引言
隔振是一种有效的振动控制方式,通过在振源和隔振对象之间合理设计隔振装置,选择合适的隔振系统的阻尼或者刚度,使得振源传至隔振对象的力或运动激励降低,减小外部扰动向系统敏感部分的传递,达到良好的隔振效果[1 -2 ] .传统的被动隔振系统结构和参数一旦确定就无法改变,无法满足复杂多变的工况条件,也无法协调共振响应与高频衰减之间的矛盾,制约了被动隔振系统性能的进一步提高. 主动隔振系统减振效果好,但是成本高、能量消耗大、结构复杂.而基于半主动控制的隔振系统具有被动控制简单易操作和主动控制良好的隔振性能的优势,近年来在车辆悬架减振系统、高精密机械系统、飞机着陆装置、建筑结构振动控制系统、船舶的可控浮阀隔振系统中得到了广泛的应用[3 -7 ] .
半主动控制属于参数控制,根据一定规则来实时改变结构的刚度或阻尼等参数,进而提高隔振系统在不同激励下的隔振性能,控制过程依赖于结构反应及外部激励信息. 相对于变刚度,采用电子控制阻尼调节的方法来实现阻尼控制更为容易,目前已有很多成熟的可控阻尼器,如电流变阻尼器和磁流变阻尼器等. 在隔振系统的半主动控制中,控制策略直接决定着隔振系统的隔振效果.Karnopp 等[8 ] 在 1974 年首次提出了半主动悬架系统速度负反馈的 "天棚" (sky-hook,SH) 阻尼控制算法;Margolis 等[9 -10 ] 在天棚阻尼控制的基础上提出了开关控制,即阻尼力与相对速度的乘积为正,则阻尼器从悬架系统吸收能量,起到减振的效果;反之表示阻尼器要向悬架系统提供能量.Valasek 等[11 ] 根据 SH 原理,提出了与 SH 算法相似的 "地棚" (ground-hook,GH) 阻尼控制算法,将非簧载质量与大地连接在一起,以大地作为系统坐标,目的是减小非簧载质量加速度;Savaresi 等提出了加速度驱动阻尼 (acceleration driven damper,ADD) 控制算法[12 ] 用以优化簧载质量加速度,以及混合 SH-ADD 控制算法[13 -14 ] ,结合两种算法优势,在整个频域内提高车辆舒适性;Riccardo 等[15 ] 提出了动力驱动阻尼器 (power-driven-damper,PDD) 算法. Nirala 等[16 ] 提出了冲击驱动阻尼 (jerk drivendamper,JDD) 控制算法,在突然刹车时能有效减小垂向加速度.Poussot-Vassal 等[17 ] 对 SH,GH,ADD,SH-ADD 等多种半主动悬架控制方法进行了综述.
开关控制的思想是在高阻尼和低阻尼之间切换来实现减振的效果.由于半主动开关控制算法简单、响应快、易于实现,并能实现较好的控制效果,在实际工程中有很好的应用前景. 半主动控制系统中依据不同开关控制算法和切换条件,根据系统状态的不同来实现开、关两种不同状态下阻尼的快速切换,属于强非线性系统.其中,依据相对速度和不同变量的乘积作为切换条件的控制策略包括天棚阻尼控制算法、地棚阻尼控制算法和加速度驱动阻尼控制算法等.Shen 等[18 ] 对 4 种基于不同反馈的地棚阻尼控制策略的半主动吸振器进行了解析研究;Díaz 等[19 ] 分析了 3 种基于速度反馈的非线性开关控制在高增益和显著振级的振动下的饱和问题;Eslaminasab 等[20 ] 研究了半主动相对控制的单自由度悬架系统的控制效果;申永军等[21 -24 ] 分别采用有限相对位移控制、天棚控制等策略对含有时滞的单自由度半主动悬架系统进行了动力学分析;Yu 等[25 ] 分析了基于磁流变液阻尼器组成的天棚阻尼控制隔振系统的非线性和时滞特性;Fischer 等[26 ] 分析了主动和半主动车辆悬架系统;王昊等[27 ] 以某磁流变阻尼器作为作动器,研究了4种开关半主动控制策略对整车悬架系统参数的影响;Kim 等[28 ] 对比了在不同激励下主动、半主动和混合质量调谐阻尼器的控制效果;Dong 等[29 ] 对比分析了包括天棚阻尼控制、混合控制、滑模控制、LQG 控制和模糊逻辑控制等 5 种磁流变半主动悬架的控制效果.目前,大多数研究是采用数值分析的方法对控制性能进行分析,而且针对多种半主动控制策略的对比分析较少.
本文从近似解析分析的角度,以含立方刚度的单自由度半主动隔振系统为例,通过平均法建立系统的近似解析解,进而对 3 种基于相对速度反馈的半主动开关控制策略的动力学性能进行分析,利用 Lyapunov 理论分析系统的稳定性;通过数值解和解析解的比较,验证解析结果的正确性;详细分析了 3 种控制策略在简谐激励和随机激励下的控制效果.
1 近似解析解
1.1 数学模型
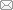
通常非线性半主动隔振系统都是基于"质量-弹簧-阻尼"结构体系来近似简化模型,其单自由度半主动隔振系统的模型[30 ] 如图1 所示,可用一个并联的弹性元件和阻尼器来表示.此模型中,除线性刚度和线性阻尼外,引入非 线性刚度,用以克服线性隔振技术的缺陷,改善系统隔振性能[25 ] .可控阻尼通过传感器对系统状态进行判断后,依据不同的变化规律,在一定范围内对可控阻尼进行调节,从而达到减振的效果.具有这种形式的如 1/4 车辆悬架系统、船舶浮阀减振系统等.以 1/4 车辆悬架为例,图1 中 $m$ 为车体质量,$x$ 为车体的位移,$x_0 $ 为路面激励,$F_1$ 为非线性弹性力:$F_1 = k_{1} (x_0 - x) + k_{2} (x_0 - x)^{3}$,其中 $k_{1} $ 表示线性刚度系数,$k_{2}$ 表示非线性刚度系数;$F_2 $ 为阻尼力:$F_2 = c(\dot {x}_0 - \dot {x})$,其中 $c$ 表示线性阻尼系数.
图1
图1
单自由度半主动隔振系统模型
Fig. 1
Model of a single-degree-of-freedom semi-active vibration isolation system
(1) $m\ddot {x} + k_{1} (x - x_0 ) + k_{2} (x - x_0 )^{3} + c(\dot {x} - \dot {x}_0 ) = 0$
令 $y = x - x_0 $,路面激励取简谐激励 $x_0 = A\cos (\omega t)$,$A$ 为简谐激励的幅值,且为常数,$\omega $ 为简谐激励的角频率. 代入式 (1) 得
(2) $m\ddot {y} + k_{1} y + k_{2} y^{3} + c\dot {y} = mA\omega^2\cos (\omega t)$
令 $\omega _0 = \sqrt {\dfrac{k_{1} }{m}} $,$\gamma = \dfrac{k_2 }{k_1 }$,$\xi = \dfrac{c}{2\sqrt {mk_{1}} }$,$\xi $ 为悬架系统阻尼比. 式 (2) 可简化为
(3) $\ddot {y} + 2\xi \omega _0 \dot {y} + \omega _0^2 y + \omega _0^2 \gamma y^{3} = A\omega ^2\cos (\omega t)$
分析系统的主共振,即路面激励频率 $\omega $ 接近系统固有频率 $\omega_{0}$ 时的共振,引入 $\omega^2 = \omega _0^2 + \varepsilon \sigma $ ($\sigma $ 为调谐参数),定量表示两个频率之间的接近程度,且限制 $\xi \omega _0 = \varepsilon \mu $,$\gamma = \varepsilon \gamma _{1} $,$A\omega ^2 = \varepsilon f$,代入式 (3) 可得
(4) $\ddot {y} + \omega ^2y = \varepsilon [f\cos (\omega t) - 2\mu \dot {y} + \sigma y - \omega _0^2 \gamma _{1} y^3]$
1.2 未加控制时的近似解析解
采用平均法求解方程的近似解析解[31 ] ,假设振幅 $a$ 和相位 $\psi $ 是时间的慢变函数
(5) $\left.\begin{array}{l} y = a(t)\cos \psi (t) \\ \dot {y} = - \omega a(t)\sin \psi (t) \end{array} \right \}$
其中,$\psi (t) = \omega t + \varphi (t)$. 根据平均法可得到一阶近似解振幅和相位满足的方程
(6) $\left.\begin{array}{l} \dot {a}(t) = - \dfrac{\varepsilon }{\omega }L(a,\varphi )\sin \psi \\ a(t)\dot {\varphi } = - \dfrac{\varepsilon }{\omega }L(a,\varphi )\cos \psi \end{array} \right \}$
$\begin{array}{l} L(a,\varphi ) = f\cos (\psi - \varphi ) + 2\mu a\omega \sin \psi + \\ \sigma a\cos \psi - \omega _0^2 \gamma_1 a^3\cos ^3\psi \end{array} $
由于振幅和相位是随时间变化的 $\varepsilon $ 的同阶小量,可以将式 (6) 在一个周期内进行平均处理,得到近似解振幅和相位的显式,即
(7) $ \left.\begin{array}{l} \dot {a}(t) = - \dfrac{\varepsilon }{2\pi \omega }\int_0^T {L(a,\varphi )\sin \psi \text{d}\psi } \\ a(t)\dot {\varphi } = - \dfrac{\varepsilon }{2\pi \omega }\int_0^T {L(a,\varphi )\cos \psi \text{d}\psi } \end{array} \!\! \right \}$
当不采取任何控制策略时,在一个周期 $[0,2\pi ]$ 内进行积分,得到幅值和相位的近似值为
(8) $\dot {a}(t) = - \dfrac{\varepsilon }{2\omega }(f\sin \varphi + 2a\mu \omega )$
(9) $\dot {\varphi } = - \dfrac{\varepsilon }{2\omega a}(f\cos \varphi + a\sigma - \dfrac{3}{4}\omega _0^2 \gamma _1 a^3)$
1.3 加速度驱动阻尼控制下的近似解析解
非线性隔振系统采用加速度-相对速度的加速度驱动阻尼 ADD 的控制策略,根据簧载质量加速度和相对速度得出期望阻尼力,ADD 控制策略为
(10) $ c = \left\{ \begin{array}{ll} c_{on} , & \ddot {x}(\dot {x} - \dot {x}_0 ) \geqslant 0 \\ c_{off} , & {others} \end{array} \right.$
其中,$c_{on}$表示状态"开"时的阻尼系数,$c_{off}$表示状态"关"时的阻尼系数.
根据前述对参数的定义,可利用定义的参数$\mu $来表示控制策略,即参数$\mu $需要根据系统变化进行调节
(11) $ \mu = \left\{ \begin{array}{ll} \mu _{on} , & (\ddot {y} + \ddot {x}_0 )\dot {y} \geqslant 0 \\ \mu _{off} , & {others} \end{array} \right.$
为简化判断条件,由于振幅 $a(t)$ 和相位 $\varphi (t)$ 随时间的变化是与 $\varepsilon$ 的同阶小量,与 $\psi (t)$ 相比,是缓慢变化的,因此根据式 (5) 可近似取 $\ddot {y} = - \omega ^2a\cos\psi $,则有
(12) $ (\ddot {y} + \ddot {x}_0 )\dot {y} = \\ a\omega ^3\sqrt {(a + A\cos \varphi )^2 + (A\sin \varphi )^2} \sin \psi \cos (\psi - \beta ) $
其中,$\beta = \arctan \dfrac{A\sin \varphi }{a + A\cos \varphi }$. 由此可得,参数 $\mu$ 依据加速度阻尼控制 (ADD) 策略在一个周期内的变化规律为
(13) $ \mu = \left\{ \begin{array}{ll} \mu _{on} , & 0 \leqslant \psi < \dfrac{\pi }{2} + \beta \\ \mu _{off} , & \dfrac{\pi }{2} + \beta \leqslant \psi < \pi \\ \mu _{on} , & \pi \leqslant \psi < \dfrac{3\pi }{2} + \beta \\ \mu _{off} , & \dfrac{3\pi }{2} + \beta \leqslant \psi < 2\pi \end{array} \right.$
采用平均法,在一个周期内进行积分,可得振幅和相位的近似值为
(14) $ \dot {a}(t) = - \dfrac{\varepsilon }{2\pi \omega }\Big [f\pi \sin \varphi + a\omega b(2\beta + \sin 2\beta ) + a\omega \pi (\mu _{on} + \mu _{off} )\Big ]$
(15) $\dot {\varphi } = - \dfrac{\varepsilon }{2\pi \omega a}\Big [f\pi \cos \varphi + a\pi \sigma + a\omega b(1 + \cos 2\beta )- \dfrac{3}{4}\pi \omega _0^2 \gamma _1 a^3 \Big ]$
其中,$b = \mu _{on} - \mu _{off} $.
1.4 天棚阻尼控制下的近似解析解
非线性隔振系统采用速度-相对速度的天棚 SH 阻尼的控制策略为
(16) $ c = \left\{ \begin{array}{ll} c_{on} , & \dot {x}(\dot {x} - \dot {x}_0 ) \geqslant 0 \\ c_{off} , & {others} \end{array} \right.$
类似地可以得到采用 SH 控制策略时,控制策略用参数 $\mu $ 表示为
(17) $ \mu = \left\{ \begin{array}{ll} \mu _{on} , & (\dot {y} + \dot {x}_0 )\dot {y} \geqslant 0 \\ \mu _{off} , & {others } \end{array} \right.$
$ (\dot {y} + \dot {x}_0 )\dot {y} = a\omega ^2\sqrt {(a + A\cos \varphi )^2 + (A\sin \varphi )^2} \sin \psi \sin (\psi - \beta ) $
$\beta$ 同为 $\beta = \arctan \dfrac{A\sin \varphi }{a + A\cos \varphi }$. 当 $\beta > 0$ 时控制策略在一个周期内的变化规律为
(18) $ \mu = \left\{ \begin{array}{ll} \mu _{off} , &0 < \psi < \beta \\ \mu _{on} , & \beta \leqslant \psi < \pi \\ \mu _{off} , & \pi \leqslant \psi < \pi + \beta \\ \mu _{on} , &\pi + \beta \leqslant \psi < 2\pi \end{array} \right.$
当 $\beta > 0$ 时, 振幅和相位的近似值为
(19) $ \dot {a}(t) = - \dfrac{\varepsilon }{2\pi \omega }\Big [f\pi \sin \varphi + a\omega b( - 2\beta + \sin 2\beta ) + 2\pi a\omega \mu _{on} \Big ]$
(20) $ \dot {\varphi } = - \dfrac{\varepsilon }{2\pi \omega a}\Big [f\pi \cos \varphi + a\pi \sigma - a\omega b(1 - \cos 2\beta ) - \dfrac{3}{4}\pi \omega _0^2 \gamma _1 a^3\Big ]$
当 $\beta < 0$ 时, 控制策略在一个周期内的变化规 律为
(21) $ \mu = \left\{ \begin{array}{ll} \mu _{on} , & 0 \leq \psi < \pi + \beta \\ \mu _{off} , & \pi + \beta \leqslant \psi < \pi \\ \mu _{on} , & \pi \leqslant \psi < 2\pi + \beta \\ \mu _{off} , & 2\pi + \beta \leqslant \psi < 2\pi \end{array} \right.$
采用平均法,在一个周期内进行积分,可以得到当 $\beta < 0$ 时振幅和相位的近似值为
(22) $ \dot {a}(t) = - \dfrac{\varepsilon }{2\pi \omega }\Big[f\pi \sin \varphi + a\omega b(2\beta - \sin 2\beta ) + 2\pi a\omega \mu _{on}\Big ]$
(23) $ \dot {\varphi } = - \dfrac{\varepsilon }{2\pi \omega a}\Big [f\pi \cos \varphi + a\pi \sigma + a\omega b(1 - \cos 2\beta ) - \dfrac{3}{4}\pi \omega _0^2 \gamma _1 a^3 \Big ]$
1.5 地棚阻尼控制下的近似解析解
非线性隔振系统采用位移-相对速度的地棚 GH 阻尼控制策略为
(24) $ c = \left\{ \begin{array}{ll} c_{on} , & x(\dot {x} - \dot {x}_0 ) \geqslant 0 \\ c_{off} , & {others} \end{array} \right.$
类似地,采用 GH 控制策略时,控制策略用参数 $\mu $ 表示为
(25) $ \mu = \left\{ \begin{array}{ll} \mu _{on} , & (y + x_0 )\dot {y} \geqslant 0 \\ \mu _{off} , & {others} \end{array} \right.$
$ \begin{array}{l} (y + x_0 )\dot {y} = - a\omega \sqrt {(a + A\cos \varphi )^2 + (A\sin \varphi )^2} \sin \psi \cos (\psi - \beta ) \end{array} $
$\beta $ 表达式同为 $\beta = \arctan \dfrac{A\sin \varphi }{a + A\cos \varphi }$. 在一个周期内的变化规律为
(26) $ \mu = \left\{ \begin{array}{ll} \mu _{off} , & 0 \leq \psi < \dfrac{\pi }{2} + \beta \\ \mu _{on} , & \dfrac{\pi }{2} + \beta \leqslant \psi < \pi \\ \mu _{off} , & \pi \leqslant \psi < \dfrac{3\pi }{2} + \beta \\ \mu _{on} , & \dfrac{3\pi }{2} + \beta \leqslant \psi < 2\pi \end{array} \right.$
采用平均法,在一个周期内进行积分,可得振幅和相位的近似值为
(27) $ \dot {a}(t) = - \dfrac{\varepsilon }{2\pi \omega }\Big[f\pi \sin \varphi - a\omega b(2\beta + \sin 2\beta ) + a\omega \pi (\mu _{on} + \mu _{off} )\Big] $
(28) $ \dot {\varphi } = - \dfrac{\varepsilon }{2\pi \omega a}\Big[f\pi \cos \varphi + a\pi \sigma - a\omega b(1 + \cos 2\beta )- \dfrac{3}{4}\pi \omega _0^2 \gamma _1 a^3\Big]$
对比发现,此类控制策略均以相同的相对速度项 $(\dot {x} - \dot {x}_0)$ 作为控制条件的一部分,而且切换条件中的参数 $\beta$ 具有相同的表达形式,因此可作为一类控制策略研究系统在其控制下的解析解及相关的动力学分析.
