excitation can be made.
Research on a new damper and its application in vibration control of a building
It is explored the vibrational energy dissipation theory of a new dry friction damper and its application in vibration control of a building.The research shows that the new dampers have traditional dampers′ merit and overcome the shortcoming that can only offer invariable friction.At the same time,they can be controlled by the signal of the vibration of the building.So the ability of energy dissipation and vibration control effect is augmented.The simulation using finite element program proved that the vibration of the building is reduced with the use of this damper.
Displacement-proportional friction (DPF) in base isolation
Friction Damping and Isolation Systems
Free response of a system with negative viscous damping and displacement-dependent dry friction damping
A stability analysis is conducted of an autonomous single-degree-of-freedom system damped with negative viscous damping and a displacement-dependent Coulomb friction force. The geometry of the dry friction damping element yields a friction force that grows linearly with the system displacement. The most direct application of this system is in the study of a turbomachinery blade with shroud interfaces designed to achieve this geometry. Recent studies have shown that the damping of systems with this type of displacement-dependent dry friction force resembles linear structural damping and suggests that this arrangement may be an effective means of flutter suppression in these turbine and fan blade applications. For this study, the inclusion of negative viscous damping is used in order to approximate destabilizing aerodynamic forces. An exact analysis is conducted to determine the stability of this autonomous system. Results show that energy losses from the displacement-dependent dry friction damper are large enough to achieve local and even global stability under certain conditions.
Displacement-dependent dry friction damping of a beam-like structure
The flexural vibration of a beam-like structure damped with a displacement dependent Coulomb friction force has been examined. Due to the geometry of the dry friction damping element, the friction force grows linearly with the beam's transverse displacement. Harmonic excitation of the system is analyzed using first order harmonic balance and then using an "exact" time domain method. The stick-slip behaviour of the system has also been studied. Even though the only source of damping is dry friction, the system was seen to exhibit damping characteristics similar to linear structural damping. The equivalent natural frequency and equivalent viscous damping were also investigated, and found to depend on the amplitude of response and on the design parameters of the frictional interface. In particular, the overall damping levels as well as the amount of stick-slip motion are seen to depend strongly on the amount of displacement dependence. Another significant result was the appearance of two stable steady-state solutions at certain parameter values. The results suggest that the overall characteristics of mechanical systems may be improved by properly configuring frictional interfaces to allow normal forces to vary with displacement.
A comparison of two nonlinear damping mechanisms in a vibration isolator
78 The influence of two nonlinear dampers on vibration transmissibility are compared. 78 An isolator with geometric nonlinear damping force is studied. 78 Analytical expressions and numerical simulations are used for the analysis. 78 An isolation system with geometrically nonlinear damping has some advantages compared to a linear damper.