2 定常解和稳定性分析
2.1 控制策略下的定常解
对于振动控制系统而言,系统的稳态运动更 有意义. 以下以 ADD 控制的系统为例说明此类控制策略下的系统的定常解和稳定性分析. 设 $\bar {a}$ 和 $\bar {\varphi}$ 分别表示稳态幅值和稳态相位,令式 (14) 和式 (15) 中 $\dot {a}(t) = 0$ 和 $\dot {\varphi}(t) = 0$,可以得到系统的稳态方程组
(29) $ A\omega ^2\pi \sin \bar {\varphi } = - \dfrac{\bar {a}\omega }{2m}(c_{on} - c_{off} )(2\beta + \sin 2\beta ) - \dfrac{\bar {a}\omega \pi }{2m}(c_{on} + c_{off} )$
(30) $ A\omega ^2\pi \cos \bar {\varphi } = - \bar {a}\pi (\omega ^2 - \omega _0^2 )- \dfrac{\bar {a}\omega }{2m}(c_{on} - c_{off} )(1 + \cos 2\beta )+ \dfrac{3}{4}\pi \omega _0^2 \gamma \bar {a}^3$
根据式 (29) 和式 (30) 可以得到频率 $\omega $ 和稳态幅值 $\bar {a}$ 之间的幅频响应方程为
(31) $\begin{array}{l} \Bigg \{ \Big [\dfrac{\omega }{2m}(c_{on} - c_{off} )(2\beta + \sin 2\beta ) + \dfrac{\omega \pi }{2m}(c_{on} + c_{off} )\Big ]^2 + \\ \Big [\pi (\omega ^2 - \omega _0^2 ) + \dfrac{\omega }{2m}(c_{on} - c_{off} )(1 + \cos 2\beta )- \\ \dfrac{3}{4}\pi \omega _0^2 \gamma \bar {a}^2\Big ]^2\Bigg \}\bar {a}^2 = (A\omega ^2)^2\pi ^2 \end{array}$
以及频率 $\omega $ 和稳态相位 $\bar {\varphi }$ 之间的相频响应方程
(32) $ \tan \bar {\varphi } = \dfrac{\omega (c_{on} - c_{off} )(2\beta + \sin 2\beta ) + \omega \pi (c_{on} + c_{off} )}{2m\pi (\omega ^2 - \omega _0^2 ) + \omega (c_{on} - c_{off} )(1 + \cos 2\beta )- \dfrac{3}{2}\pi m\omega _0^2 \gamma \bar {a}^2}$
(33) $\bar {a}_{\max } = \dfrac{2mA\pi \cdot \omega }{(c_{on} - c_{off} )(2\beta + \sin 2\beta ) + \pi (c_{on} + c_{off} )}$
该值与外激励的振幅、稳态振幅出现峰值的激励频率即共振频率、开关控制的阻尼有关.
由于 $\omega > 0$ 解得主共振的骨架线方程为
(34) $ \omega = - \dfrac{(c_{on} - c_{off} )(1 + \cos 2\beta )}{4\pi m} + \\ \sqrt {\dfrac{(c_{on} - c_{off} )^2(1 + \cos 2\beta )^2 - (3\gamma \bar {a}^2 + 4)\pi^2}{8\pi^2m^2}} $
将 $\bar {a}_{\max } $ 代入上式可以得到主共振峰所对应的激励频率,显然与非线性因素有关.
类似可以得到在 SH 控制下,$\beta > 0$ 时稳态的幅频响应方程为
(35) $\begin{array}{l} \Bigg \{ \Big [\dfrac{\omega }{2m}(c_{on} - c_{off} )( - 2\beta + \sin 2\beta ) + \dfrac{c_{\rm on} \pi \omega }{m} \Big ]^2 +\\ \Big [\pi (\omega ^2 - \omega _0^2 ) - \dfrac{\omega }{2m}(c_{on} - c_{off} )\cdot \\ (1 - \cos 2\beta ) - \dfrac{3}{4}\pi \omega _0^2 \gamma \bar {a}^2\Big ]^2 \Bigg \}\bar {a}^2 = (A\omega ^2)^2\pi ^2 \end{array}$
(36) $ \tan \bar {\varphi } = \\ \dfrac{\omega (c_{on} - c_{off} )( - 2\beta + \sin 2\beta ) + 2c_{on} \pi \omega }{2m\pi (\omega ^2 - \omega _0^2 ) - \omega (c_{on} - c_{off} )(1 - \cos 2\beta ) - \dfrac{3}{2}\pi m\omega _0^2 \gamma \bar {a}^2}$
(37) $\begin{array}{l} \Bigg \{ \Big [\dfrac{\omega }{2m}(c_{on} - c_{off} )(2\beta - \sin 2\beta ) + \dfrac{c_{\rm on} \pi \omega }{m} \Big ]^2 +\\ \Big [\pi (\omega ^2 - \omega _0^2 ) + \dfrac{\omega }{2m}(c_{on} - c_{off} )\cdot \\ (1 - \cos 2\beta ) - \dfrac{3}{4}\pi \omega _0^2 \gamma \bar {a}^2 \Big]^2 \Bigg \}\bar {a}^2 = (A\omega ^2)^2\pi ^2 \end{array}$
(38) $\tan \bar {\varphi } = \dfrac{\omega (c_{on} - c_{off} )(2\beta - \sin 2\beta ) + 2c_{on} \pi \omega }{2m\pi (\omega ^2 - \omega _0^2 ) + \omega (c_{on} - c_{off} )(1 - \cos 2\beta ) - \dfrac{3}{2}\pi m\omega _0^2 \gamma \bar {a}^2}$
(39) $\begin{array}{l}\Bigg \{\Big [ - \dfrac{\omega }{2m}(c_{on} - c_{off} )(2\beta + \sin 2\beta ) + \dfrac{\omega \pi }{2m}(c_{on} + c_{off} ) \Big]^2 + \\ \Big [\pi (\omega ^2 - \omega _0^2 ) - \dfrac{\omega }{2m}(c_{on} - c_{off} )(1 + \cos 2\beta )- \\ \dfrac{3}{4}\pi \omega _0^2 \gamma \bar {a}^2\Big ]^2\Bigg \}\bar {a}^2 =(A\omega ^2)^2\pi^2 \end{array}$
(40) $ \tan \bar {\varphi } = \\ \dfrac{ - \omega (c_{on} - c_{off} )(2\beta + \sin 2\beta ) + \omega \pi (c_{on} + c_{off} )}{2m\pi (\omega ^2 - \omega _0^2 ) - \omega (c_{on} - c_{off} )(1 + \cos 2\beta )- \dfrac{3}{2}\pi m\omega _0^2 \gamma \bar {a}^2}$
2.2 稳定性分析
对于 ADD 控制的系统,采用 Lyapunov 理论研究其稳态解的稳定性. 对稳态解引入小扰动,令 $a = \bar {a} + \Delta a$,$\varphi = \bar {\varphi } + \Delta \varphi$,并代入式 (14) 和式 (15) 中,进行泰勒展开并略去高阶项,得
(41) $ \dfrac{\text{d}\Delta a}{\text{d} t} = - \dfrac{{1}}{2\pi \omega }\Bigg\{ \Bigg[\Big (\dfrac{c_{on} - c_{off} }{2m}\Big) \Big (2\beta + \sin 2\beta \Big)\omega + \\ \dfrac{\pi (c_{on} + c_{off} )}{2m}\omega \Bigg ] \Delta a + A\pi \omega ^2\cos \bar {\varphi } \cdot \Delta \varphi \Bigg\}$
(42) $ \dfrac{\text{d}\Delta \varphi }{\text{d} t} = - \dfrac{1}{2\pi \omega }\Bigg[ \Big( - \dfrac{3}{2}\pi \omega _0^2 \gamma \bar {a} - \dfrac{A\pi \omega ^2\cos \bar {\varphi }}{\bar {a}^2}\Big ) \cdot \Delta a - \\ \dfrac{A\pi \omega ^2}{\bar {a}}\sin \bar {\varphi } \cdot \varDelta \varphi \Bigg ] $
利用式 (29) 和式 (30) 消去上式中的 $\bar {\varphi }$,得到特征行列式为
(43) $\det \left[ \!\! \begin{array}{cc} {H_1 - \lambda } & {H_2 - H_3 } \\ {\dfrac{3H_3 - H_2 }{\bar {a}^2}} & {H_1 - \lambda } \end{array} \!\! \right] = 0$
$H_1 = - \dfrac{{1}}{2\pi }\Bigg [ \Big (\dfrac{c_{on} - c_{off} }{2m}\Big )(2\beta + \sin 2\beta ) + \dfrac{\pi (c_{on} + c_{off} )}{2m}\Bigg] $
$H_2 = \dfrac{{1}}{2\pi \omega }\Bigg [\bar {a}\pi (\omega ^2 - \omega _0^2 ) +\dfrac{\bar {a}\omega }{2m}(c_{on} - c_{off} )(1 + \cos 2\beta ) \Bigg ]$
$H_3 = \dfrac{3\omega _0^2 \gamma \bar {a}^3}{8\omega }$
(44) $ \lambda ^2 - 2H_1 \lambda + H_1^2 - \dfrac{(H_2 - H_3 )(3H_3 - H_2 )}{\bar {a}^2} = 0$
由于 $H_1 < 0$,因此得到系统周期解的稳定性条件为
(45) $H_1^2 - \dfrac{(H_2 - H_3 )(3H_3 - H_2 )}{\bar {a}^2} > 0$
分析上式可知,当幅频特性曲线方程中存在 3 个定常解时中间解为不稳定解,存在不稳定解的原因是在于弹性元件存在非线性刚度. 若模型中不存在非线性刚度 $k_2$,那么式 (43) 中 $H_3 = 0$,则特征方程 (44) 可变换为
(46) $\lambda ^2 - 2H_1 \lambda + H_1^2 + \dfrac{H_2^2 }{\bar {a}^2} = 0$
类似地,对于 GH 控制下系统周期解的稳定性进行分析,得到特征方程为
(47) $\lambda ^2 - 2H_4 \lambda + H_4^2 - \dfrac{(H_5 - H_3 )(3H_3 - H_5 )}{\bar {a}^2} = 0$
$H_4 = - \dfrac{{1}}{2\pi }\Bigg [ - \Big (\dfrac{c_{on} - c_{off} }{2m}\Big) (2\beta + \sin 2\beta ) + \dfrac{\pi (c_{on} + c_{off} )}{2m}\Bigg] $
$ H_5 = \dfrac{{1}}{2\pi \omega }\Bigg [\bar {a}\pi (\omega ^2 - \omega _0^2 ) - \dfrac{\bar {a}\omega }{2m}(c_{on} - c_{off} )(1 + \cos 2\beta ) \Bigg] $
由于 $H_4 < 0$,因此得到系统周期解的稳定性条件为
(48) $H_4^2 - \dfrac{(H_5 - H_3 )(3H_3 - H_5 )}{\bar {a}^2} > 0$
对于 SH 控制下 $\beta > 0$ 时系统周期解的稳定性进行分析,得到特征方程为
(49) $\lambda ^2 - 2H_6 \lambda + H_6^2 - \dfrac{(H_7 - H_3 )(3H_3 - H_7 )}{\bar {a}^2} = 0$
$ H_6 = - \dfrac{{1}}{2\pi }\Bigg [ \Big (\dfrac{c_{on} - c_{off} }{2m} \Big)( - 2\beta + \sin 2\beta ) + \dfrac{\pi c_{on} }{m}\Bigg ] $
$ H_7 = \dfrac{{1}}{2\pi \omega } \Bigg [\bar {a}\pi (\omega ^2 - \omega _0^2 ) - \dfrac{\bar {a}\omega }{2m} (c_{on} - c_{off} )(1 - \cos 2\beta ) \Bigg] $
由于 $H_6 < 0$,得到系统周期解的稳定性条件为
(50) $H_6^2 - \dfrac{(H_7 - H_3 )(3H_3 - H_7 )}{\bar {a}^2} > 0$
(51) $ \lambda ^2 - 2H_8 \lambda + H_8^2 - \dfrac{(H_9 - H_3 )(3H_3 - H_9 )}{\bar {a}^2} = 0$
$ H_8 = - \dfrac{{1}}{2\pi }\Bigg [ \Big (\dfrac{c_{on} - c_{off} }{2m} \Big)(2\beta - \sin 2\beta ) + \dfrac{\pi c_{on} }{m}\Bigg ] $
$ H_9 = \dfrac{{1}}{2\pi \omega } \Bigg [\bar {a}\pi (\omega ^2 - \omega _0^2 ) + \dfrac{\bar {a}\omega }{2m}(c_{on} - c_{off} )(1 - \cos 2\beta ) \Bigg] $
由于 $H_8 < 0$,得到系统周期解的稳定性条件为
(52) $H_8^2 - \dfrac{(H_9 - H_3 )(3H_3 - H_9 )}{\bar {a}^2} > 0$
3 数值解验证
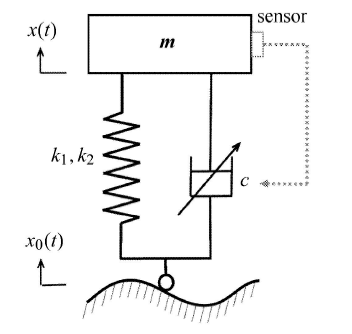
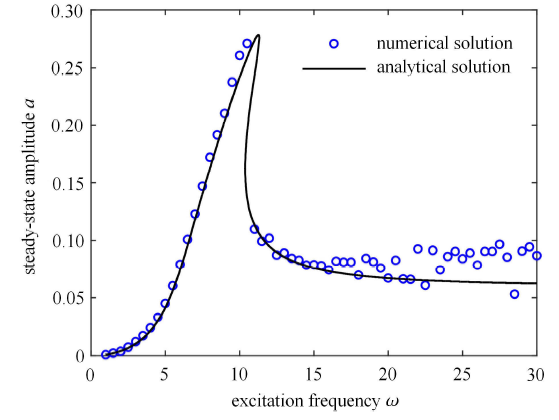
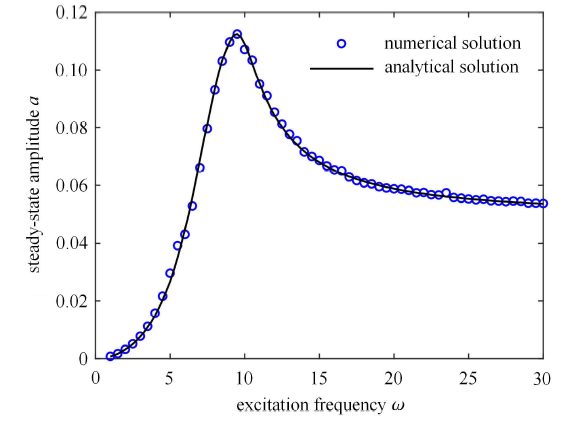
对于给定的某一悬架系统,取各参数为[32 -33 ] :车体质量 $m =240$ kg,弹簧线性 刚度 $k_{1}=16 000$ N/m,非线性刚度 $k_{2} =320 000$ N/m.为对比在不同条件下近似解析解和数值解的吻合程度,在 3 种不同控制策略下的开/关阻尼系数及路面简谐激励振幅取值略有不同.数值解的求解采用 Runge-Kutta 法,计算时间为 800 s,将后 10% 的响应的最大值作为稳态响应的幅值.图2 ~图4 分别为在 ADD、SH 和 GH 控制策略下数值解和近似解析解得到的幅频响应曲线,图中横轴为激励频率 $\omega$,纵轴为响应振幅 $a$.从图2 ~图4 可以看出,3 种控制策略的解析解在不同的激励幅值和系统参数下,在低频区和共振区均和相应的数值解均具有较好的一致性,证明了系统解析解的求解方式的正确性和准确性. 需要注意的是,由于半主动控制系统响应中存在高阶奇次谐波成分,因此在高频区可能会表现出颤振现象[23 ] .
图2
图2
ADD 下的幅频响应曲线
Fig. 2
Amplitude-frequency response with acceleration driven damper control ($c_{on} =1500 $N$\cdot$s/m, $c_{off} =50$ N$\cdot$s/m, $A =0.06$ m)
图3
图3
SH 下的幅频响应曲线
Fig. 3
Amplitude-frequency response with sky-hook control ($c_{on} =1000 $N$\cdot$s/m, $c_{off} =50$ N$\cdot$s/m, $A =0.05$ m)
图4
图4
GH 下的幅频响应曲线
Fig. 4
Amplitude-frequency response with ground-hook control ($c_{on} =1000 $N$\cdot$s/m, $c_{off} =50$ N$\cdot$s/m, $A =0.04$ m)
4 控制效果分析
4.1 开关控制阻尼的变化分析
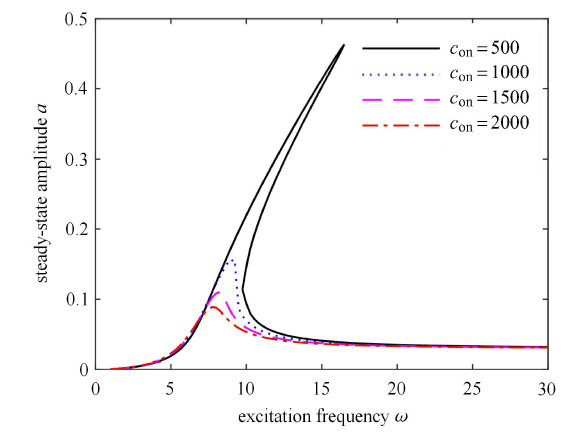
以 ADD 控制为例,分析半主动开关控制的开/关阻尼变化时对主共振振幅的影响.令 $c_{off} \!=\!50$ N$\cdot$s/m 并且保持不变,$c_{on}$ 分别取 500,1000,1500 和 2000 N$\cdot$s/m 时系 统的幅频响应曲线如图5 所示. 可以看出,增大阻尼 $c_{\rm on}$,系统在全频域内共振振幅都逐渐减小,而且系统的非线性 特性被抑制,分析结果与式 (33) 吻合.
图5
图5
$c_{on}$ 变化时的幅频响应曲线
Fig. 5
Amplitude-frequency responses with different $c_{on}$
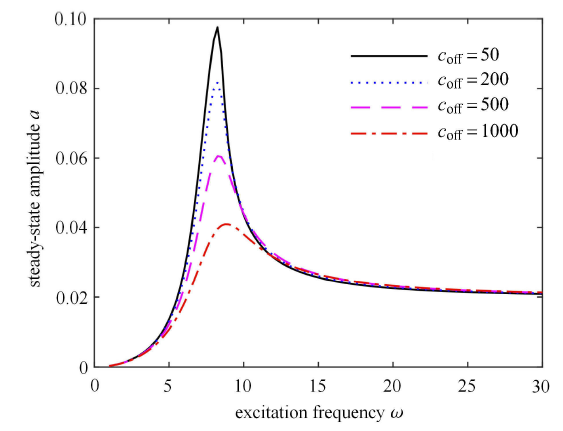
令 $c_{on}=1000$ N$\cdot$s/m 且保持不变,$c_{off}$ 分别取 50,200,500 和 1000 N$\cdot$s/m 时系统 的幅频响应曲线如图6 所示. 从图6 可以看出,随着 $c_{\rm off}$ 增大,在低频域系统的共振振幅逐渐减小,而在高频域内系统的共振振幅逐渐增大,式 (33) 也表明,幅值 $a$ 除与阻尼有关外,也与外激励频率 $\omega $ 有关.
图 6
图 6
$c_{off}$ 变化时的幅频响应曲线
Fig. 6
Amplitude-frequency responses with different $c_{off}$
4.2 外激励振幅的变化分析
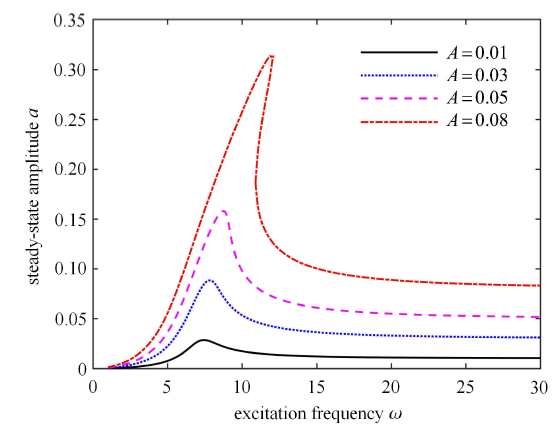
以 ADD 控制为例,半主动开关控制的开/关阻尼保持不变,取 $c_{on} =2000$ N$\cdot$s/m,$c_{off} =0.02 c_{on}$,分析外激励幅值$A$变化时对主共振振幅的影响. $A$ 分别取 0.01,0.03,0.05 和 0.08 m 时系统的幅频响应曲线如图7 所示. 从图7 中可以看出,外激励幅值 $A$ 越大,系统的共振振幅越大.
图7
图7
外激励振幅变化时的幅频响应曲线
Fig. 7
Amplitude-frequency responses with different $A$
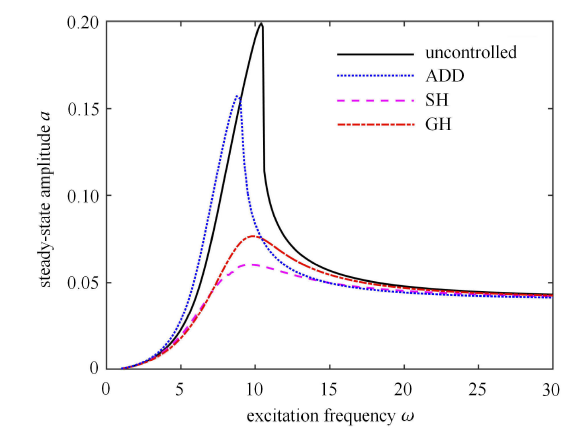
4.3 3 种控制策略的控制效果分析
这里分析 3 种半主动控制策略对于同一个悬架系统的控制效果,并与未加控制的悬架系统进行比较. 外激励振幅 $A=0.04$ m,开关 控制阻尼分别为 $c_{on}=1500$ N$\cdot$s/m,$c_{off}=0.02c_{\rm on}$,得到 3 种控制策略下系统解析解的幅频响应曲线和未加半主动控制时系统解析解的幅频响应曲线,如图8 所示. 从图中看出,3 种控制策略下系统的共振响应振幅与未加半主动控制时相比均有明显的降低:在低频时,基于速度-相对速度反馈的 SH 控制策略在降低振幅方面最优,减振效果最好;在高频时,基于加速度-相对速度反馈的 ADD 控制策略在降低振幅方面最优. ADD 控制策略在降低共振峰值的同时,共振的频率也发生了偏移. 由此可见,采用控制策略改变了幅频曲线的弯曲程度,即改变了系统的频率特性,对共振振幅、定常解的多值性以及系统的稳定性均有影响.
图8
图8
不同控制策略下的幅频响应曲线
Fig. 8
Amplitude-frequency responses with different control approaches
对比主共振频率附近 $\omega = 10$ rad/s 时的时域响应,图9 ~图11 依次为簧载质量的位移 时间历程、加速度时间历程以及速度-位移相平面图.从图9 中可以得出与图8 相同的结论,即采用半主动控制策略可明显降低系统的相对位移响应振幅.在主共振频率附近,基于速度-相对速度反馈的 SH 控制策略的减振效果最优,均优于基于加速度-相对速度反馈的 ADD 控制策略和基于位移-相对速度反馈的 GH 控制策略.从图10 中可以看出,采用半主动控制策略在降低垂直加速度的幅值上具有明显的效果.此外,半主动控制策略下的加速度响应存在明显的突变,这是半主动开关控制的分段线性导致的系统强非线性引起的,这也是开关控制的本质特征,在切换过程中会产生的抖振现象,突变的强度依次为 ADD 控制策略、SH 控制策略、GH 控制策略.从图11 相平面图中可以看出,采用半主动控制同时能够降低簧载质量振动的位移和速度,而且 SH 控制策略的效果最佳.
图9
图9
簧载质量的位移时间历程
Fig. 9
Time history of relative displacement
图10
图10
簧载质量的加速度时间历程
Fig. 10
Time history of relative acceleration
图11
图11
簧载质量的相平面图
Fig. 11
Phase-portrait of sprung mass
5 随机激励下的控制效果
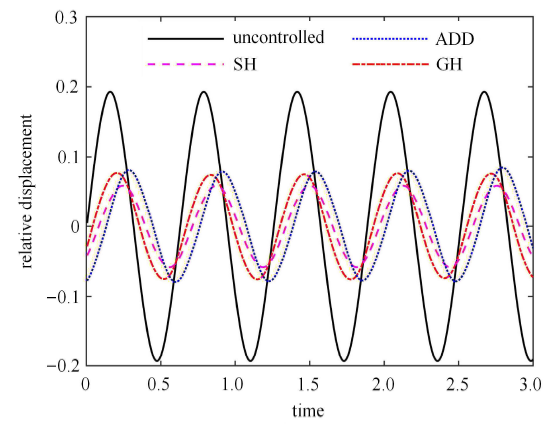
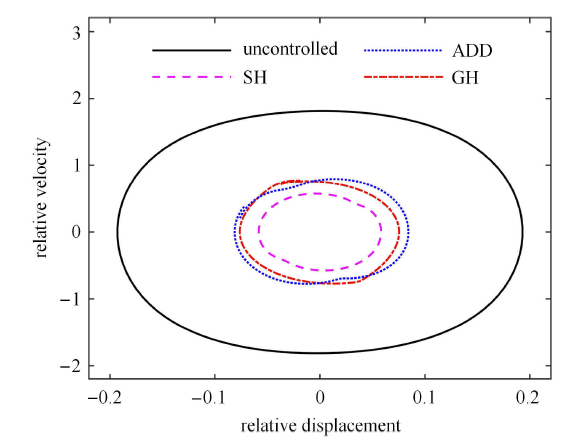
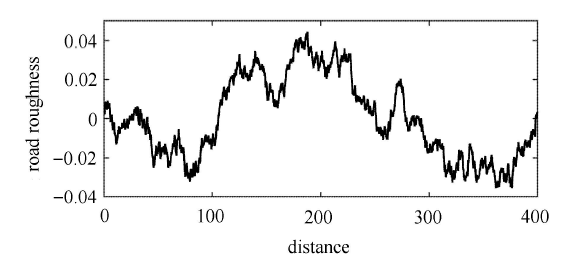
在实际的工程应用中,非线性隔振系统较多情况下所受到的外力更接近于随机激励,半主动隔振系统在随机激励下的响应更具有实际意义[34 -39 ] .采用刘献栋等[40 ] 的数值模拟方法建立 D 级路面不平度值来模拟随机激励,如图12 所示. 选取车速为 10 m/s 情况下时,时间间隔为 0.01 s 的 40 s 随机激励,得到 3 种控制策略下和未加半主动控制时的位移时间历程曲线分别如图13 (a)~图13 (d) 所示.
图12
图12
D 级路面的不平度
Fig. 12
Road roughness of D grade
图13
图13
不同控制策略下相对位移的时间历程曲线
Fig. 13
Time history of stochastic relative displacement responses
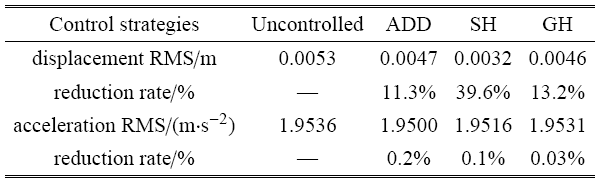
采用车身基于路面的相对位移量的均方根值和加权加速度均方根值对平顺性进行评价[41 ] ,按下式计算加权加速度均方根值
(53) $\ddot {y}_w = \left[ {\dfrac{1}{T}\int_0^T {(\ddot {y}_w (t))^2 \text{d} t} } \right]^{\tfrac{1}{2}}$
不同控制策略下位移均方根值和加权加速度均方根值的结果如表1 所示. 由图13 和表1 中可以看出,相对于未加控制策略来说,3 种控制策略都能够有效降低系统的相对位移量和加权加速度均方根值,提升平顺性效果明显.基于速度-相对速度反馈的 SH 控制策略在降低相对位移量方面更突出,而基于加速度-相对速度反馈的 ADD 控制策略更侧重于降低加权加速度均方根值.
6 结论
本文对一类基于相对速度反馈控制的半主动隔振系统的解析求解以及动力学行为进行了研究.首先利用平均法求解了未加控制时含立方刚度的单自由度隔振系统在主共振情况下的响应,进而分别采用加速度-相对速度反馈的 ADD 控制策略、速度-相对速度反馈的 SH 控制策略和位移-相对速度反馈的 GH 控制策略对系统的一阶近似解进行了分析,利用 Lyapunov 理论分析了系统的稳定性,得到了系统定常解的稳定条件.利用数值仿真对一阶近似解进行了验证,结果表明解析研究结果和数值解具有很好的一致性.最后对 3 种控制策略分别在简谐激励和随机激励下的控制效果进行了对比分析,分析结果表明,在抑制共振响应振幅方面,低频时SH控制策略的减振效果最好;高频时 ADD 控制策略的减振效果最优.ADD 控制策略在降低加权加速度均方根值方面更为突出,可以有效提升平顺性.本文提供的半主动控制隔振系统的解析研究,也可应用到其他半主动开关控制策略中,为半主动隔振系统的控制策略研究提供了参考.
参考文献
View Option
[1]
刘兴天 , 陈树海 , 王嘉登 等 . 几何非线性摩擦阻尼隔振系统动力学行为研究
力学学报 , 2019 ,51 (2 ):371 -379
[本文引用: 1]
( Liu Xingtian Chen Shuhai Wang Jiadeng , et al . Analysis of the dynamic behavior and performance of a vibration isolation system with geometric nonlinear friction damping
Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics 2019 ,51 (2 ):371 -379 (in Chinese))
[本文引用: 1]
[2]
陆泽琦 , 陈立群 . 非线性被动隔振的若干进展
力学学报 , 2017 ,49 (3 ):550 -564
[本文引用: 1]
( Lu Zeqi Chen Liqun , Some recent progresses in nonlinear passive isolations of vibrations
Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics 2017 ,49 (3 ):550 -564 (in Chinese))
[本文引用: 1]
[3]
Fu B Giossi RL Persson R , et al . Active suspension in railway vehicles: a literature survey
Railway Engineering Science 2020 ,28 (1 ):3 -35
DOI
URL
[本文引用: 1]
[4]
朱雅辉 , 翁泽宇 , 耿超 等 . 半主动控制浮筏隔振系统的开关算法与仿真研究
机电工程 , 2016 ,33 (3 ):265 -270
( Zhu Yahui Weng Zeyu Geng Chao , et al , Switching algorithms and simulation research on semi-active control of floating raft vibration isolation system
Journal of Mechanical & Electrical Engineering 2016 ,33 (3 ):265 -270 (in Chinese))
[5]
Savaresi SM Poussot-Vassal C Spelta C , et al . Semi-active suspension control design for vehicles
Butterworth-Heinemann Publications 2010
[6]
高雪 , 陈前 , 刘先斌 . 一类分段光滑隔振系统的非线性动力学设计方法
力学学报 , 2016 ,48 (1 ):192 -200
( Gao Xue Chen Qian Liu Xianbin , Nonlinear dynamics design for piecewise smooth vibration isolation system
Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics 2016 ,48 (1 ):192 -200 (in Chinese))
[7]
La VD . Semi-active on-off damping control of a dynamic vibration absorber using Coriolis force
Journal of Sound and Vibration 2012 ,331 (15 ):3429 -3436
DOI
URL
[本文引用: 1]
A passive dynamic vibration absorber (DVA) moving along a pendulum can cause the nonlinear Coriolis damping to reduce the pendulum swing. This paper proposes a simple semi-active on-off damping controller to improve the passive Coriolis DVA. The aim of the on-off damping control is to amplify the DVA resonance motion to increase the energy dissipated. Moreover, the paper finds the analytical solution of the harmonic vibration of semi-active controlled system. The accuracy of the analytical formulas and the superior performance of the semi-active DVA are verified by numerical simulations. (C) 2012 Elsevier Ltd.
[8]
Karnopp D Crosby MJ Harwood RA . Vibration control using semi-active force generators
Journal of Engineering for Industry 1974 ,96 (2 ):619 -626
[本文引用: 1]
[9]
Margolis DL Tylee JL Hrovat D . Heave mode dynamics of a tracked air cushion vehicle with semiactive airbag secondary suspension
Journal of Dynamic Systems,Measurement, and Control 1975 : 399 -407
[本文引用: 1]
[10]
Margolis DL . A procedure for comparing passive, active, and semi-active approaches to vibration isolation
Journal of the Franklin Institute 1983 : 225 -238
[本文引用: 1]
[11]
ValÁŠEk M NovÁK M ŠIka Z , et al . Extended ground-hook - new concept of semi-active control of truck's suspension
Vehicle System Dynamics 1997 ,27 (5-6 ):289 -303
[本文引用: 1]
[12]
Sergio MS Silani E Bittanti S . Acceleration-driven-damper (ADD)-An optimal control algorithm for comfort-oriented semiactive suspensions
Transactions of the ASME 2005 ,127 :218 -229
[本文引用: 1]
[13]
Savaresi SM Spelta C . Mixed sky-hook and ADD-Approaching the filtering limits of a semi-active suspension
Journal of Dynamic Systems, Measurement, and Control 2007 ,129 :382 -392
DOI
URL
[本文引用: 1]
[14]
Savaresi SM Spelta C . Mix-1-sensor: A control strategy for semi-active suspension
IFAC Proceedings Volumes 2007 ,40 (10 ):367 -374
[本文引用: 1]
[15]
Morselli R Zanasi R . Control of port Hamiltonian systems by dissipative devices and its application to improve the semi-active suspension behaviour
Mechatronics 2008 ,18 (7 ):364 -369
DOI
URL
[本文引用: 1]
AbstractThe port Hamiltonian framework is a powerful tool for modeling a wide class of nonlinear systems such as robots and, more generally, mechatronic systems. The standard approaches used for the control of the port Hamiltonian systems are not applicable to a wide variety of mechatronic systems. This happens, for example, when the input control variable acts directly on some dissipative components of the system. In these cases the controlled devices can only dissipate power and the problem is to find a proper control law in order to meet the control requirements. This paper proposes four control laws for the controlled dissipative components which allow to satisfy a set of control requirements by acting on the energy stored in a subsection of the given system or by controlling the power flowing through a physical section of the system. Although some important issues remain open, the example of the semi-active suspension shows that some positive results can be achieved by applying the proposed approach.]]>
[16]
Nirala CK Kumar RP . A new semi-active suspension system based on Jerk Driven Damper (JDD) Control
// Proceedings of the International Conference on Computational Methods in Manufacturing (ICCMM 2011) , 2011 : 562 -568
[本文引用: 1]
[17]
Poussot-Vassal C Spelta C Sename O , et al . Survey and performance evaluation on some automotive semi-active suspension control methods: A comparative study on a single-corner model
Annual Reviews in Control 2012 ,36 (1 ):148 -160
DOI
URL
[本文引用: 1]
In this paper, an overview and a benchmark of some semi-active suspension control strategy performances is proposed. Based on a recent result of the authors, where the optimal semi-active performance trade-off was addressed, here a complete benchmark to evaluate any controlled semi-active suspension is proposed, and applied to different control approaches. This paper aims at providing a picture - as complete as possible - of the present state of the art in the semi-active suspension control field in terms of comfort and road-holding performance evaluation and trade-off. (C) 2012 Elsevier Ltd.
[18]
Shen Y Wang L Yang S , et al . Nonlinear dynamical analysis and parameters optimization of four semi-active on-off dynamic vibration absorbers
Journal of Vibration and Control 2012 ,19 (1 ):143 -160
DOI
URL
[本文引用: 1]
[19]
Díaz IM Reynolds P . On-off nonlinear active control of floor vibrations
Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing 2010 ,24 (6 ):1711 -1726
DOI
URL
[本文引用: 1]
AbstractHuman-induced floor vibrations can be mitigated by means of active control via an electromagnetic proof-mass actuator. Previous researchers have developed a system for floor vibration comprising linear velocity feedback control (LVFC) with a command limiter (saturation in the command signal to avoid actuator overloading). The performance of this control is highly dependent on the linear gain utilised, which has to be designed for a particular excitation and might not be optimum for other excitations. This work explores the use of on-off nonlinear velocity feedback control (NLVFC) as the natural evolution of LVFC when high gains and/or significant vibration level are present together with saturation in the control law. Firstly, the describing function tool is employed to analyse the stability properties of: (1) LVFC with saturation, (2) on-off NLVFC with a dead zone and (3) on-off NLVFC with a switching-off function. Particular emphasis is paid to the resulting limit cycle behaviour and the design of appropriate dead zone and switching-off levels to avoid it. Secondly, experimental trials using the three control laws are conducted on a laboratory test floor. The results corroborate the analytical stability predictions. The pros of on-off NLVFC are that no gain has to be chosen and maximum actuator energy is delivered to cancel the vibration. In contrast, the requirement to select a dead zone or switching-off function provides a drawback in its application.]]>
[20]
Eslaminasab N Vahid AO Golnaraghi F . Nonlinear analysis of switched semi-active controlled systems
Vehicle System Dynamics 2011 ,49 (1-2 ):291 -309
DOI
URL
[本文引用: 1]
Semi-active systems improve suspension performance of the vehicles more effectively than conventional passive systems by simultaneously improving ride comfort and road handling. Also, because of size, weight, price and performance advantages, they have gained more interest over the active as well as passive systems. Probably the most neglected aspect of the semi-active on-off control systems and strategies is the effects of the added nonlinearities of those systems, which are introduced and analysed in this paper. To do so, numerical techniques, analytical method of averaging and experimental analysis are deployed. In this paper, a new method to analyse, calculate and compare the performances of the semi-active controlled systems is proposed; further, a new controller based on the observations of actual test data is proposed to eliminate the adverse effects of added nonlinearities. The significance of the proposed new system is the simplicity of the algorithm and ease of implementation. In fact, this new semi-active control strategy could be easily adopted and used with most of the existing semi-active control systems.
[21]
申永军 , 杨绍普 , 陈恩利 等 . 一类半主动控制非线性系统的动力学分析
振动工程学报 , 2005 ,18 (2 ):219 -222
[本文引用: 1]
( Shen Yongjun Yang Shaopu Chen Enli , et al . Dynamic analysis of a nonlinear system under semi-active control
Journal of Vibration Engineering 2005 ,18 (2 ):219 -222 (in Chinese))
[本文引用: 1]
[22]
申永军 , 祁玉玲 , 杨绍普 等 . 含时滞的单自由度半主动悬架系统的动力学分析
振动与冲击 , 2012 ,31 (24 ):38 -40
URL
对含时滞的单自由度半主动开关控制悬架系统进行了研究。首先对系统进行无量纲化处理,然后利用平均法求出了系统方程的一次近似解析解。通过解析解与数值解得到的幅频曲线进行比较,验证了本文方法和结果的正确性。最后对系统的稳定性做了分析,得到了导致系统产生不稳定运动的条件和临界时滞,发现系统的稳定性随着时滞会发生周期性变化。]]>
( Shen Yongjun Qi Yuling Yang Shaopu , et al , Dynamic analysis of a SDOF semi-active suspension system with time-delay
Journal of Vibration and Shock 2012 ,31 (24 ):38 -40 (in Chinese))
URL
A single degree-of-freedom (SDOF) semi-active on-off control suspension system with time-delay is studied in this paper.After the dimensionless form is deduced, the first-order approximately analytical solution is obtained by the averaging method.The comparison of the amplitude-frequency curves obtained by the analytical solution and the numerical one shows the correctness of the method and results in this paper.At last, the system stability is analyzed, and the instability condition and the critical time-delay are presented.The periodical change of stability with the time-delay is also illustrated.]]>
[23]
申永军 , 赵永香 , 田佳雨 等 . 一类含时滞的半主动悬架系统的动力学分析
力学学报 , 2013 ,45 (5 ):756 -762
[本文引用: 1]
( Shen Yongjun Zhao Yongxiang Tian Jiayu , et al , Dynamical analysis on a kind of semi-active suspension with time delay
Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics 2013 ,45 (5 ):756 -762 (in Chinese))
[本文引用: 1]
[24]
申永军 , 田佳雨 , 赵永香 等 . 含时滞半主动天棚悬架系统的解析研究
振动、测试与诊断 , 2014 ,34 (6 ):1110 -1117
[本文引用: 1]
( Shen Yongjun Tian Jiayu Zhao Yongxiang , et al . Analytical study on semi-active skyhook suspension with time delay
Journal of Vibration, Measurement & Diagnosis 2014 ,34 (6 ):1110 -1117 (in Chinese))
[本文引用: 1]
[25]
Yu H Sun X Xu J , et al . The time-delay coupling nonlinear effect in sky-hook control of vibration isolation systems using Magneto-Rheological Fluid dampers
Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology 2016 ,30 (9 ):4157 -4166
DOI
URL
[本文引用: 2]
[26]
Fischer D Isermann R . Mechatronic semi-active and active vehicle suspensions
Control Engineering Practice 2004 ,12 (11 ):1353 -1367
DOI
URL
[本文引用: 1]
[27]
王昊 , 胡海岩 . 基于磁流变阻尼器整车半主动悬架的开关控制
动力学与控制学报 , 2004 ,2 (4 ):71 -76
[本文引用: 1]
( Wang Hao Hu Haiyan . The on-off control of a semi-active suspension of the full-vehicle model based on MR dampers
Journal of Dynamics and Control 2004 ,2 (4 ):71 -76 (in Chinese))
[本文引用: 1]
[28]
Kim HS Chang C Kang JW . Control performance evaluation of semi-active tmd subjected to various types of loads
International Journal of Steel Structures 2015 ,15 (3 ):581 -594
[本文引用: 1]
[29]
Dong X Yu M Liao C , et al . Comparative research on semi-active control strategies for~magneto-rheological suspension
Nonlinear Dynamics 2010 ,59 (3 ):433 -453
[本文引用: 1]
[30]
Sun X Xu J Fu J . The effect and design of time delay in feedback control for a nonlinear isolation system
Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing 2017 ,87 :206 -217
[本文引用: 1]
[31]
胡海岩 . 应用非线性动力学 . 北京 : 航空工业出版社 , 2000 : 48 -51
[本文引用: 1]
( Hu Haiyan . Applied Nonlinear Dynamics . Beijing : Aviation Industry Press , 2000 : 48 -51 (in Chinese))
[本文引用: 1]
[32]
Li S Yang S Guo W . Investigation on chaotic motion in hysteretic non-linear suspension system with multi-frequency excitations
Mechanics Research Communications 2004 ,31 (2 ):229 -236
[本文引用: 1]
[33]
张洪欣 . 汽车系统动力学 . 上海 : 同济大学出版社 , 1996 : 126 -140
[本文引用: 1]
( Zhang Hongxin . Automobile System Dynamics . Shanghai : Tongji University Publishing House , 1996 : 126 -140 (in Chinese))
[本文引用: 1]
[34]
Wang W Song Y . Analytical computation method for steady-state stochastic response of a time-delay nonlinear automotive suspension system
Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing 2019 ,131 :434 -445
[本文引用: 1]
[35]
Xu Y Liu Q Guo G , et al . Dynamical responses of airfoil models with harmonic excitation under uncertain disturbance
Nonlinear Dynamics 2017 ,89 :1579 -1590
[36]
Liu Q Xu Y Kurths J . Bistability and stochastic jumps in an airfoil system with viscoelastic material property and random fluctuations
Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simulat 2020 ,84 :105184
[37]
刘俊 , 陈林聪 , 孙建桥 . 随机激励下滞迟系统的稳态响应闭合解
力学学报 , 2017 ,49 (3 ):685 -692
( Liu Jun Chen Lincong Sun Jianqiao . The closed-form solution of steady state response of hysteretic system under stochastic excitation
Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics 2017 ,49 (3 ):685 -692 (in Chinese))
[38]
公徐路 , 许鹏飞 . 含时滞反馈与涨落质量的记忆阻尼系统的随机共振
力学学报 , 2018 ,50 (4 ):880 -889
( Gong Xulu Xu Pengfei . Stochastic resonance of a memorial-damped system with time delay feedback and fluctuating mass
Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics 2018 ,50 (4 ):880 -889 (in Chinese))
[39]
邢昭阳 , 申永军 , 邢海军 等 . 一种含放大机构的负刚度动力吸振器的参数优化
力学学报 , 2019 ,51 (3 ):894 -903
[本文引用: 1]
( Xing Zhaoyang Shen Yongjun Xing Haijun , et al . Parameters optimization of a dynamic vibration absorber with amplifying mechanism and negative stiffness
Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics 2019 ,51 (3 ):894 -903 (in Chinese))
[本文引用: 1]
[40]
刘献栋 , 邓志党 , 高峰 . 公路路面不平度的数值模拟方法研究
北京航空航天大学学报 , 2003 ,29 (9 ):843 -846
[本文引用: 1]
( Liu Xiandong Deng Zhidang Gao Feng . Research on the method of simulating road roughness numerically
Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics 2003 ,29 (9 ):843 -846 (in Chinese))
[本文引用: 1]
[41]
ISO 2631-1: 1997 (E) . Mechanical vibration and shock-evaluation of human exposure to whole-body vibration . 1997
[本文引用: 1]
几何非线性摩擦阻尼隔振系统动力学行为研究
1
2019
... 隔振是一种有效的振动控制方式,通过在振源和隔振对象之间合理设计隔振装置,选择合适的隔振系统的阻尼或者刚度,使得振源传至隔振对象的力或运动激励降低,减小外部扰动向系统敏感部分的传递,达到良好的隔振效果[1 -2 ] .传统的被动隔振系统结构和参数一旦确定就无法改变,无法满足复杂多变的工况条件,也无法协调共振响应与高频衰减之间的矛盾,制约了被动隔振系统性能的进一步提高. 主动隔振系统减振效果好,但是成本高、能量消耗大、结构复杂.而基于半主动控制的隔振系统具有被动控制简单易操作和主动控制良好的隔振性能的优势,近年来在车辆悬架减振系统、高精密机械系统、飞机着陆装置、建筑结构振动控制系统、船舶的可控浮阀隔振系统中得到了广泛的应用[3 -7 ] . ...
几何非线性摩擦阻尼隔振系统动力学行为研究
1
2019
... 隔振是一种有效的振动控制方式,通过在振源和隔振对象之间合理设计隔振装置,选择合适的隔振系统的阻尼或者刚度,使得振源传至隔振对象的力或运动激励降低,减小外部扰动向系统敏感部分的传递,达到良好的隔振效果[1 -2 ] .传统的被动隔振系统结构和参数一旦确定就无法改变,无法满足复杂多变的工况条件,也无法协调共振响应与高频衰减之间的矛盾,制约了被动隔振系统性能的进一步提高. 主动隔振系统减振效果好,但是成本高、能量消耗大、结构复杂.而基于半主动控制的隔振系统具有被动控制简单易操作和主动控制良好的隔振性能的优势,近年来在车辆悬架减振系统、高精密机械系统、飞机着陆装置、建筑结构振动控制系统、船舶的可控浮阀隔振系统中得到了广泛的应用[3 -7 ] . ...
非线性被动隔振的若干进展
1
2017
... 隔振是一种有效的振动控制方式,通过在振源和隔振对象之间合理设计隔振装置,选择合适的隔振系统的阻尼或者刚度,使得振源传至隔振对象的力或运动激励降低,减小外部扰动向系统敏感部分的传递,达到良好的隔振效果[1 -2 ] .传统的被动隔振系统结构和参数一旦确定就无法改变,无法满足复杂多变的工况条件,也无法协调共振响应与高频衰减之间的矛盾,制约了被动隔振系统性能的进一步提高. 主动隔振系统减振效果好,但是成本高、能量消耗大、结构复杂.而基于半主动控制的隔振系统具有被动控制简单易操作和主动控制良好的隔振性能的优势,近年来在车辆悬架减振系统、高精密机械系统、飞机着陆装置、建筑结构振动控制系统、船舶的可控浮阀隔振系统中得到了广泛的应用[3 -7 ] . ...
非线性被动隔振的若干进展
1
2017
... 隔振是一种有效的振动控制方式,通过在振源和隔振对象之间合理设计隔振装置,选择合适的隔振系统的阻尼或者刚度,使得振源传至隔振对象的力或运动激励降低,减小外部扰动向系统敏感部分的传递,达到良好的隔振效果[1 -2 ] .传统的被动隔振系统结构和参数一旦确定就无法改变,无法满足复杂多变的工况条件,也无法协调共振响应与高频衰减之间的矛盾,制约了被动隔振系统性能的进一步提高. 主动隔振系统减振效果好,但是成本高、能量消耗大、结构复杂.而基于半主动控制的隔振系统具有被动控制简单易操作和主动控制良好的隔振性能的优势,近年来在车辆悬架减振系统、高精密机械系统、飞机着陆装置、建筑结构振动控制系统、船舶的可控浮阀隔振系统中得到了广泛的应用[3 -7 ] . ...
Active suspension in railway vehicles: a literature survey
1
2020
... 隔振是一种有效的振动控制方式,通过在振源和隔振对象之间合理设计隔振装置,选择合适的隔振系统的阻尼或者刚度,使得振源传至隔振对象的力或运动激励降低,减小外部扰动向系统敏感部分的传递,达到良好的隔振效果[1 -2 ] .传统的被动隔振系统结构和参数一旦确定就无法改变,无法满足复杂多变的工况条件,也无法协调共振响应与高频衰减之间的矛盾,制约了被动隔振系统性能的进一步提高. 主动隔振系统减振效果好,但是成本高、能量消耗大、结构复杂.而基于半主动控制的隔振系统具有被动控制简单易操作和主动控制良好的隔振性能的优势,近年来在车辆悬架减振系统、高精密机械系统、飞机着陆装置、建筑结构振动控制系统、船舶的可控浮阀隔振系统中得到了广泛的应用[3 -7 ] . ...
半主动控制浮筏隔振系统的开关算法与仿真研究
0
2016
半主动控制浮筏隔振系统的开关算法与仿真研究
0
2016
Semi-active suspension control design for vehicles
0
2010
一类分段光滑隔振系统的非线性动力学设计方法
0
2016
一类分段光滑隔振系统的非线性动力学设计方法
0
2016
Semi-active on-off damping control of a dynamic vibration absorber using Coriolis force
1
2012
... 隔振是一种有效的振动控制方式,通过在振源和隔振对象之间合理设计隔振装置,选择合适的隔振系统的阻尼或者刚度,使得振源传至隔振对象的力或运动激励降低,减小外部扰动向系统敏感部分的传递,达到良好的隔振效果[1 -2 ] .传统的被动隔振系统结构和参数一旦确定就无法改变,无法满足复杂多变的工况条件,也无法协调共振响应与高频衰减之间的矛盾,制约了被动隔振系统性能的进一步提高. 主动隔振系统减振效果好,但是成本高、能量消耗大、结构复杂.而基于半主动控制的隔振系统具有被动控制简单易操作和主动控制良好的隔振性能的优势,近年来在车辆悬架减振系统、高精密机械系统、飞机着陆装置、建筑结构振动控制系统、船舶的可控浮阀隔振系统中得到了广泛的应用[3 -7 ] . ...
Vibration control using semi-active force generators
1
1974
... 半主动控制属于参数控制,根据一定规则来实时改变结构的刚度或阻尼等参数,进而提高隔振系统在不同激励下的隔振性能,控制过程依赖于结构反应及外部激励信息. 相对于变刚度,采用电子控制阻尼调节的方法来实现阻尼控制更为容易,目前已有很多成熟的可控阻尼器,如电流变阻尼器和磁流变阻尼器等. 在隔振系统的半主动控制中,控制策略直接决定着隔振系统的隔振效果.Karnopp 等[8 ] 在 1974 年首次提出了半主动悬架系统速度负反馈的 "天棚" (sky-hook,SH) 阻尼控制算法;Margolis 等[9 -10 ] 在天棚阻尼控制的基础上提出了开关控制,即阻尼力与相对速度的乘积为正,则阻尼器从悬架系统吸收能量,起到减振的效果;反之表示阻尼器要向悬架系统提供能量.Valasek 等[11 ] 根据 SH 原理,提出了与 SH 算法相似的 "地棚" (ground-hook,GH) 阻尼控制算法,将非簧载质量与大地连接在一起,以大地作为系统坐标,目的是减小非簧载质量加速度;Savaresi 等提出了加速度驱动阻尼 (acceleration driven damper,ADD) 控制算法[12 ] 用以优化簧载质量加速度,以及混合 SH-ADD 控制算法[13 -14 ] ,结合两种算法优势,在整个频域内提高车辆舒适性;Riccardo 等[15 ] 提出了动力驱动阻尼器 (power-driven-damper,PDD) 算法. Nirala 等[16 ] 提出了冲击驱动阻尼 (jerk drivendamper,JDD) 控制算法,在突然刹车时能有效减小垂向加速度.Poussot-Vassal 等[17 ] 对 SH,GH,ADD,SH-ADD 等多种半主动悬架控制方法进行了综述. ...
Heave mode dynamics of a tracked air cushion vehicle with semiactive airbag secondary suspension
1
1975
... 半主动控制属于参数控制,根据一定规则来实时改变结构的刚度或阻尼等参数,进而提高隔振系统在不同激励下的隔振性能,控制过程依赖于结构反应及外部激励信息. 相对于变刚度,采用电子控制阻尼调节的方法来实现阻尼控制更为容易,目前已有很多成熟的可控阻尼器,如电流变阻尼器和磁流变阻尼器等. 在隔振系统的半主动控制中,控制策略直接决定着隔振系统的隔振效果.Karnopp 等[8 ] 在 1974 年首次提出了半主动悬架系统速度负反馈的 "天棚" (sky-hook,SH) 阻尼控制算法;Margolis 等[9 -10 ] 在天棚阻尼控制的基础上提出了开关控制,即阻尼力与相对速度的乘积为正,则阻尼器从悬架系统吸收能量,起到减振的效果;反之表示阻尼器要向悬架系统提供能量.Valasek 等[11 ] 根据 SH 原理,提出了与 SH 算法相似的 "地棚" (ground-hook,GH) 阻尼控制算法,将非簧载质量与大地连接在一起,以大地作为系统坐标,目的是减小非簧载质量加速度;Savaresi 等提出了加速度驱动阻尼 (acceleration driven damper,ADD) 控制算法[12 ] 用以优化簧载质量加速度,以及混合 SH-ADD 控制算法[13 -14 ] ,结合两种算法优势,在整个频域内提高车辆舒适性;Riccardo 等[15 ] 提出了动力驱动阻尼器 (power-driven-damper,PDD) 算法. Nirala 等[16 ] 提出了冲击驱动阻尼 (jerk drivendamper,JDD) 控制算法,在突然刹车时能有效减小垂向加速度.Poussot-Vassal 等[17 ] 对 SH,GH,ADD,SH-ADD 等多种半主动悬架控制方法进行了综述. ...
A procedure for comparing passive, active, and semi-active approaches to vibration isolation
1
1983
... 半主动控制属于参数控制,根据一定规则来实时改变结构的刚度或阻尼等参数,进而提高隔振系统在不同激励下的隔振性能,控制过程依赖于结构反应及外部激励信息. 相对于变刚度,采用电子控制阻尼调节的方法来实现阻尼控制更为容易,目前已有很多成熟的可控阻尼器,如电流变阻尼器和磁流变阻尼器等. 在隔振系统的半主动控制中,控制策略直接决定着隔振系统的隔振效果.Karnopp 等[8 ] 在 1974 年首次提出了半主动悬架系统速度负反馈的 "天棚" (sky-hook,SH) 阻尼控制算法;Margolis 等[9 -10 ] 在天棚阻尼控制的基础上提出了开关控制,即阻尼力与相对速度的乘积为正,则阻尼器从悬架系统吸收能量,起到减振的效果;反之表示阻尼器要向悬架系统提供能量.Valasek 等[11 ] 根据 SH 原理,提出了与 SH 算法相似的 "地棚" (ground-hook,GH) 阻尼控制算法,将非簧载质量与大地连接在一起,以大地作为系统坐标,目的是减小非簧载质量加速度;Savaresi 等提出了加速度驱动阻尼 (acceleration driven damper,ADD) 控制算法[12 ] 用以优化簧载质量加速度,以及混合 SH-ADD 控制算法[13 -14 ] ,结合两种算法优势,在整个频域内提高车辆舒适性;Riccardo 等[15 ] 提出了动力驱动阻尼器 (power-driven-damper,PDD) 算法. Nirala 等[16 ] 提出了冲击驱动阻尼 (jerk drivendamper,JDD) 控制算法,在突然刹车时能有效减小垂向加速度.Poussot-Vassal 等[17 ] 对 SH,GH,ADD,SH-ADD 等多种半主动悬架控制方法进行了综述. ...
Extended ground-hook - new concept of semi-active control of truck's suspension
1
1997
... 半主动控制属于参数控制,根据一定规则来实时改变结构的刚度或阻尼等参数,进而提高隔振系统在不同激励下的隔振性能,控制过程依赖于结构反应及外部激励信息. 相对于变刚度,采用电子控制阻尼调节的方法来实现阻尼控制更为容易,目前已有很多成熟的可控阻尼器,如电流变阻尼器和磁流变阻尼器等. 在隔振系统的半主动控制中,控制策略直接决定着隔振系统的隔振效果.Karnopp 等[8 ] 在 1974 年首次提出了半主动悬架系统速度负反馈的 "天棚" (sky-hook,SH) 阻尼控制算法;Margolis 等[9 -10 ] 在天棚阻尼控制的基础上提出了开关控制,即阻尼力与相对速度的乘积为正,则阻尼器从悬架系统吸收能量,起到减振的效果;反之表示阻尼器要向悬架系统提供能量.Valasek 等[11 ] 根据 SH 原理,提出了与 SH 算法相似的 "地棚" (ground-hook,GH) 阻尼控制算法,将非簧载质量与大地连接在一起,以大地作为系统坐标,目的是减小非簧载质量加速度;Savaresi 等提出了加速度驱动阻尼 (acceleration driven damper,ADD) 控制算法[12 ] 用以优化簧载质量加速度,以及混合 SH-ADD 控制算法[13 -14 ] ,结合两种算法优势,在整个频域内提高车辆舒适性;Riccardo 等[15 ] 提出了动力驱动阻尼器 (power-driven-damper,PDD) 算法. Nirala 等[16 ] 提出了冲击驱动阻尼 (jerk drivendamper,JDD) 控制算法,在突然刹车时能有效减小垂向加速度.Poussot-Vassal 等[17 ] 对 SH,GH,ADD,SH-ADD 等多种半主动悬架控制方法进行了综述. ...
Acceleration-driven-damper (ADD)-An optimal control algorithm for comfort-oriented semiactive suspensions
1
2005
... 半主动控制属于参数控制,根据一定规则来实时改变结构的刚度或阻尼等参数,进而提高隔振系统在不同激励下的隔振性能,控制过程依赖于结构反应及外部激励信息. 相对于变刚度,采用电子控制阻尼调节的方法来实现阻尼控制更为容易,目前已有很多成熟的可控阻尼器,如电流变阻尼器和磁流变阻尼器等. 在隔振系统的半主动控制中,控制策略直接决定着隔振系统的隔振效果.Karnopp 等[8 ] 在 1974 年首次提出了半主动悬架系统速度负反馈的 "天棚" (sky-hook,SH) 阻尼控制算法;Margolis 等[9 -10 ] 在天棚阻尼控制的基础上提出了开关控制,即阻尼力与相对速度的乘积为正,则阻尼器从悬架系统吸收能量,起到减振的效果;反之表示阻尼器要向悬架系统提供能量.Valasek 等[11 ] 根据 SH 原理,提出了与 SH 算法相似的 "地棚" (ground-hook,GH) 阻尼控制算法,将非簧载质量与大地连接在一起,以大地作为系统坐标,目的是减小非簧载质量加速度;Savaresi 等提出了加速度驱动阻尼 (acceleration driven damper,ADD) 控制算法[12 ] 用以优化簧载质量加速度,以及混合 SH-ADD 控制算法[13 -14 ] ,结合两种算法优势,在整个频域内提高车辆舒适性;Riccardo 等[15 ] 提出了动力驱动阻尼器 (power-driven-damper,PDD) 算法. Nirala 等[16 ] 提出了冲击驱动阻尼 (jerk drivendamper,JDD) 控制算法,在突然刹车时能有效减小垂向加速度.Poussot-Vassal 等[17 ] 对 SH,GH,ADD,SH-ADD 等多种半主动悬架控制方法进行了综述. ...
Mixed sky-hook and ADD-Approaching the filtering limits of a semi-active suspension
1
2007
... 半主动控制属于参数控制,根据一定规则来实时改变结构的刚度或阻尼等参数,进而提高隔振系统在不同激励下的隔振性能,控制过程依赖于结构反应及外部激励信息. 相对于变刚度,采用电子控制阻尼调节的方法来实现阻尼控制更为容易,目前已有很多成熟的可控阻尼器,如电流变阻尼器和磁流变阻尼器等. 在隔振系统的半主动控制中,控制策略直接决定着隔振系统的隔振效果.Karnopp 等[8 ] 在 1974 年首次提出了半主动悬架系统速度负反馈的 "天棚" (sky-hook,SH) 阻尼控制算法;Margolis 等[9 -10 ] 在天棚阻尼控制的基础上提出了开关控制,即阻尼力与相对速度的乘积为正,则阻尼器从悬架系统吸收能量,起到减振的效果;反之表示阻尼器要向悬架系统提供能量.Valasek 等[11 ] 根据 SH 原理,提出了与 SH 算法相似的 "地棚" (ground-hook,GH) 阻尼控制算法,将非簧载质量与大地连接在一起,以大地作为系统坐标,目的是减小非簧载质量加速度;Savaresi 等提出了加速度驱动阻尼 (acceleration driven damper,ADD) 控制算法[12 ] 用以优化簧载质量加速度,以及混合 SH-ADD 控制算法[13 -14 ] ,结合两种算法优势,在整个频域内提高车辆舒适性;Riccardo 等[15 ] 提出了动力驱动阻尼器 (power-driven-damper,PDD) 算法. Nirala 等[16 ] 提出了冲击驱动阻尼 (jerk drivendamper,JDD) 控制算法,在突然刹车时能有效减小垂向加速度.Poussot-Vassal 等[17 ] 对 SH,GH,ADD,SH-ADD 等多种半主动悬架控制方法进行了综述. ...
Mix-1-sensor: A control strategy for semi-active suspension
1
2007
... 半主动控制属于参数控制,根据一定规则来实时改变结构的刚度或阻尼等参数,进而提高隔振系统在不同激励下的隔振性能,控制过程依赖于结构反应及外部激励信息. 相对于变刚度,采用电子控制阻尼调节的方法来实现阻尼控制更为容易,目前已有很多成熟的可控阻尼器,如电流变阻尼器和磁流变阻尼器等. 在隔振系统的半主动控制中,控制策略直接决定着隔振系统的隔振效果.Karnopp 等[8 ] 在 1974 年首次提出了半主动悬架系统速度负反馈的 "天棚" (sky-hook,SH) 阻尼控制算法;Margolis 等[9 -10 ] 在天棚阻尼控制的基础上提出了开关控制,即阻尼力与相对速度的乘积为正,则阻尼器从悬架系统吸收能量,起到减振的效果;反之表示阻尼器要向悬架系统提供能量.Valasek 等[11 ] 根据 SH 原理,提出了与 SH 算法相似的 "地棚" (ground-hook,GH) 阻尼控制算法,将非簧载质量与大地连接在一起,以大地作为系统坐标,目的是减小非簧载质量加速度;Savaresi 等提出了加速度驱动阻尼 (acceleration driven damper,ADD) 控制算法[12 ] 用以优化簧载质量加速度,以及混合 SH-ADD 控制算法[13 -14 ] ,结合两种算法优势,在整个频域内提高车辆舒适性;Riccardo 等[15 ] 提出了动力驱动阻尼器 (power-driven-damper,PDD) 算法. Nirala 等[16 ] 提出了冲击驱动阻尼 (jerk drivendamper,JDD) 控制算法,在突然刹车时能有效减小垂向加速度.Poussot-Vassal 等[17 ] 对 SH,GH,ADD,SH-ADD 等多种半主动悬架控制方法进行了综述. ...
Control of port Hamiltonian systems by dissipative devices and its application to improve the semi-active suspension behaviour
1
2008
... 半主动控制属于参数控制,根据一定规则来实时改变结构的刚度或阻尼等参数,进而提高隔振系统在不同激励下的隔振性能,控制过程依赖于结构反应及外部激励信息. 相对于变刚度,采用电子控制阻尼调节的方法来实现阻尼控制更为容易,目前已有很多成熟的可控阻尼器,如电流变阻尼器和磁流变阻尼器等. 在隔振系统的半主动控制中,控制策略直接决定着隔振系统的隔振效果.Karnopp 等[8 ] 在 1974 年首次提出了半主动悬架系统速度负反馈的 "天棚" (sky-hook,SH) 阻尼控制算法;Margolis 等[9 -10 ] 在天棚阻尼控制的基础上提出了开关控制,即阻尼力与相对速度的乘积为正,则阻尼器从悬架系统吸收能量,起到减振的效果;反之表示阻尼器要向悬架系统提供能量.Valasek 等[11 ] 根据 SH 原理,提出了与 SH 算法相似的 "地棚" (ground-hook,GH) 阻尼控制算法,将非簧载质量与大地连接在一起,以大地作为系统坐标,目的是减小非簧载质量加速度;Savaresi 等提出了加速度驱动阻尼 (acceleration driven damper,ADD) 控制算法[12 ] 用以优化簧载质量加速度,以及混合 SH-ADD 控制算法[13 -14 ] ,结合两种算法优势,在整个频域内提高车辆舒适性;Riccardo 等[15 ] 提出了动力驱动阻尼器 (power-driven-damper,PDD) 算法. Nirala 等[16 ] 提出了冲击驱动阻尼 (jerk drivendamper,JDD) 控制算法,在突然刹车时能有效减小垂向加速度.Poussot-Vassal 等[17 ] 对 SH,GH,ADD,SH-ADD 等多种半主动悬架控制方法进行了综述. ...
A new semi-active suspension system based on Jerk Driven Damper (JDD) Control
1
2011
... 半主动控制属于参数控制,根据一定规则来实时改变结构的刚度或阻尼等参数,进而提高隔振系统在不同激励下的隔振性能,控制过程依赖于结构反应及外部激励信息. 相对于变刚度,采用电子控制阻尼调节的方法来实现阻尼控制更为容易,目前已有很多成熟的可控阻尼器,如电流变阻尼器和磁流变阻尼器等. 在隔振系统的半主动控制中,控制策略直接决定着隔振系统的隔振效果.Karnopp 等[8 ] 在 1974 年首次提出了半主动悬架系统速度负反馈的 "天棚" (sky-hook,SH) 阻尼控制算法;Margolis 等[9 -10 ] 在天棚阻尼控制的基础上提出了开关控制,即阻尼力与相对速度的乘积为正,则阻尼器从悬架系统吸收能量,起到减振的效果;反之表示阻尼器要向悬架系统提供能量.Valasek 等[11 ] 根据 SH 原理,提出了与 SH 算法相似的 "地棚" (ground-hook,GH) 阻尼控制算法,将非簧载质量与大地连接在一起,以大地作为系统坐标,目的是减小非簧载质量加速度;Savaresi 等提出了加速度驱动阻尼 (acceleration driven damper,ADD) 控制算法[12 ] 用以优化簧载质量加速度,以及混合 SH-ADD 控制算法[13 -14 ] ,结合两种算法优势,在整个频域内提高车辆舒适性;Riccardo 等[15 ] 提出了动力驱动阻尼器 (power-driven-damper,PDD) 算法. Nirala 等[16 ] 提出了冲击驱动阻尼 (jerk drivendamper,JDD) 控制算法,在突然刹车时能有效减小垂向加速度.Poussot-Vassal 等[17 ] 对 SH,GH,ADD,SH-ADD 等多种半主动悬架控制方法进行了综述. ...
Survey and performance evaluation on some automotive semi-active suspension control methods: A comparative study on a single-corner model
1
2012
... 半主动控制属于参数控制,根据一定规则来实时改变结构的刚度或阻尼等参数,进而提高隔振系统在不同激励下的隔振性能,控制过程依赖于结构反应及外部激励信息. 相对于变刚度,采用电子控制阻尼调节的方法来实现阻尼控制更为容易,目前已有很多成熟的可控阻尼器,如电流变阻尼器和磁流变阻尼器等. 在隔振系统的半主动控制中,控制策略直接决定着隔振系统的隔振效果.Karnopp 等[8 ] 在 1974 年首次提出了半主动悬架系统速度负反馈的 "天棚" (sky-hook,SH) 阻尼控制算法;Margolis 等[9 -10 ] 在天棚阻尼控制的基础上提出了开关控制,即阻尼力与相对速度的乘积为正,则阻尼器从悬架系统吸收能量,起到减振的效果;反之表示阻尼器要向悬架系统提供能量.Valasek 等[11 ] 根据 SH 原理,提出了与 SH 算法相似的 "地棚" (ground-hook,GH) 阻尼控制算法,将非簧载质量与大地连接在一起,以大地作为系统坐标,目的是减小非簧载质量加速度;Savaresi 等提出了加速度驱动阻尼 (acceleration driven damper,ADD) 控制算法[12 ] 用以优化簧载质量加速度,以及混合 SH-ADD 控制算法[13 -14 ] ,结合两种算法优势,在整个频域内提高车辆舒适性;Riccardo 等[15 ] 提出了动力驱动阻尼器 (power-driven-damper,PDD) 算法. Nirala 等[16 ] 提出了冲击驱动阻尼 (jerk drivendamper,JDD) 控制算法,在突然刹车时能有效减小垂向加速度.Poussot-Vassal 等[17 ] 对 SH,GH,ADD,SH-ADD 等多种半主动悬架控制方法进行了综述. ...
Nonlinear dynamical analysis and parameters optimization of four semi-active on-off dynamic vibration absorbers
1
2012
... 开关控制的思想是在高阻尼和低阻尼之间切换来实现减振的效果.由于半主动开关控制算法简单、响应快、易于实现,并能实现较好的控制效果,在实际工程中有很好的应用前景. 半主动控制系统中依据不同开关控制算法和切换条件,根据系统状态的不同来实现开、关两种不同状态下阻尼的快速切换,属于强非线性系统.其中,依据相对速度和不同变量的乘积作为切换条件的控制策略包括天棚阻尼控制算法、地棚阻尼控制算法和加速度驱动阻尼控制算法等.Shen 等[18 ] 对 4 种基于不同反馈的地棚阻尼控制策略的半主动吸振器进行了解析研究;Díaz 等[19 ] 分析了 3 种基于速度反馈的非线性开关控制在高增益和显著振级的振动下的饱和问题;Eslaminasab 等[20 ] 研究了半主动相对控制的单自由度悬架系统的控制效果;申永军等[21 -24 ] 分别采用有限相对位移控制、天棚控制等策略对含有时滞的单自由度半主动悬架系统进行了动力学分析;Yu 等[25 ] 分析了基于磁流变液阻尼器组成的天棚阻尼控制隔振系统的非线性和时滞特性;Fischer 等[26 ] 分析了主动和半主动车辆悬架系统;王昊等[27 ] 以某磁流变阻尼器作为作动器,研究了4种开关半主动控制策略对整车悬架系统参数的影响;Kim 等[28 ] 对比了在不同激励下主动、半主动和混合质量调谐阻尼器的控制效果;Dong 等[29 ] 对比分析了包括天棚阻尼控制、混合控制、滑模控制、LQG 控制和模糊逻辑控制等 5 种磁流变半主动悬架的控制效果.目前,大多数研究是采用数值分析的方法对控制性能进行分析,而且针对多种半主动控制策略的对比分析较少. ...
On-off nonlinear active control of floor vibrations
1
2010
... 开关控制的思想是在高阻尼和低阻尼之间切换来实现减振的效果.由于半主动开关控制算法简单、响应快、易于实现,并能实现较好的控制效果,在实际工程中有很好的应用前景. 半主动控制系统中依据不同开关控制算法和切换条件,根据系统状态的不同来实现开、关两种不同状态下阻尼的快速切换,属于强非线性系统.其中,依据相对速度和不同变量的乘积作为切换条件的控制策略包括天棚阻尼控制算法、地棚阻尼控制算法和加速度驱动阻尼控制算法等.Shen 等[18 ] 对 4 种基于不同反馈的地棚阻尼控制策略的半主动吸振器进行了解析研究;Díaz 等[19 ] 分析了 3 种基于速度反馈的非线性开关控制在高增益和显著振级的振动下的饱和问题;Eslaminasab 等[20 ] 研究了半主动相对控制的单自由度悬架系统的控制效果;申永军等[21 -24 ] 分别采用有限相对位移控制、天棚控制等策略对含有时滞的单自由度半主动悬架系统进行了动力学分析;Yu 等[25 ] 分析了基于磁流变液阻尼器组成的天棚阻尼控制隔振系统的非线性和时滞特性;Fischer 等[26 ] 分析了主动和半主动车辆悬架系统;王昊等[27 ] 以某磁流变阻尼器作为作动器,研究了4种开关半主动控制策略对整车悬架系统参数的影响;Kim 等[28 ] 对比了在不同激励下主动、半主动和混合质量调谐阻尼器的控制效果;Dong 等[29 ] 对比分析了包括天棚阻尼控制、混合控制、滑模控制、LQG 控制和模糊逻辑控制等 5 种磁流变半主动悬架的控制效果.目前,大多数研究是采用数值分析的方法对控制性能进行分析,而且针对多种半主动控制策略的对比分析较少. ...
Nonlinear analysis of switched semi-active controlled systems
1
2011
... 开关控制的思想是在高阻尼和低阻尼之间切换来实现减振的效果.由于半主动开关控制算法简单、响应快、易于实现,并能实现较好的控制效果,在实际工程中有很好的应用前景. 半主动控制系统中依据不同开关控制算法和切换条件,根据系统状态的不同来实现开、关两种不同状态下阻尼的快速切换,属于强非线性系统.其中,依据相对速度和不同变量的乘积作为切换条件的控制策略包括天棚阻尼控制算法、地棚阻尼控制算法和加速度驱动阻尼控制算法等.Shen 等[18 ] 对 4 种基于不同反馈的地棚阻尼控制策略的半主动吸振器进行了解析研究;Díaz 等[19 ] 分析了 3 种基于速度反馈的非线性开关控制在高增益和显著振级的振动下的饱和问题;Eslaminasab 等[20 ] 研究了半主动相对控制的单自由度悬架系统的控制效果;申永军等[21 -24 ] 分别采用有限相对位移控制、天棚控制等策略对含有时滞的单自由度半主动悬架系统进行了动力学分析;Yu 等[25 ] 分析了基于磁流变液阻尼器组成的天棚阻尼控制隔振系统的非线性和时滞特性;Fischer 等[26 ] 分析了主动和半主动车辆悬架系统;王昊等[27 ] 以某磁流变阻尼器作为作动器,研究了4种开关半主动控制策略对整车悬架系统参数的影响;Kim 等[28 ] 对比了在不同激励下主动、半主动和混合质量调谐阻尼器的控制效果;Dong 等[29 ] 对比分析了包括天棚阻尼控制、混合控制、滑模控制、LQG 控制和模糊逻辑控制等 5 种磁流变半主动悬架的控制效果.目前,大多数研究是采用数值分析的方法对控制性能进行分析,而且针对多种半主动控制策略的对比分析较少. ...
一类半主动控制非线性系统的动力学分析
1
2005
... 开关控制的思想是在高阻尼和低阻尼之间切换来实现减振的效果.由于半主动开关控制算法简单、响应快、易于实现,并能实现较好的控制效果,在实际工程中有很好的应用前景. 半主动控制系统中依据不同开关控制算法和切换条件,根据系统状态的不同来实现开、关两种不同状态下阻尼的快速切换,属于强非线性系统.其中,依据相对速度和不同变量的乘积作为切换条件的控制策略包括天棚阻尼控制算法、地棚阻尼控制算法和加速度驱动阻尼控制算法等.Shen 等[18 ] 对 4 种基于不同反馈的地棚阻尼控制策略的半主动吸振器进行了解析研究;Díaz 等[19 ] 分析了 3 种基于速度反馈的非线性开关控制在高增益和显著振级的振动下的饱和问题;Eslaminasab 等[20 ] 研究了半主动相对控制的单自由度悬架系统的控制效果;申永军等[21 -24 ] 分别采用有限相对位移控制、天棚控制等策略对含有时滞的单自由度半主动悬架系统进行了动力学分析;Yu 等[25 ] 分析了基于磁流变液阻尼器组成的天棚阻尼控制隔振系统的非线性和时滞特性;Fischer 等[26 ] 分析了主动和半主动车辆悬架系统;王昊等[27 ] 以某磁流变阻尼器作为作动器,研究了4种开关半主动控制策略对整车悬架系统参数的影响;Kim 等[28 ] 对比了在不同激励下主动、半主动和混合质量调谐阻尼器的控制效果;Dong 等[29 ] 对比分析了包括天棚阻尼控制、混合控制、滑模控制、LQG 控制和模糊逻辑控制等 5 种磁流变半主动悬架的控制效果.目前,大多数研究是采用数值分析的方法对控制性能进行分析,而且针对多种半主动控制策略的对比分析较少. ...
一类半主动控制非线性系统的动力学分析
1
2005
... 开关控制的思想是在高阻尼和低阻尼之间切换来实现减振的效果.由于半主动开关控制算法简单、响应快、易于实现,并能实现较好的控制效果,在实际工程中有很好的应用前景. 半主动控制系统中依据不同开关控制算法和切换条件,根据系统状态的不同来实现开、关两种不同状态下阻尼的快速切换,属于强非线性系统.其中,依据相对速度和不同变量的乘积作为切换条件的控制策略包括天棚阻尼控制算法、地棚阻尼控制算法和加速度驱动阻尼控制算法等.Shen 等[18 ] 对 4 种基于不同反馈的地棚阻尼控制策略的半主动吸振器进行了解析研究;Díaz 等[19 ] 分析了 3 种基于速度反馈的非线性开关控制在高增益和显著振级的振动下的饱和问题;Eslaminasab 等[20 ] 研究了半主动相对控制的单自由度悬架系统的控制效果;申永军等[21 -24 ] 分别采用有限相对位移控制、天棚控制等策略对含有时滞的单自由度半主动悬架系统进行了动力学分析;Yu 等[25 ] 分析了基于磁流变液阻尼器组成的天棚阻尼控制隔振系统的非线性和时滞特性;Fischer 等[26 ] 分析了主动和半主动车辆悬架系统;王昊等[27 ] 以某磁流变阻尼器作为作动器,研究了4种开关半主动控制策略对整车悬架系统参数的影响;Kim 等[28 ] 对比了在不同激励下主动、半主动和混合质量调谐阻尼器的控制效果;Dong 等[29 ] 对比分析了包括天棚阻尼控制、混合控制、滑模控制、LQG 控制和模糊逻辑控制等 5 种磁流变半主动悬架的控制效果.目前,大多数研究是采用数值分析的方法对控制性能进行分析,而且针对多种半主动控制策略的对比分析较少. ...
含时滞的单自由度半主动悬架系统的动力学分析
0
2012
含时滞的单自由度半主动悬架系统的动力学分析
0
2012
一类含时滞的半主动悬架系统的动力学分析
1
2013
... 对于给定的某一悬架系统,取各参数为[32 -33 ] :车体质量 $m =240$ kg,弹簧线性 刚度 $k_{1}=16 000$ N/m,非线性刚度 $k_{2} =320 000$ N/m.为对比在不同条件下近似解析解和数值解的吻合程度,在 3 种不同控制策略下的开/关阻尼系数及路面简谐激励振幅取值略有不同.数值解的求解采用 Runge-Kutta 法,计算时间为 800 s,将后 10% 的响应的最大值作为稳态响应的幅值.图2 ~图4 分别为在 ADD、SH 和 GH 控制策略下数值解和近似解析解得到的幅频响应曲线,图中横轴为激励频率 $\omega$,纵轴为响应振幅 $a$.从图2 ~图4 可以看出,3 种控制策略的解析解在不同的激励幅值和系统参数下,在低频区和共振区均和相应的数值解均具有较好的一致性,证明了系统解析解的求解方式的正确性和准确性. 需要注意的是,由于半主动控制系统响应中存在高阶奇次谐波成分,因此在高频区可能会表现出颤振现象[23 ] . ...
一类含时滞的半主动悬架系统的动力学分析
1
2013
... 对于给定的某一悬架系统,取各参数为[32 -33 ] :车体质量 $m =240$ kg,弹簧线性 刚度 $k_{1}=16 000$ N/m,非线性刚度 $k_{2} =320 000$ N/m.为对比在不同条件下近似解析解和数值解的吻合程度,在 3 种不同控制策略下的开/关阻尼系数及路面简谐激励振幅取值略有不同.数值解的求解采用 Runge-Kutta 法,计算时间为 800 s,将后 10% 的响应的最大值作为稳态响应的幅值.图2 ~图4 分别为在 ADD、SH 和 GH 控制策略下数值解和近似解析解得到的幅频响应曲线,图中横轴为激励频率 $\omega$,纵轴为响应振幅 $a$.从图2 ~图4 可以看出,3 种控制策略的解析解在不同的激励幅值和系统参数下,在低频区和共振区均和相应的数值解均具有较好的一致性,证明了系统解析解的求解方式的正确性和准确性. 需要注意的是,由于半主动控制系统响应中存在高阶奇次谐波成分,因此在高频区可能会表现出颤振现象[23 ] . ...
含时滞半主动天棚悬架系统的解析研究
1
2014
... 开关控制的思想是在高阻尼和低阻尼之间切换来实现减振的效果.由于半主动开关控制算法简单、响应快、易于实现,并能实现较好的控制效果,在实际工程中有很好的应用前景. 半主动控制系统中依据不同开关控制算法和切换条件,根据系统状态的不同来实现开、关两种不同状态下阻尼的快速切换,属于强非线性系统.其中,依据相对速度和不同变量的乘积作为切换条件的控制策略包括天棚阻尼控制算法、地棚阻尼控制算法和加速度驱动阻尼控制算法等.Shen 等[18 ] 对 4 种基于不同反馈的地棚阻尼控制策略的半主动吸振器进行了解析研究;Díaz 等[19 ] 分析了 3 种基于速度反馈的非线性开关控制在高增益和显著振级的振动下的饱和问题;Eslaminasab 等[20 ] 研究了半主动相对控制的单自由度悬架系统的控制效果;申永军等[21 -24 ] 分别采用有限相对位移控制、天棚控制等策略对含有时滞的单自由度半主动悬架系统进行了动力学分析;Yu 等[25 ] 分析了基于磁流变液阻尼器组成的天棚阻尼控制隔振系统的非线性和时滞特性;Fischer 等[26 ] 分析了主动和半主动车辆悬架系统;王昊等[27 ] 以某磁流变阻尼器作为作动器,研究了4种开关半主动控制策略对整车悬架系统参数的影响;Kim 等[28 ] 对比了在不同激励下主动、半主动和混合质量调谐阻尼器的控制效果;Dong 等[29 ] 对比分析了包括天棚阻尼控制、混合控制、滑模控制、LQG 控制和模糊逻辑控制等 5 种磁流变半主动悬架的控制效果.目前,大多数研究是采用数值分析的方法对控制性能进行分析,而且针对多种半主动控制策略的对比分析较少. ...
含时滞半主动天棚悬架系统的解析研究
1
2014
... 开关控制的思想是在高阻尼和低阻尼之间切换来实现减振的效果.由于半主动开关控制算法简单、响应快、易于实现,并能实现较好的控制效果,在实际工程中有很好的应用前景. 半主动控制系统中依据不同开关控制算法和切换条件,根据系统状态的不同来实现开、关两种不同状态下阻尼的快速切换,属于强非线性系统.其中,依据相对速度和不同变量的乘积作为切换条件的控制策略包括天棚阻尼控制算法、地棚阻尼控制算法和加速度驱动阻尼控制算法等.Shen 等[18 ] 对 4 种基于不同反馈的地棚阻尼控制策略的半主动吸振器进行了解析研究;Díaz 等[19 ] 分析了 3 种基于速度反馈的非线性开关控制在高增益和显著振级的振动下的饱和问题;Eslaminasab 等[20 ] 研究了半主动相对控制的单自由度悬架系统的控制效果;申永军等[21 -24 ] 分别采用有限相对位移控制、天棚控制等策略对含有时滞的单自由度半主动悬架系统进行了动力学分析;Yu 等[25 ] 分析了基于磁流变液阻尼器组成的天棚阻尼控制隔振系统的非线性和时滞特性;Fischer 等[26 ] 分析了主动和半主动车辆悬架系统;王昊等[27 ] 以某磁流变阻尼器作为作动器,研究了4种开关半主动控制策略对整车悬架系统参数的影响;Kim 等[28 ] 对比了在不同激励下主动、半主动和混合质量调谐阻尼器的控制效果;Dong 等[29 ] 对比分析了包括天棚阻尼控制、混合控制、滑模控制、LQG 控制和模糊逻辑控制等 5 种磁流变半主动悬架的控制效果.目前,大多数研究是采用数值分析的方法对控制性能进行分析,而且针对多种半主动控制策略的对比分析较少. ...
The time-delay coupling nonlinear effect in sky-hook control of vibration isolation systems using Magneto-Rheological Fluid dampers
2
2016
... 开关控制的思想是在高阻尼和低阻尼之间切换来实现减振的效果.由于半主动开关控制算法简单、响应快、易于实现,并能实现较好的控制效果,在实际工程中有很好的应用前景. 半主动控制系统中依据不同开关控制算法和切换条件,根据系统状态的不同来实现开、关两种不同状态下阻尼的快速切换,属于强非线性系统.其中,依据相对速度和不同变量的乘积作为切换条件的控制策略包括天棚阻尼控制算法、地棚阻尼控制算法和加速度驱动阻尼控制算法等.Shen 等[18 ] 对 4 种基于不同反馈的地棚阻尼控制策略的半主动吸振器进行了解析研究;Díaz 等[19 ] 分析了 3 种基于速度反馈的非线性开关控制在高增益和显著振级的振动下的饱和问题;Eslaminasab 等[20 ] 研究了半主动相对控制的单自由度悬架系统的控制效果;申永军等[21 -24 ] 分别采用有限相对位移控制、天棚控制等策略对含有时滞的单自由度半主动悬架系统进行了动力学分析;Yu 等[25 ] 分析了基于磁流变液阻尼器组成的天棚阻尼控制隔振系统的非线性和时滞特性;Fischer 等[26 ] 分析了主动和半主动车辆悬架系统;王昊等[27 ] 以某磁流变阻尼器作为作动器,研究了4种开关半主动控制策略对整车悬架系统参数的影响;Kim 等[28 ] 对比了在不同激励下主动、半主动和混合质量调谐阻尼器的控制效果;Dong 等[29 ] 对比分析了包括天棚阻尼控制、混合控制、滑模控制、LQG 控制和模糊逻辑控制等 5 种磁流变半主动悬架的控制效果.目前,大多数研究是采用数值分析的方法对控制性能进行分析,而且针对多种半主动控制策略的对比分析较少. ...
... 通常非线性半主动隔振系统都是基于"质量-弹簧-阻尼"结构体系来近似简化模型,其单自由度半主动隔振系统的模型[30 ] 如图1 所示,可用一个并联的弹性元件和阻尼器来表示.此模型中,除线性刚度和线性阻尼外,引入非 线性刚度,用以克服线性隔振技术的缺陷,改善系统隔振性能[25 ] .可控阻尼通过传感器对系统状态进行判断后,依据不同的变化规律,在一定范围内对可控阻尼进行调节,从而达到减振的效果.具有这种形式的如 1/4 车辆悬架系统、船舶浮阀减振系统等.以 1/4 车辆悬架为例,图1 中 $m$ 为车体质量,$x$ 为车体的位移,$x_0 $ 为路面激励,$F_1$ 为非线性弹性力:$F_1 = k_{1} (x_0 - x) + k_{2} (x_0 - x)^{3}$,其中 $k_{1} $ 表示线性刚度系数,$k_{2}$ 表示非线性刚度系数;$F_2 $ 为阻尼力:$F_2 = c(\dot {x}_0 - \dot {x})$,其中 $c$ 表示线性阻尼系数. ...
Mechatronic semi-active and active vehicle suspensions
1
2004
... 开关控制的思想是在高阻尼和低阻尼之间切换来实现减振的效果.由于半主动开关控制算法简单、响应快、易于实现,并能实现较好的控制效果,在实际工程中有很好的应用前景. 半主动控制系统中依据不同开关控制算法和切换条件,根据系统状态的不同来实现开、关两种不同状态下阻尼的快速切换,属于强非线性系统.其中,依据相对速度和不同变量的乘积作为切换条件的控制策略包括天棚阻尼控制算法、地棚阻尼控制算法和加速度驱动阻尼控制算法等.Shen 等[18 ] 对 4 种基于不同反馈的地棚阻尼控制策略的半主动吸振器进行了解析研究;Díaz 等[19 ] 分析了 3 种基于速度反馈的非线性开关控制在高增益和显著振级的振动下的饱和问题;Eslaminasab 等[20 ] 研究了半主动相对控制的单自由度悬架系统的控制效果;申永军等[21 -24 ] 分别采用有限相对位移控制、天棚控制等策略对含有时滞的单自由度半主动悬架系统进行了动力学分析;Yu 等[25 ] 分析了基于磁流变液阻尼器组成的天棚阻尼控制隔振系统的非线性和时滞特性;Fischer 等[26 ] 分析了主动和半主动车辆悬架系统;王昊等[27 ] 以某磁流变阻尼器作为作动器,研究了4种开关半主动控制策略对整车悬架系统参数的影响;Kim 等[28 ] 对比了在不同激励下主动、半主动和混合质量调谐阻尼器的控制效果;Dong 等[29 ] 对比分析了包括天棚阻尼控制、混合控制、滑模控制、LQG 控制和模糊逻辑控制等 5 种磁流变半主动悬架的控制效果.目前,大多数研究是采用数值分析的方法对控制性能进行分析,而且针对多种半主动控制策略的对比分析较少. ...
基于磁流变阻尼器整车半主动悬架的开关控制
1
2004
... 开关控制的思想是在高阻尼和低阻尼之间切换来实现减振的效果.由于半主动开关控制算法简单、响应快、易于实现,并能实现较好的控制效果,在实际工程中有很好的应用前景. 半主动控制系统中依据不同开关控制算法和切换条件,根据系统状态的不同来实现开、关两种不同状态下阻尼的快速切换,属于强非线性系统.其中,依据相对速度和不同变量的乘积作为切换条件的控制策略包括天棚阻尼控制算法、地棚阻尼控制算法和加速度驱动阻尼控制算法等.Shen 等[18 ] 对 4 种基于不同反馈的地棚阻尼控制策略的半主动吸振器进行了解析研究;Díaz 等[19 ] 分析了 3 种基于速度反馈的非线性开关控制在高增益和显著振级的振动下的饱和问题;Eslaminasab 等[20 ] 研究了半主动相对控制的单自由度悬架系统的控制效果;申永军等[21 -24 ] 分别采用有限相对位移控制、天棚控制等策略对含有时滞的单自由度半主动悬架系统进行了动力学分析;Yu 等[25 ] 分析了基于磁流变液阻尼器组成的天棚阻尼控制隔振系统的非线性和时滞特性;Fischer 等[26 ] 分析了主动和半主动车辆悬架系统;王昊等[27 ] 以某磁流变阻尼器作为作动器,研究了4种开关半主动控制策略对整车悬架系统参数的影响;Kim 等[28 ] 对比了在不同激励下主动、半主动和混合质量调谐阻尼器的控制效果;Dong 等[29 ] 对比分析了包括天棚阻尼控制、混合控制、滑模控制、LQG 控制和模糊逻辑控制等 5 种磁流变半主动悬架的控制效果.目前,大多数研究是采用数值分析的方法对控制性能进行分析,而且针对多种半主动控制策略的对比分析较少. ...
基于磁流变阻尼器整车半主动悬架的开关控制
1
2004
... 开关控制的思想是在高阻尼和低阻尼之间切换来实现减振的效果.由于半主动开关控制算法简单、响应快、易于实现,并能实现较好的控制效果,在实际工程中有很好的应用前景. 半主动控制系统中依据不同开关控制算法和切换条件,根据系统状态的不同来实现开、关两种不同状态下阻尼的快速切换,属于强非线性系统.其中,依据相对速度和不同变量的乘积作为切换条件的控制策略包括天棚阻尼控制算法、地棚阻尼控制算法和加速度驱动阻尼控制算法等.Shen 等[18 ] 对 4 种基于不同反馈的地棚阻尼控制策略的半主动吸振器进行了解析研究;Díaz 等[19 ] 分析了 3 种基于速度反馈的非线性开关控制在高增益和显著振级的振动下的饱和问题;Eslaminasab 等[20 ] 研究了半主动相对控制的单自由度悬架系统的控制效果;申永军等[21 -24 ] 分别采用有限相对位移控制、天棚控制等策略对含有时滞的单自由度半主动悬架系统进行了动力学分析;Yu 等[25 ] 分析了基于磁流变液阻尼器组成的天棚阻尼控制隔振系统的非线性和时滞特性;Fischer 等[26 ] 分析了主动和半主动车辆悬架系统;王昊等[27 ] 以某磁流变阻尼器作为作动器,研究了4种开关半主动控制策略对整车悬架系统参数的影响;Kim 等[28 ] 对比了在不同激励下主动、半主动和混合质量调谐阻尼器的控制效果;Dong 等[29 ] 对比分析了包括天棚阻尼控制、混合控制、滑模控制、LQG 控制和模糊逻辑控制等 5 种磁流变半主动悬架的控制效果.目前,大多数研究是采用数值分析的方法对控制性能进行分析,而且针对多种半主动控制策略的对比分析较少. ...
Control performance evaluation of semi-active tmd subjected to various types of loads
1
2015
... 开关控制的思想是在高阻尼和低阻尼之间切换来实现减振的效果.由于半主动开关控制算法简单、响应快、易于实现,并能实现较好的控制效果,在实际工程中有很好的应用前景. 半主动控制系统中依据不同开关控制算法和切换条件,根据系统状态的不同来实现开、关两种不同状态下阻尼的快速切换,属于强非线性系统.其中,依据相对速度和不同变量的乘积作为切换条件的控制策略包括天棚阻尼控制算法、地棚阻尼控制算法和加速度驱动阻尼控制算法等.Shen 等[18 ] 对 4 种基于不同反馈的地棚阻尼控制策略的半主动吸振器进行了解析研究;Díaz 等[19 ] 分析了 3 种基于速度反馈的非线性开关控制在高增益和显著振级的振动下的饱和问题;Eslaminasab 等[20 ] 研究了半主动相对控制的单自由度悬架系统的控制效果;申永军等[21 -24 ] 分别采用有限相对位移控制、天棚控制等策略对含有时滞的单自由度半主动悬架系统进行了动力学分析;Yu 等[25 ] 分析了基于磁流变液阻尼器组成的天棚阻尼控制隔振系统的非线性和时滞特性;Fischer 等[26 ] 分析了主动和半主动车辆悬架系统;王昊等[27 ] 以某磁流变阻尼器作为作动器,研究了4种开关半主动控制策略对整车悬架系统参数的影响;Kim 等[28 ] 对比了在不同激励下主动、半主动和混合质量调谐阻尼器的控制效果;Dong 等[29 ] 对比分析了包括天棚阻尼控制、混合控制、滑模控制、LQG 控制和模糊逻辑控制等 5 种磁流变半主动悬架的控制效果.目前,大多数研究是采用数值分析的方法对控制性能进行分析,而且针对多种半主动控制策略的对比分析较少. ...
Comparative research on semi-active control strategies for~magneto-rheological suspension
1
2010
... 开关控制的思想是在高阻尼和低阻尼之间切换来实现减振的效果.由于半主动开关控制算法简单、响应快、易于实现,并能实现较好的控制效果,在实际工程中有很好的应用前景. 半主动控制系统中依据不同开关控制算法和切换条件,根据系统状态的不同来实现开、关两种不同状态下阻尼的快速切换,属于强非线性系统.其中,依据相对速度和不同变量的乘积作为切换条件的控制策略包括天棚阻尼控制算法、地棚阻尼控制算法和加速度驱动阻尼控制算法等.Shen 等[18 ] 对 4 种基于不同反馈的地棚阻尼控制策略的半主动吸振器进行了解析研究;Díaz 等[19 ] 分析了 3 种基于速度反馈的非线性开关控制在高增益和显著振级的振动下的饱和问题;Eslaminasab 等[20 ] 研究了半主动相对控制的单自由度悬架系统的控制效果;申永军等[21 -24 ] 分别采用有限相对位移控制、天棚控制等策略对含有时滞的单自由度半主动悬架系统进行了动力学分析;Yu 等[25 ] 分析了基于磁流变液阻尼器组成的天棚阻尼控制隔振系统的非线性和时滞特性;Fischer 等[26 ] 分析了主动和半主动车辆悬架系统;王昊等[27 ] 以某磁流变阻尼器作为作动器,研究了4种开关半主动控制策略对整车悬架系统参数的影响;Kim 等[28 ] 对比了在不同激励下主动、半主动和混合质量调谐阻尼器的控制效果;Dong 等[29 ] 对比分析了包括天棚阻尼控制、混合控制、滑模控制、LQG 控制和模糊逻辑控制等 5 种磁流变半主动悬架的控制效果.目前,大多数研究是采用数值分析的方法对控制性能进行分析,而且针对多种半主动控制策略的对比分析较少. ...
The effect and design of time delay in feedback control for a nonlinear isolation system
1
2017
... 通常非线性半主动隔振系统都是基于"质量-弹簧-阻尼"结构体系来近似简化模型,其单自由度半主动隔振系统的模型[30 ] 如图1 所示,可用一个并联的弹性元件和阻尼器来表示.此模型中,除线性刚度和线性阻尼外,引入非 线性刚度,用以克服线性隔振技术的缺陷,改善系统隔振性能[25 ] .可控阻尼通过传感器对系统状态进行判断后,依据不同的变化规律,在一定范围内对可控阻尼进行调节,从而达到减振的效果.具有这种形式的如 1/4 车辆悬架系统、船舶浮阀减振系统等.以 1/4 车辆悬架为例,图1 中 $m$ 为车体质量,$x$ 为车体的位移,$x_0 $ 为路面激励,$F_1$ 为非线性弹性力:$F_1 = k_{1} (x_0 - x) + k_{2} (x_0 - x)^{3}$,其中 $k_{1} $ 表示线性刚度系数,$k_{2}$ 表示非线性刚度系数;$F_2 $ 为阻尼力:$F_2 = c(\dot {x}_0 - \dot {x})$,其中 $c$ 表示线性阻尼系数. ...
1
2000
... 采用平均法求解方程的近似解析解[31 ] ,假设振幅 $a$ 和相位 $\psi $ 是时间的慢变函数 ...
1
2000
... 采用平均法求解方程的近似解析解[31 ] ,假设振幅 $a$ 和相位 $\psi $ 是时间的慢变函数 ...
Investigation on chaotic motion in hysteretic non-linear suspension system with multi-frequency excitations
1
2004
... 对于给定的某一悬架系统,取各参数为[32 -33 ] :车体质量 $m =240$ kg,弹簧线性 刚度 $k_{1}=16 000$ N/m,非线性刚度 $k_{2} =320 000$ N/m.为对比在不同条件下近似解析解和数值解的吻合程度,在 3 种不同控制策略下的开/关阻尼系数及路面简谐激励振幅取值略有不同.数值解的求解采用 Runge-Kutta 法,计算时间为 800 s,将后 10% 的响应的最大值作为稳态响应的幅值.图2 ~图4 分别为在 ADD、SH 和 GH 控制策略下数值解和近似解析解得到的幅频响应曲线,图中横轴为激励频率 $\omega$,纵轴为响应振幅 $a$.从图2 ~图4 可以看出,3 种控制策略的解析解在不同的激励幅值和系统参数下,在低频区和共振区均和相应的数值解均具有较好的一致性,证明了系统解析解的求解方式的正确性和准确性. 需要注意的是,由于半主动控制系统响应中存在高阶奇次谐波成分,因此在高频区可能会表现出颤振现象[23 ] . ...
1
1996
... 对于给定的某一悬架系统,取各参数为[32 -33 ] :车体质量 $m =240$ kg,弹簧线性 刚度 $k_{1}=16 000$ N/m,非线性刚度 $k_{2} =320 000$ N/m.为对比在不同条件下近似解析解和数值解的吻合程度,在 3 种不同控制策略下的开/关阻尼系数及路面简谐激励振幅取值略有不同.数值解的求解采用 Runge-Kutta 法,计算时间为 800 s,将后 10% 的响应的最大值作为稳态响应的幅值.图2 ~图4 分别为在 ADD、SH 和 GH 控制策略下数值解和近似解析解得到的幅频响应曲线,图中横轴为激励频率 $\omega$,纵轴为响应振幅 $a$.从图2 ~图4 可以看出,3 种控制策略的解析解在不同的激励幅值和系统参数下,在低频区和共振区均和相应的数值解均具有较好的一致性,证明了系统解析解的求解方式的正确性和准确性. 需要注意的是,由于半主动控制系统响应中存在高阶奇次谐波成分,因此在高频区可能会表现出颤振现象[23 ] . ...
1
1996
... 对于给定的某一悬架系统,取各参数为[32 -33 ] :车体质量 $m =240$ kg,弹簧线性 刚度 $k_{1}=16 000$ N/m,非线性刚度 $k_{2} =320 000$ N/m.为对比在不同条件下近似解析解和数值解的吻合程度,在 3 种不同控制策略下的开/关阻尼系数及路面简谐激励振幅取值略有不同.数值解的求解采用 Runge-Kutta 法,计算时间为 800 s,将后 10% 的响应的最大值作为稳态响应的幅值.图2 ~图4 分别为在 ADD、SH 和 GH 控制策略下数值解和近似解析解得到的幅频响应曲线,图中横轴为激励频率 $\omega$,纵轴为响应振幅 $a$.从图2 ~图4 可以看出,3 种控制策略的解析解在不同的激励幅值和系统参数下,在低频区和共振区均和相应的数值解均具有较好的一致性,证明了系统解析解的求解方式的正确性和准确性. 需要注意的是,由于半主动控制系统响应中存在高阶奇次谐波成分,因此在高频区可能会表现出颤振现象[23 ] . ...
Analytical computation method for steady-state stochastic response of a time-delay nonlinear automotive suspension system
1
2019
... 在实际的工程应用中,非线性隔振系统较多情况下所受到的外力更接近于随机激励,半主动隔振系统在随机激励下的响应更具有实际意义[34 -39 ] .采用刘献栋等[40 ] 的数值模拟方法建立 D 级路面不平度值来模拟随机激励,如图12 所示. 选取车速为 10 m/s 情况下时,时间间隔为 0.01 s 的 40 s 随机激励,得到 3 种控制策略下和未加半主动控制时的位移时间历程曲线分别如图13 (a)~图13 (d) 所示. ...
Dynamical responses of airfoil models with harmonic excitation under uncertain disturbance
0
2017
Bistability and stochastic jumps in an airfoil system with viscoelastic material property and random fluctuations
0
2020
含时滞反馈与涨落质量的记忆阻尼系统的随机共振
0
2018
含时滞反馈与涨落质量的记忆阻尼系统的随机共振
0
2018
一种含放大机构的负刚度动力吸振器的参数优化
1
2019
... 在实际的工程应用中,非线性隔振系统较多情况下所受到的外力更接近于随机激励,半主动隔振系统在随机激励下的响应更具有实际意义[34 -39 ] .采用刘献栋等[40 ] 的数值模拟方法建立 D 级路面不平度值来模拟随机激励,如图12 所示. 选取车速为 10 m/s 情况下时,时间间隔为 0.01 s 的 40 s 随机激励,得到 3 种控制策略下和未加半主动控制时的位移时间历程曲线分别如图13 (a)~图13 (d) 所示. ...
一种含放大机构的负刚度动力吸振器的参数优化
1
2019
... 在实际的工程应用中,非线性隔振系统较多情况下所受到的外力更接近于随机激励,半主动隔振系统在随机激励下的响应更具有实际意义[34 -39 ] .采用刘献栋等[40 ] 的数值模拟方法建立 D 级路面不平度值来模拟随机激励,如图12 所示. 选取车速为 10 m/s 情况下时,时间间隔为 0.01 s 的 40 s 随机激励,得到 3 种控制策略下和未加半主动控制时的位移时间历程曲线分别如图13 (a)~图13 (d) 所示. ...
公路路面不平度的数值模拟方法研究
1
2003
... 在实际的工程应用中,非线性隔振系统较多情况下所受到的外力更接近于随机激励,半主动隔振系统在随机激励下的响应更具有实际意义[34 -39 ] .采用刘献栋等[40 ] 的数值模拟方法建立 D 级路面不平度值来模拟随机激励,如图12 所示. 选取车速为 10 m/s 情况下时,时间间隔为 0.01 s 的 40 s 随机激励,得到 3 种控制策略下和未加半主动控制时的位移时间历程曲线分别如图13 (a)~图13 (d) 所示. ...
公路路面不平度的数值模拟方法研究
1
2003
... 在实际的工程应用中,非线性隔振系统较多情况下所受到的外力更接近于随机激励,半主动隔振系统在随机激励下的响应更具有实际意义[34 -39 ] .采用刘献栋等[40 ] 的数值模拟方法建立 D 级路面不平度值来模拟随机激励,如图12 所示. 选取车速为 10 m/s 情况下时,时间间隔为 0.01 s 的 40 s 随机激励,得到 3 种控制策略下和未加半主动控制时的位移时间历程曲线分别如图13 (a)~图13 (d) 所示. ...
1
1997
... 采用车身基于路面的相对位移量的均方根值和加权加速度均方根值对平顺性进行评价[41 ] ,按下式计算加权加速度均方根值 ...